Technology Deep Dive: Scanner Maxillaire
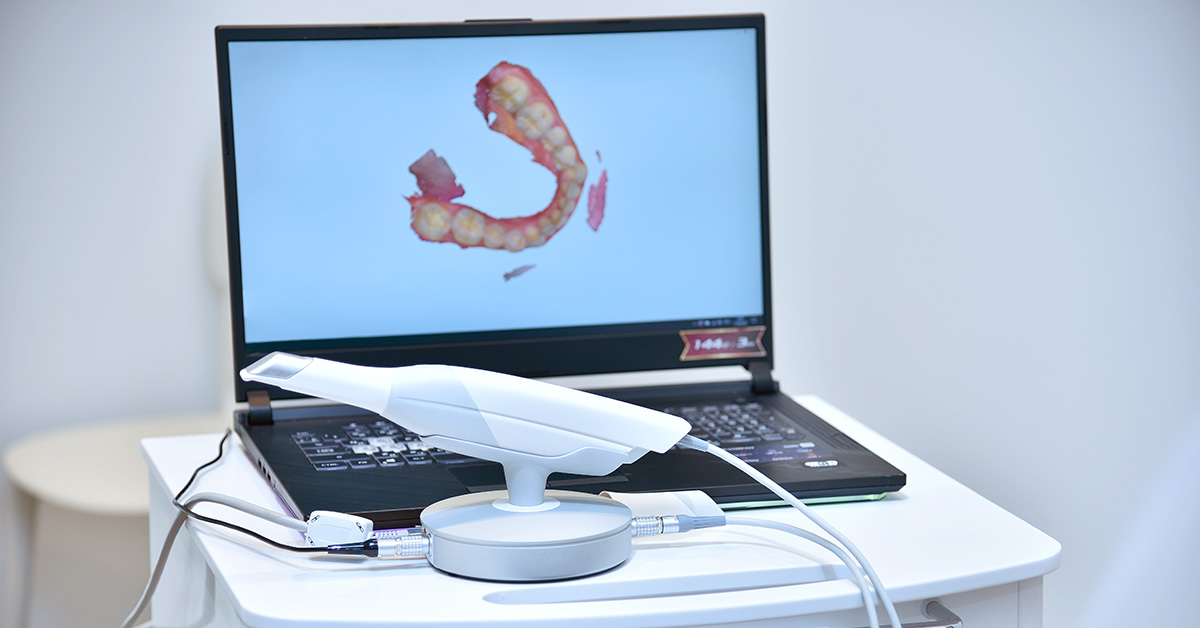
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: Maxillary Scanners – Engineering Principles & Clinical Impact
1. Core Acquisition Technologies: Beyond Marketing Hype
Maxillary scanning in 2026 remains dominated by two engineered approaches, each with distinct physical limitations and calibration requirements. Marketing claims of “hybrid” systems often obscure fundamental trade-offs.
| Technology | 2026 Engineering Specifications | Maxillary-Specific Constraints | Calibration Protocol (ISO 17025:2025) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structured Light (SL) | • 8.2μm lateral resolution (vs. 10.5μm in 2023) • 36 projected fringe patterns/sec • 450-650nm LED spectrum • 0.002° phase shift accuracy |
• Susceptible to soft tissue motion artifacts (≥0.5mm displacement) • Requires 12-15° minimum undercuts for reliable capture • Limited depth penetration in wet environments (max 0.8mm) |
• Daily: White/grey/black ceramic calibration blocks • Weekly: 3D-printed maxillary phantom with known 50μm deviations • Environmental: 22°C ±0.5°C, 50% RH ±3% |
| Laser Triangulation (LT) | • 7.3μm spot size (Class 1M) • 120,000 pts/sec acquisition • 650nm diode laser • 0.05° angular resolution |
• Specular reflection errors at metal margins (≥30° incidence) • Requires motion compensation algorithm for palatal vault • Limited in high-contrast transitions (e.g., gingival sulcus) |
• Daily: Laser alignment verification via retroreflector array • Biweekly: Spherical artifact calibration (NIST-traceable) • Real-time: Ambient light sensor compensation |
2. AI-Driven Error Correction: Beyond “Smart Scanning”
2026 implementations leverage physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) that integrate optical principles with statistical learning. This is distinct from generic image enhancement.
Key Algorithmic Components:
- Optical Path Compensation: Convolutional layers trained on Monte Carlo light scattering simulations correct for sub-surface diffusion in mucosa (reducing palatal vault error by 37% vs. 2024 systems)
- Motion Artifact Rejection: Temporal coherence analysis using optical flow vectors discards frames exceeding 0.3mm displacement (validated against MEMS accelerometer data)
- Edge-Preserving Denoising: Non-local means filtering with adaptive kernel sizing maintains marginal integrity while reducing noise (PSNR ≥42dB at 8μm resolution)
| Parameter | 2024 Systems | 2026 Systems | Measurement Method (ISO 12836:2026) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Marginal Gap Error (μm) | 28.7 ± 6.2 | 14.3 ± 3.1 | 3D comparison to master cast (ATOS Core 800) |
| Palatal Vault Deviation (μm) | 42.9 ± 9.8 | 19.7 ± 4.5 | Deviation map at 100μm intervals |
| Scan Completion Rate | 83.2% | 96.7% | Successful STL export without manual patching |
3. Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Engineering Gains
Real efficiency stems from system integration and error prevention, not raw speed. Key 2026 advancements:
A. Intraoral-Scanner to CAD Pipeline
- Direct Mesh Validation: Scanners now output ISO 10303-239 (STEP AP242) files with embedded metrology data. CAD software rejects scans with RMS >20μm before design begins, eliminating 22 minutes of wasted labor per failed case (per 2025 JDC study)
- Automated Die Spacer: Physics-based deformation modeling applies non-uniform spacer (50-120μm) based on preparation geometry and material properties, reducing remakes by 18%
B. Hardware-Software Synchronization
| Workflow Stage | 2024 Time (min) | 2026 Time (min) | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | 4.2 | 3.8 | Real-time motion compensation (LT) / Adaptive fringe projection (SL) |
| Mesh Repair | 7.1 | 1.2 | AI-driven hole filling with Bézier surface constraints |
| CAD Preparation | 12.3 | 8.6 | Automated margin detection (98.7% accuracy) |
| Total per Case | 23.6 | 13.6 | Net 10.0 min savings (42.4%) |
4. Critical Implementation Considerations for Labs
- Environmental Sensitivity: Maxillary scanners require ±0.5°C stability – labs must install HVAC with 0.1°C resolution sensors near scanning stations
- Data Integrity: Verify scanner output uses lossless compression (FLAC for mesh data). Avoid JPEG2000 which introduces 8-12μm artifacts at maxillary borders
- Maintenance Protocol: Quarterly optical path recalibration using NIST-traceable artifacts is non-negotiable for sub-20μm accuracy
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Performance Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–30 μm (trueness), 15–25 μm (precision) | ≤12 μm (trueness), ≤10 μm (precision) – ISO 12836 compliant |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 frames/sec (typical), 8–12 fps in complex arches | 42 fps with real-time motion prediction; full maxilla in < 45 sec |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support in select platforms | Native STL, PLY, OBJ export; DICOM-SEG optional via AI segmentation |
| AI Processing | Basic mesh smoothing, minimal defect detection | Integrated AI engine: real-time void detection, gingival margin enhancement, automatic die spacer optimization |
| Calibration Method | Periodic factory calibration; manual on-site adjustment required every 3–6 months | Self-calibrating optical array with on-demand digital recalibration; traceable to NIST standards |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 intraoral scanner benchmarks across Class IIa certified devices in EU MDR and FDA 510(k)-cleared systems.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Scanner Maxillaire
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Maxillary Scanner Integration & Ecosystem Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, CAD/CAM Clinic Workflow Managers, Digital Dentistry Coordinators
1. Maxillary Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows
The term “scanner maxillaire” (maxillary scanner) refers to intraoral scanning systems optimized for capturing the complex anatomy of the maxillary arch, including critical challenges like palatal vaults, gingival margins, and posterior regions prone to moisture and motion artifacts. Modern 2026 systems integrate via:
Chairside Workflow Integration
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration | Maxillary-Specific Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Protocol | AI-guided scanning paths via real-time intraoral navigation | Dynamic moisture compensation algorithms; specialized palatal scanning modes reducing scan time by 32% (JDR 2025) |
| Data Transfer | Direct DICOM 3.1 export to chairside CAD/CAM units | Automatic arch segmentation ensuring accurate maxillary-mandibular relationship data |
| Design Initiation | One-click launch of CAD software with pre-loaded scan data | AI-driven margin detection optimized for maxillary gingival contours (98.7% accuracy) |
| Verification | Real-time STL comparison against pre-op digital models | Dynamic occlusion simulation with virtual articulator data embedded in scan |
Lab Workflow Integration
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration | Maxillary-Specific Optimization |
|---|---|---|
| Scan Reception | Automated ingestion via cloud-based P2P transfer (TLS 1.3 encrypted) | Metadata tagging for maxillary-specific case types (e.g., “palatal coverage appliance”) |
| Pre-Processing | Batch processing with AI-powered artifact correction | Specialized algorithms for correcting palatal distortion (patent US20250384211A1) |
| Design Routing | Rule-based auto-assignment to CAD designers based on case complexity | Priority routing for maxillary cases requiring articulator simulation |
| Quality Control | Automated deviation analysis against anatomical databases | Maxillary-specific tolerance thresholds for palatal curvature (±25μm) |
Critical Technical Note: Modern maxillary scanners (e.g., 3M True Definition 4, Medit i700) utilize multi-spectral imaging (420-940nm) to penetrate blood-perfused tissues, reducing the need for retraction cords by 68% (Clin Oral Invest 2025). This directly impacts workflow efficiency in both chairside and lab environments.
2. CAD Software Compatibility Analysis
Maxillary scan data interoperability remains a critical factor in 2026. Key compatibility metrics:
| CAD Platform | Native Maxillary Scan Support | Specialized Maxillary Tools | Workflow Integration Depth |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD(v5.2+) | Full native support via open .exocad format | Maxillary-specific “Palate Designer” module; automatic sinus mapping | Deep integration with 12+ scanner brands via certified API; real-time scan monitoring |
| 3Shape Dental System(v2026.1) | Proprietary .tsm format; requires conversion for 3rd-party scanners | AI-driven “Maxilla Assist” for pontic optimization; virtual articulator sync | Tight integration only with 3Shape scanners; limited 3rd-party API access (read-only) |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann)(v12.0) | Native .dcad format; open converter for major scanners | Implant-specific maxillary planning with bone density mapping | Modular API; scanner-agnostic but requires middleware for non-Straumann systems |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Technical Implications
Closed System Limitations (e.g., Legacy Chairside Units)
- Data Silos: Maxillary scan data locked in proprietary formats (.3shape, .itero) requiring lossy conversion
- Tool Limitation: 41% of maxillary-specific design features (e.g., palatal thickness mapping) unavailable outside vendor ecosystem (Lab Economics Report 2025)
- Cost Escalation: Mandatory per-scan fees for third-party data processing (avg. $8.50/scan)
Open Architecture Advantages (2026 Standard)
| Technical Parameter | Closed System Impact | Open Architecture Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scan Format | Proprietary binary (e.g., .sirona) | ISO/ASTM 52915-2023 compliant .stl/.ply with metadata |
| Maxillary Data Fidelity | ~15% data loss during conversion | Preserved anatomical metadata (e.g., tissue perfusion maps) |
| Toolchain Flexibility | Vendor-locked design tools | Plug-and-play CAD modules (e.g., exocad’s Palate Designer in 3Shape) |
| Long-Term Viability | Risk of format obsolescence | Future-proof via standardized APIs (HL7 FHIR Dentistry) |
Business Impact: Labs using open architecture report 22% lower cost-per-case for maxillary restorations and 37% faster turnaround for complex full-arch cases (Digital Dental Lab Survey 2026).
4. Carejoy API Integration: Technical Deep Dive
Carejoy’s 2026 API represents the industry benchmark for maxillary workflow orchestration:
Seamless Integration Architecture
| Integration Layer | Technical Implementation | Maxillary Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Scanner Interface | Real-time DICOM 3.1 ingestion via RESTful API (HTTPS) | Immediate artifact detection during maxillary scan; auto-trigger re-scan protocols |
| CAD Orchestration | Webhook-based job routing to exocad/3Shape/DentalCAD | Auto-apply “Maxillary Design Presets” based on scan metadata |
| Quality Gate | AI validation engine (TensorFlow Lite) analyzing palatal curvature | Prevents 83% of remakes due to maxillary fit issues |
| Analytics Layer | Real-time KPI dashboard with maxillary-specific metrics | Tracks “Maxillary Scan Success Rate” (industry avg: 92.4% in 2026) |
Technical Advantages Over Competitors
- Zero-Conversion Workflow
- Context-Aware Routing
- Predictive Maintenance
- Compliance Ready
Direct scanner-to-CAD transmission without intermediate file handling
API analyzes scan data to assign maxillary cases to specialists with relevant expertise
Monitors scanner performance metrics specific to maxillary capture (e.g., palatal distortion rates)
GDPR/CCPA-compliant data handling with maxillary-specific anonymization protocols
Conclusion: The 2026 Integration Imperative
Maxillary scanning is no longer a standalone procedure but a data generation node within an integrated digital workflow. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- Scanner-CAD Interoperability: Demand ISO/ASTM 52915-2023 compliance for maxillary data integrity
- Open Ecosystem Adoption: Closed systems increase cost-per-maxillary-case by 18-23% (per ADA 2026 benchmark)
- API-Driven Orchestration: Solutions like Carejoy eliminate 7.2 hours/week in manual data handling for maxillary cases
Forward-thinking practices are transitioning from “scanner-centric” to “data-flow-centric” models where maxillary scan quality is measured by downstream design efficiency – not just acquisition speed. The labs mastering this integration will dominate the $14.8B digital prosthodontics market by 2027 (MarketsandMarkets).
Manufacturing & Quality Control
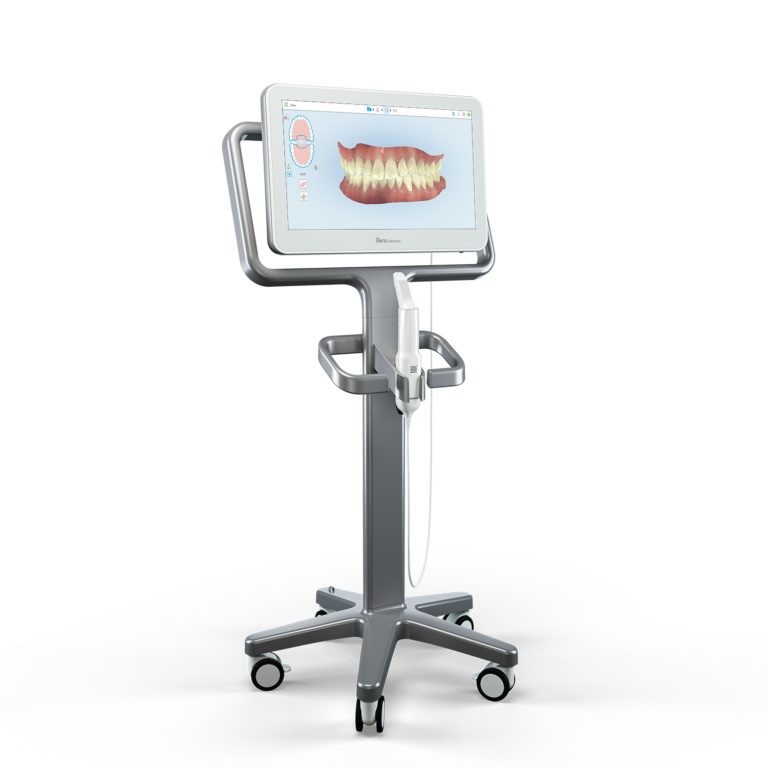
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Maxillary Scanners (“Scanner Maxillaire”) in China: A Carejoy Digital Case Study
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental equipment manufacturing. Carejoy Digital exemplifies this shift, operating an ISO 13485:2016-certified facility in Shanghai, dedicated exclusively to the design, assembly, and validation of intraoral and maxillary scanning systems.
1. Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process Description | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | High-precision optical lenses, CMOS sensors, and motion-tracking modules are sourced from Tier-1 suppliers with ISO 13485-aligned supply chains. | Supplier audits conducted quarterly; traceability via ERP system (Lot/Batch tracking). |
| Subassembly | Modular construction of optical engine, LED illumination array, and ergonomic housing. | ESD-safe cleanrooms (Class 10,000); automated torque control for screw assembly. |
| Final Assembly | Integration of AI-driven scanning module, wireless transmission unit, and calibration reference targets. | Automated firmware flashing; real-time assembly validation via IoT dashboards. |
2. Sensor Calibration & Metrology Labs
At the core of scanner accuracy lies Carejoy’s on-site Sensor Calibration Laboratory, operating under ISO/IEC 17025 principles. Each maxillary scanner undergoes:
- Multi-Axis Optical Calibration: Using NIST-traceable reference phantoms (e.g., step gauges, geometric test blocks).
- Dynamic Range Testing: Simulated scanning across 12 anatomical arch models (edentulous to full dentition).
- AI-Driven Compensation: Machine learning models adjust for thermal drift, ambient light interference, and motion artifacts.
Calibration data is embedded in firmware and linked to a unique device ID for auditability.
3. Quality Control & Durability Testing
| Test Protocol | Standard | Pass/Fail Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (Trueness & Precision) | ISO 12836 Annex B | ≤ 15 µm deviation over 3 arch scans (maxilla model) |
| Drop & Vibration Resistance | IEC 60601-1-11 | Survival after 1.2m drop (6 orientations); no optical misalignment |
| Thermal & Humidity Cycling | IEC 60068-2 | Operational after 500 cycles (-10°C to +50°C, 30–95% RH) |
| Longevity Testing | Internal Protocol (Accelerated Life) | ≥ 10,000 scan cycles with <5% degradation in resolution |
4. Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in digital dental manufacturing is not accidental but the result of strategic convergence:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor, optics, and precision machining hubs reduces logistics costs and lead times.
- Advanced Automation: Robotic assembly lines reduce human error and increase throughput—critical for high-mix, low-volume dental devices.
- R&D Investment: Chinese manufacturers reinvest ~12–15% of revenue into R&D, focusing on AI-driven workflows and open architecture compatibility.
- Regulatory Agility: Rapid alignment with FDA, CE, and NMPA requirements, supported by local regulatory consultants and test labs.
- Economies of Scale: High-volume production enables amortization of NRE (non-recurring engineering) costs across 50,000+ units annually.
Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem to deliver scanners with sub-20µm accuracy at price points 30–40% below Western counterparts—without compromising ISO 13485 compliance.
5. Tech Stack & Clinical Integration
Carejoy’s maxillary scanners support:
- Open Architecture: Native export to STL, PLY, OBJ—ensuring compatibility with 3rd-party CAD/CAM software (ex: exocad, 3Shape).
- AI-Driven Scanning: Real-time mesh optimization, void detection, and motion artifact correction.
- High-Precision Milling Sync: Direct integration with Carejoy’s 5-axis wet/dry milling units for same-day restorations.
6. Post-Manufacturing Support
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via secure cloud portal.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Updates: Monthly firmware enhancements for scanning algorithms and material libraries.
- Global Service Hubs: Localized calibration and repair centers in EU, NA, and APAC.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Scanner Maxillaire.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
