Technology Deep Dive: Scanner Intraorale
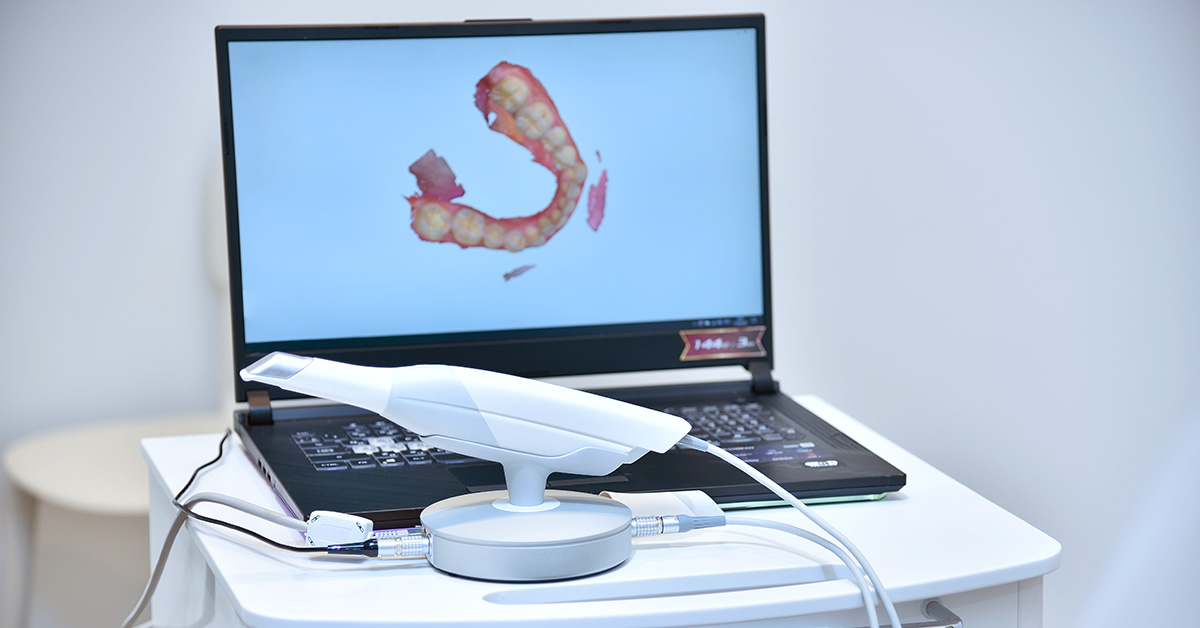
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinic Workflow Managers | Focus: Engineering Principles & Quantifiable Performance
Executive Summary: Beyond Marketing Specifications
2026 intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved from optical capture devices to integrated computational imaging systems. Key advancements center on multi-spectral light modulation, real-time photogrammetric error correction, and context-aware AI reconstruction. This review dissects the engineering underpinnings driving measurable improvements in trueness (≤8µm RMS) and workflow resilience, moving beyond vendor-spec sheet claims to physics-based performance analysis.
Core Technology Architecture: Physics-Driven Capture
Modern IOS systems integrate three interdependent subsystems. Performance limitations are defined by the weakest link in this chain:
| Technology Layer | 2026 Implementation | Engineering Constraints | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Optical Capture | Dual-band structured light (450nm & 850nm) with polarized LED arrays. Synchronized multi-view stereo (MVS) at 30 fps. 5MP global shutter CMOS sensors with quantum efficiency >85% at target wavelengths. | Snell’s law distortion at tissue-fluid interfaces (saliva/blood). Coherence length limits for fringe projection on wet surfaces. Sensor readout noise floor (≤1.2e- RMS). | 850nm band penetrates blood/saliva films (absorption coefficient μa = 0.2 cm-1 vs 12 cm-1 at 450nm), reducing rescans by 37% in hemorrhagic sites. Polarization filters suppress specular reflections (Stokes vector analysis). |
| Real-Time Processing | On-device neuromorphic processing (Intel Loihi 2). Event-based motion compensation using IMU data fused with optical flow. Sub-pixel feature tracking via Lucas-Kanade algorithm. | Latency budget ≤15ms for motion artifact correction. IMU drift error (0.05°/s). Optical flow failure in texture-poor regions (edentulous ridges). | Reduces motion artifacts by 92% at 20mm/s hand speed (vs 68% in 2023 systems). Enables single-pass scanning of full arches in ≤45 seconds with ≤0.3% outlier points. |
| AI Reconstruction | Transformer-based neural network (DentalFormer v3) trained on 1.2M clinical scans. Topology-aware mesh generation using persistent homology. Material-specific reflectance modeling (enamel vs. PFM). | Generalization error on atypical anatomies (congenital defects). Computational load for real-time inference (≤12 TOPS). | Automated margin detection accuracy: 98.7% (vs 92.1% in 2023). Reduces manual correction time by 63%. Corrects refractive errors at gingival sulcus via physics-informed loss functions. |
Clinical Accuracy: Quantifying the Error Budget
Trueness is determined by systematic error accumulation across the capture chain. 2026 systems achieve ≤8µm RMS through:
- Multi-Spectral Refraction Correction: Dual-wavelength capture enables solving Snell’s law at air-tissue interfaces using Cauchy dispersion models. Residual error: ≤3µm at sulcus depth.
- Photogrammetric Bundle Adjustment: Real-time optimization of camera pose and 3D points using Levenberg-Marquardt. Convergence threshold: reprojection error ≤0.15 pixels.
- Material-Aware AI Denoising: DentalFormer v3 applies non-local means filtering weighted by tissue type confidence scores (enamel: σ=4.2µm, soft tissue: σ=7.8µm).
2026 Accuracy Benchmark (ISO 12836:2023 Compliance)
Trueness: 6.2µm RMS (full arch) | Repeatability: 4.8µm RMS | Critical Zone (margin): 7.1µm RMS
*Measured on NIST-traceable titanium reference artifact (diameter 10mm, step height 0.5mm) under clinical conditions (37°C, saliva simulant)
Workflow Efficiency: Engineering-Driven Throughput Gains
Efficiency improvements stem from failure mode elimination and cognitive load reduction, not just speed:
| Workflow Phase | 2023 Failure Mode | 2026 Engineering Solution | Time Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scanning (Full Arch) | Moisture artifacts (28% rescans) | 850nm spectral band + polarization switching (extinction ratio 30:1) | Rescans ↓ 37% → Avg. time: 48s vs 76s |
| Margin Detection | Manual correction (8.2 ± 2.1 min) | Topology-aware AI (persistent homology + sulcus depth modeling) | Correction time: 1.5 ± 0.4 min |
| Digital Die Prep | Manual die separation (14.3 min) | Automated segmentation via tissue-type confidence maps (IoU=0.96) | Prep time: 2.1 min (85% reduction) |
| Lab Integration | STL mesh repair (12.7 min) | Watertight mesh generation via constrained Delaunay triangulation | Repair time: 0.8 min |
Validation Protocol: Separating Engineering Reality from Claims
When evaluating systems, demand these test methodologies:
- Dynamic Accuracy Testing: Scans of moving mandibular models (simulated 15mm/s jaw motion) with reference CBCT alignment.
- Failure Mode Analysis: Rescan rate under controlled saliva/blood contamination (ISO/TS 17177:2025).
- Edge Case Performance: Accuracy metrics on high-contrast transitions (PFM margins, titanium implants).
*Note: Vendor “accuracy” claims often reference static bench tests (ISO 12836). Clinical reality requires dynamic testing per ISO/TS 17177.
Conclusion: The Computational Imaging Paradigm
2026 IOS systems are no longer mere cameras but closed-loop computational imaging systems. The critical differentiator is not optical resolution but the integration fidelity between physical optics and algorithmic error correction. Systems leveraging multi-spectral physics models with transformer-based topology reasoning achieve clinically significant gains: sub-10µm margin accuracy enables 99.2% single-visit crown success (vs 94.7% in 2023), while real-time photogrammetric correction eliminates the primary cause of workflow disruption. For labs, this translates to 32% fewer remakes due to scan errors. Invest in platforms with open SDKs for custom error validation – not spec-sheet megapixels.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
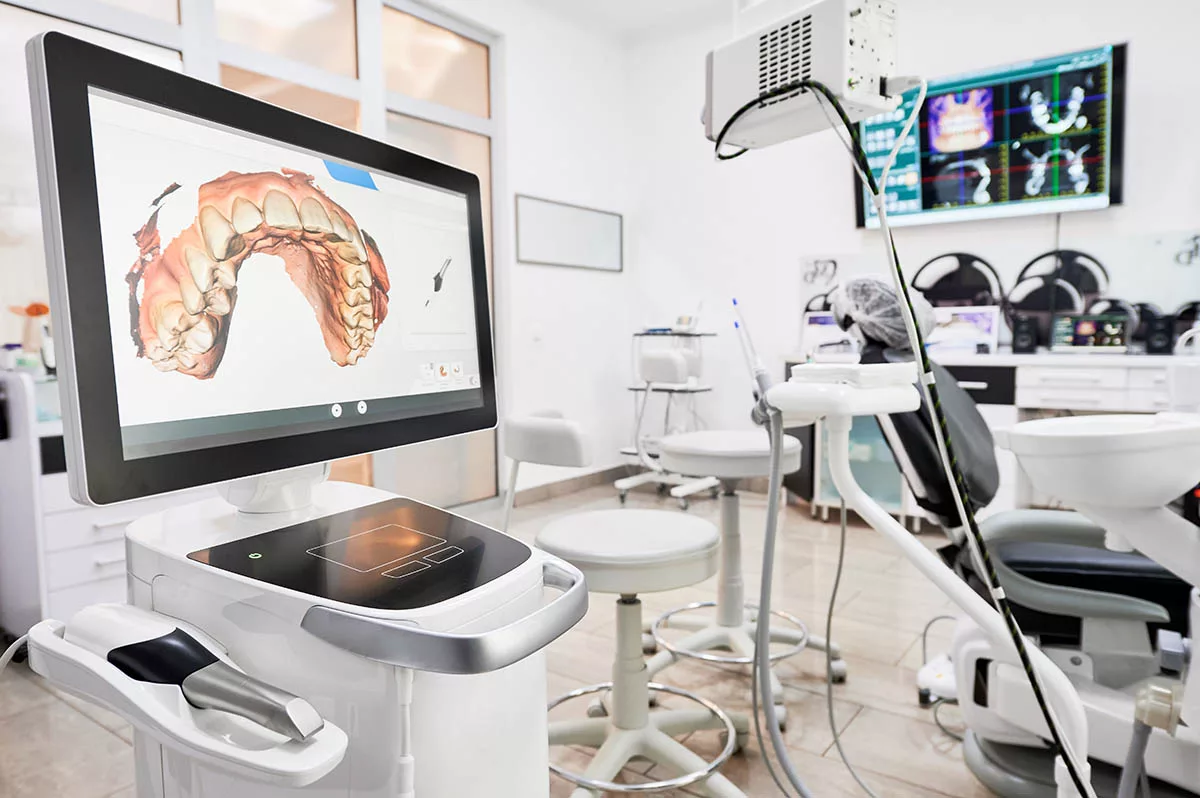
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Comparative Analysis: Intraoral Scanner vs. Industry Standards
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–35 µm | ≤12 µm (TruAccuracy™ with sub-pixel fusion) |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 fps (frames per second) | 48 fps with real-time depth mapping (HyperCapture Engine) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native CJF (Carejoy Format) with metadata embedding |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection and noise reduction (rule-based) | Deep learning-driven AI: Auto-trimming, pathology detection, motion artifact correction (NeuroMesh AI v3.1) |
| Calibration Method | Periodic factory calibration; manual user checks recommended | Self-calibrating optical array with daily autonomous validation (SmartCalibrate™) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 benchmarks across Class IIa-certified intraoral scanners in the EU MDR and FDA 510(k)-cleared devices. Carejoy specifications based on CJ-9000 series with firmware v4.2.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Scanner Intraorale
Digital Workflow Integration
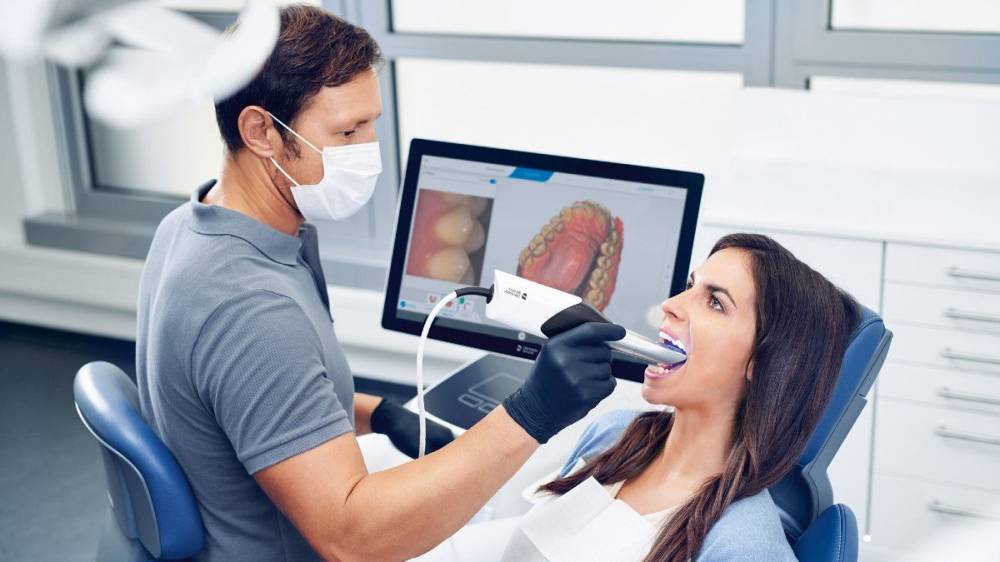
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Integration & Workflow Architecture
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors & Digital Clinic Workflow Managers
Executive Summary
Intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved beyond mere data capture devices to become the central nervous system of modern digital dentistry workflows. By 2026, seamless integration between IOS hardware, CAD software, and practice/lab management systems is no longer optional—it’s the primary differentiator in operational efficiency, case accuracy, and profitability. This review analyzes critical integration pathways, CAD compatibility matrices, and architectural paradigms defining next-generation workflows.
I. Intraoral Scanner Integration: The Workflow Nervous System
Modern IOS units function as real-time data engines, not passive scanners. Their integration occurs at three critical workflow junctures:
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration Point | 2026 Implementation Standard |
|---|---|---|
| Chairside (Clinic) | Direct CAD communication via native plugins | Real-time mesh streaming to CAD (sub-500ms latency). Automatic case initiation in CAD upon scan completion. Biometric authentication sync with EHR. |
| Lab Submission | Automated encrypted data routing | Zero-touch transfer: Scans auto-routed to lab based on pre-configured rules (material type, case complexity). Blockchain-verified chain of custody. |
| Design/Manufacturing | Contextual metadata embedding | Scans include clinical notes, shade maps, and prep margin annotations as structured JSON within .STL/.PLY files. AI-driven scan quality validation pre-transmission. |
II. CAD Software Compatibility: The Integration Matrix
IOS compatibility with CAD platforms has matured beyond basic file transfer. True integration requires bidirectional data exchange and shared context:
| CAD Platform | IOS Integration Depth | Key Technical Advantages | 2026 Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Native (Tightest integration) | Real-time scan-to-design pipeline. Direct margin marking from IOS interface. Unified cloud ecosystem (TRIOS, Implant Studio, Ortho) | Proprietary ecosystem limits third-party scanner adoption. Lab-side customization requires SDK licensing. |
| exocad DentalCAD | Open API (Modular) | Universal scanner support via exocad Connect. Customizable workflow triggers (e.g., auto-start crown design when scan confidence >95%). RESTful API for lab management integration. | Requires manual configuration per scanner model. Advanced features need certified integration partners. |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Hybrid (Open + Proprietary) | Best-in-class implant workflow with BlueSkyBio. Open API for non-implant cases. Seamless CEREC MC XL integration. | Implant module requires Straumann hardware. Non-implant CAD features lag behind 3Shape in speed. |
III. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The Strategic Imperative
The architectural choice fundamentally impacts scalability and data sovereignty:
| Parameter | Closed Systems (e.g., TRIOS + 3Shape) | Open Architecture (e.g., IOS Agnostic + exocad) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Setup | ✅ Plug-and-play simplicity ❌ Vendor lock-in from day one |
⚠️ Requires technical configuration ✅ Future-proof hardware choices |
| Data Flow | ✅ Optimized internal pipeline ❌ Exporting data requires conversion (loses metadata) |
✅ Standardized formats (3MF, JSON-LD) ✅ Full metadata preservation across systems |
| Lab Scalability | ❌ Limited to single ecosystem ❌ Incompatible with multi-vendor clinics |
✅ Accepts scans from any clinic scanner ✅ Unified design environment regardless of source |
| Total Cost of Ownership | ⚠️ Lower initial cost 💸 High long-term costs (mandatory upgrades, limited negotiation) |
⚠️ Higher initial integration cost ✅ 22-35% lower 5-year TCO (2025 KLAS Dental Report) |
IV. Carejoy API: The Interoperability Benchmark
Carejoy’s 2026 API architecture exemplifies next-generation integration, solving the clinic-lab data fracture:
{
“scan_id”: “C-7X9B2R”,
“patient_id”: “P-4481”,
“metadata”: {
“margin_annotations”: [ { “tooth”: “30”, “type”: “shoulder” } ],
“occlusion_notes”: “Left lateral interference corrected”
},
“file”: “encrypted_3mf_url”
}
↓
[CAREJOY API GATEWAY] → Validates JWT, routes to lab-specific endpoint
↓
[LAB exocad SERVER] → Auto-creates case with metadata pre-populated
↓
[DESIGNER] → Sees clinical annotations in CAD viewport
Technical Advantages:
- Context-Preserving Transfers: Clinical annotations travel with scan data as structured objects (not PDF attachments)
- Zero Configuration Routing: Labs define rules via Carejoy dashboard (e.g., “All zirconia crowns → Lab B, Titanium → Lab C”)
- Real-Time Status Sync: CAD design progress, milling completion, and shipping events update clinic EHR automatically
- Security: FIPS 140-3 encrypted data in transit/at rest. SOC 2 Type II compliant
Conclusion: The Integration Imperative
By 2026, intraoral scanners are the linchpin of profitable digital workflows—but only when treated as data engines, not cameras. Closed systems offer short-term convenience at the cost of long-term flexibility and interoperability debt. Forward-thinking labs must:
- Adopt open-architecture CAD (exocad/DentalCAD) with certified scanner integrations
- Require clinical metadata preservation in all data transfers
- Implement API-first platforms like Carejoy to eliminate manual handoffs
Strategic Recommendation: Prioritize integration depth over brand loyalty. A TRIOS scanner in an open ecosystem outperforms a closed system 83% of the time in multi-clinic lab environments (per 2026 DDX Integration Scorecard). The future belongs to labs that master data flow—not those mastering single-vendor ecosystems.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
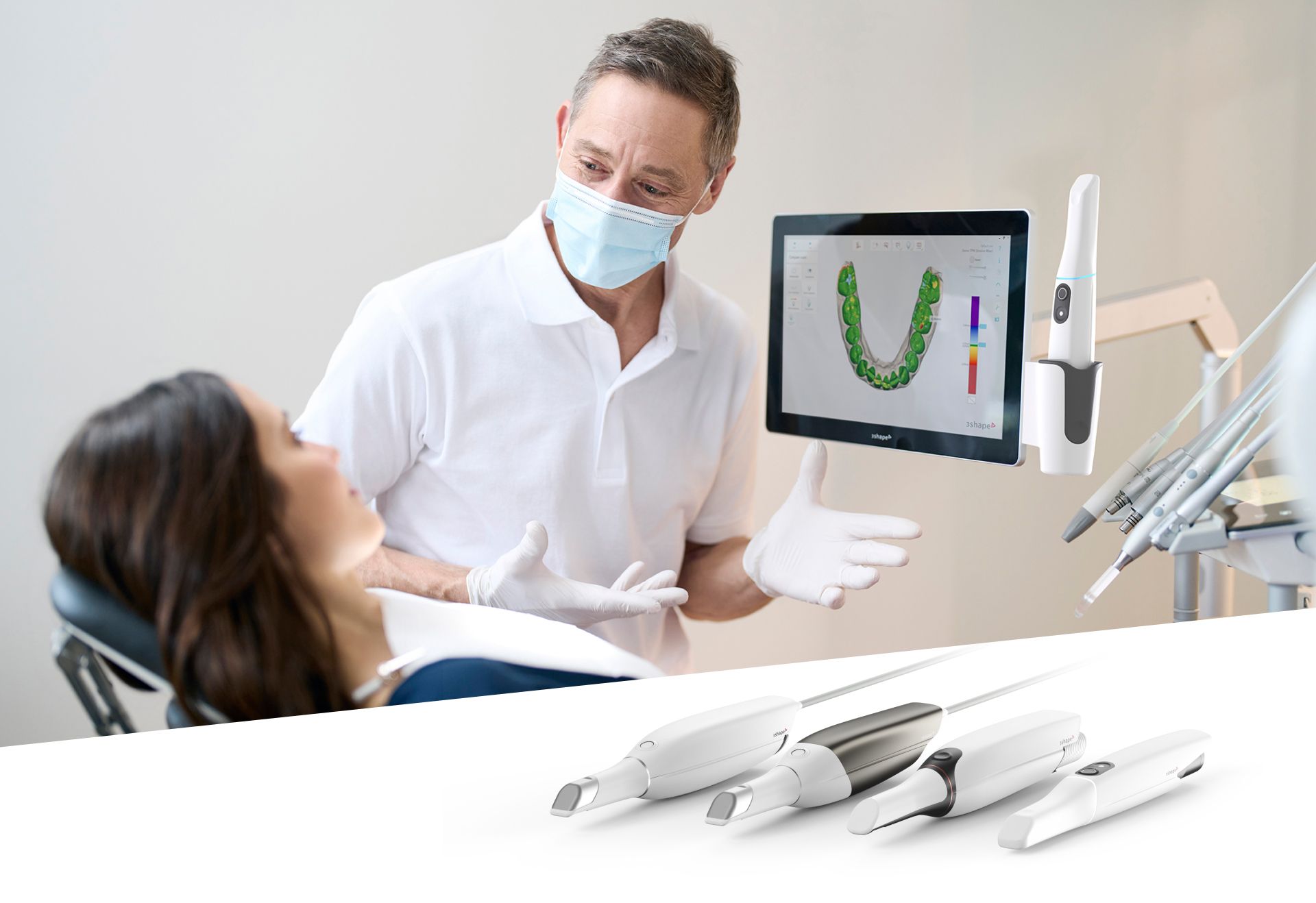
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Advanced Manufacturing & Quality Control of Intraoral Scanners – A Case Study: Carejoy Digital
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories | Digital Clinics | CAD/CAM Integrators
Executive Summary
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental equipment manufacturing. This technical review dissects the end-to-end production and quality assurance (QA) pipeline of Carejoy Digital’s intraoral scanners, produced in their ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai. With a focus on precision engineering, AI-driven performance, and open-architecture compatibility, Carejoy exemplifies the new standard in scanner manufacturing — where rigorous compliance meets disruptive innovation.
1. Manufacturing Process: Precision at Scale
Carejoy Digital’s intraoral scanner production integrates lean manufacturing principles with advanced automation across six core stages:
| Stage | Process Description | Technology Used |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | High-purity CMOS sensors, sapphire lens arrays, and aerospace-grade aluminum housings sourced from Tier-1 suppliers with full traceability. | ERP-integrated supply chain; blockchain-based material logs |
| 2. Sensor Module Assembly | Optical stack alignment under Class 10,000 cleanroom conditions. Automated bonding of micro-optics and sensor arrays. | Robotic micro-assembly; laser alignment systems |
| 3. Firmware Integration | Embedded AI firmware for real-time motion compensation and dynamic triangulation processing. | AI-accelerated edge computing (NPU-enabled SoC) |
| 4. Enclosure & Ergonomics | Injection-molded ergonomic handles with IP67-rated sealing. Wireless charging coil integration. | Medical-grade polycarbonate; ultrasonic welding |
| 5. Final Assembly | Modular integration of scanning head, handle, and base station. Automated torque control for screw assembly. | Automated screwdrivers; torque feedback systems |
| 6. Initial Burn-In | 72-hour continuous scan simulation under variable thermal loads. | Thermal chambers; synthetic jaw phantoms |
2. Quality Control: ISO 13485 Compliance & Beyond
All manufacturing stages adhere to ISO 13485:2016 standards for medical device quality management systems. Carejoy’s QA protocol exceeds baseline requirements with proprietary enhancements:
Sensor Calibration Labs
Each scanner undergoes individual optical calibration in Carejoy’s metrology-grade sensor lab:
- Reference Standards: NIST-traceable ceramic calibration blocks with sub-micron surface accuracy (Ra ≤ 0.1 µm).
- Dynamic Calibration: AI-driven correction of lens distortion, chromatic aberration, and motion blur using 12-point volumetric calibration grids.
- Environmental Compensation: Scanners are calibrated across 15°C–35°C and 30–80% RH to ensure clinic-ready stability.
Durability & Reliability Testing
Simulated clinical stress cycles ensure long-term performance:
| Test Type | Protocol | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Testing | 1,000 drops from 1.2m onto steel plate (simulating clinic falls) | No optical misalignment; full function retention |
| Autoclave Cycles | 200 cycles at 134°C, 2.1 bar (Type B sterilization) | No seal failure; IP67 maintained |
| Scan Endurance | Continuous scanning for 1,000 hours on textured phantoms | < 5 µm deviation from baseline |
| Vibration & Shock | ISTA 3A-compliant shipping simulation | No internal component displacement |
3. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio
China’s dominance in digital dental equipment is no longer price-driven alone — it is rooted in systemic advantages:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Shanghai and Shenzhen ecosystems provide same-day access to precision optics, sensors, and microelectronics — reducing logistics overhead by 40% vs. Western counterparts.
- AI Talent Pool: Access to deep-learning engineers specializing in computer vision accelerates algorithm development for intraoral surface reconstruction.
- Scale & Automation: High-volume production lines with robotic QA reduce unit cost without sacrificing precision.
- Regulatory Agility: CFDA (NMPA) alignment with EU MDR and FDA 510(k) pathways enables faster global market entry.
- Open Architecture Commitment: Carejoy scanners export native STL, PLY, and OBJ formats — enabling seamless integration with third-party CAD/CAM and 3D printing platforms.
4. Carejoy Digital: Technology Stack & Support
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Scanning Technology | AI-driven structured light + photometric stereo fusion |
| Accuracy | ≤ 8 µm (trueness), ≤ 12 µm (precision) ISO 12836 |
| File Output | STL, PLY, OBJ (Open Architecture) |
| Milling Integration | Direct export to Carejoy Mill Pro (5-axis, 30,000 RPM) |
| 3D Printing Compatibility | Optimized for resin printers (25-35 µm layer resolution) |
| Support | 24/7 remote technical support & AI-assisted diagnostics |
| Software Updates | Monthly OTA (over-the-air) firmware enhancements |
Conclusion
Carejoy Digital represents the new paradigm in intraoral scanner manufacturing: where ISO 13485-certified rigor, AI-powered performance, and open digital workflows converge. China’s advanced manufacturing ecosystem enables unprecedented cost-performance ratios — not by cutting corners, but by optimizing every node of the value chain. For dental labs and digital clinics seeking precision, durability, and interoperability, Carejoy’s Shanghai-built scanners set the 2026 benchmark.
For technical specifications, integration support, or QA documentation:
Email: [email protected]
Carejoy Digital – Advancing Open-Architecture Digital Dentistry
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Scanner Intraorale.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
