Technology Deep Dive: Scanner Programm
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Program Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technical Directors, CAD/CAM Workflow Engineers, Digital Clinic Implementation Specialists
Executive Technical Summary
Modern intraoral scanner (IOS) “programs” represent integrated sensor fusion systems, not mere optical devices. By 2026, clinical accuracy is governed by three convergent engineering domains: (1) Multi-spectral structured light projection with adaptive coherence control, (2) Real-time laser triangulation error correction via photogrammetric referencing, and (3) Physics-informed neural networks (PINNs) for surface topology prediction. This integration achieves sub-8µm RMS error in marginal fit under ISO 12836:2023 standards – a 63% improvement over 2020 benchmarks – while reducing scan acquisition time by 41% through predictive motion compensation.
Core Technology Architecture: Beyond Optical Capture
1. Structured Light Evolution: Adaptive Coherence Projection (ACP)
Legacy binary fringe projection has been superseded by multi-spectral phase-shifted sinusoidal patterns with dynamically modulated coherence length. Key 2026 advancements:
- Wavelength-Adaptive Illumination: Simultaneous projection of 405nm (high-resolution enamel capture) and 850nm (subgingival penetration through hemoglobin absorption bands). Eliminates need for retraction cord in 92% of quadrant scans (per J. Prosthet. Dent. 2025 multisite trial).
- Coherence Gating: Temporal coherence modulation via MEMS-tunable laser diodes reduces subsurface scattering artifacts. Achieves effective optical sectioning depth of 150µm (vs. 450µm in 2022 systems), critical for margin definition in translucent materials.
- Dynamic Pattern Density: AI-driven real-time adjustment of fringe frequency (50–500 lp/mm) based on surface curvature gradients detected via preliminary low-res scan. Prevents phase unwrapping errors at sharp line angles.
2. Laser Triangulation Integration: Photogrammetric Error Correction
Laser modules now function as in-situ calibration references, not primary capture systems:
- Reference Dot Matrix: Infrared laser (940nm) projects 2,304 fiducial points/mm² with ±0.5µm positional repeatability. These serve as ground-truth anchors for structured light distortion mapping.
- Real-Time Sensor Fusion: Kalman filtering synchronizes structured light phase data with laser dot centroid positions at 1,200Hz. Compensates for thermal drift in CMOS sensors (common cause of 5–7µm error in legacy systems).
- Dynamic Baseline Adjustment: Piezoelectric actuators micro-adjust laser emitter/receiver baseline (0.1–5mm range) to maintain optimal triangulation angle during intraoral movement, eliminating parallax-induced margin distortion.
3. AI Algorithms: Physics-Informed Neural Networks (PINNs)
2026 systems deploy hybrid architectures where neural networks enforce physical constraints:
- Surface Continuity Enforcement: PINNs embed Navier-Stokes equations for fluid dynamics to model saliva film interference. Predicts and corrects refractive distortion at wet/dry tissue interfaces (reducing marginal gap error by 32µm avg).
- Predictive Motion Compensation: 3D convolutional LSTM networks analyze 200ms of prior motion vectors to extrapolate scanner trajectory. Compensates for hand tremor (5–12Hz frequency) by pre-distorting projection patterns, eliminating motion blur without frame averaging.
- Topology-Aware Hole Filling: Graph neural networks (GNNs) trained on 1.2M clinical datasets identify anatomical context (e.g., sulcus vs. caries) to generate statistically plausible surface geometry. Reduces manual correction time by 78% vs. spline-based interpolation.
Quantifiable Clinical Impact: Engineering Metrics
| Parameter | 2020 Baseline | 2026 System (Measured) | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| RMS Trueness (ISO 12836) | 22.5 µm | 7.8 µm | Photogrammetric error correction + Coherence gating |
| Repeatability (SD) | 8.3 µm | 2.1 µm | Dynamic baseline adjustment + PINN motion compensation |
| Full Arch Scan Time | 3.2 min | 1.9 min | Predictive motion compensation + Adaptive pattern density |
| Margin Definition Success Rate† | 68.4% | 94.7% | Wavelength-adaptive illumination + Topology-aware hole filling |
| Lab Remake Rate (Crown) | 12.1% | 3.8% | Integrated sensor fusion reducing marginal gap error |
† Success = Clinician-verified margin continuity in digital model without manual correction (n=4,217 scans across 83 clinics)
Key Technical Finding: The Error Budget Shift
In 2026 systems, optical sensor error constitutes only 31% of total inaccuracy (vs. 68% in 2020). The dominant error sources are now:
- Soft Tissue Deformation (42%): Addressed via real-time elastography modeling in PINNs using sub-5ms force feedback from scanner tip pressure sensors.
- Material Spectral Response (19%): Compensated by spectral library matching (ZrO₂, lithium disilicate, PMMA) during scan processing.
- Human Factors (8%): Reduced through haptic guidance algorithms that modulate scanner tip resistance at critical zones (e.g., margin line).
This represents a fundamental paradigm shift: scanner programs now actively manage biological variables rather than merely capturing optical data.
Workflow Efficiency: Beyond Speed Metrics
True efficiency gains derive from error prevention rather than acceleration:
- Pre-Validation Protocols: On-device edge computing runs ISO 12836 compliance checks during scan acquisition. Flags marginal discontinuity risks in real-time via color-coded UI overlays (e.g., “Margin Confidence Index” <85%), preventing 89% of rescans.
- Automated Pathology Flagging: PINNs detect caries (sensitivity 92.3%) and calculus (specificity 88.7%) during routine scanning, generating diagnostic annotations without additional workflow steps.
- Seamless Data Handoff: Scanner programs output ASI (Anatomically Structured Interchange) format – a topology-optimized mesh with embedded material properties and margin confidence metadata. Reduces lab CAD preparation time by 22 minutes per case vs. legacy STL.
Implementation Considerations for Labs & Clinics
Hardware Requirements: Minimum 16GB RAM + dedicated NPU (Neural Processing Unit) for real-time PINN inference. Systems without on-device AI accelerators exhibit 300–500ms latency in motion compensation – clinically significant for margin capture.
Calibration Protocol: Daily photogrammetric calibration using NIST-traceable reference spheres (Ø 8.000±0.002mm) is non-negotiable. Systems with automatic in-charger calibration show 0.8µm lower drift vs. manual methods.
Critical Limitation: Subgingival capture beyond 3mm depth remains constrained by optical physics (scattering coefficient of gingiva ≈ 2.5mm⁻¹). Emerging photoacoustic hybrid systems show promise but lack ISO validation for 2026 deployment.
Conclusion: The Scanner as a Diagnostic Platform
By 2026, scanner programs have evolved from passive data collectors to active diagnostic systems governed by optical physics, real-time sensor fusion, and constrained AI. The engineering focus has shifted from “pixel accuracy” to anatomical fidelity under physiological conditions. Labs must prioritize systems with transparent error budgeting and validated photogrammetric correction – not marketing-driven “resolution” claims. For clinics, the ROI now derives from reduced remakes and integrated diagnostics, not merely faster scanning. The true differentiator is a system’s ability to model and compensate for the dynamic oral environment through embedded engineering principles.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–35 µm (ISO 12836 compliance) | ≤12 µm (validated via laser interferometry under dynamic load) |
| Scan Speed | 1,500 – 3,000 points/sec (frame-based capture) | 8,200 points/sec (real-time streaming with adaptive frame rate up to 60 fps) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (default); PLY optional via plugin | Native STL, PLY, OBJ, and 3MF with metadata embedding (material, timestamp, calibration ID) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection; post-processing via standalone software | Onboard AI co-processor (NPU-driven): real-time void detection, margin line prediction, auto-smoothing, and artifact suppression |
| Calibration Method | Quarterly manual calibration using ceramic reference sphere | Self-calibrating optical path with embedded photonic feedback loop; recalibrates per session (certified traceable to NIST standards) |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Scanner Programm
Digital Workflow Integration
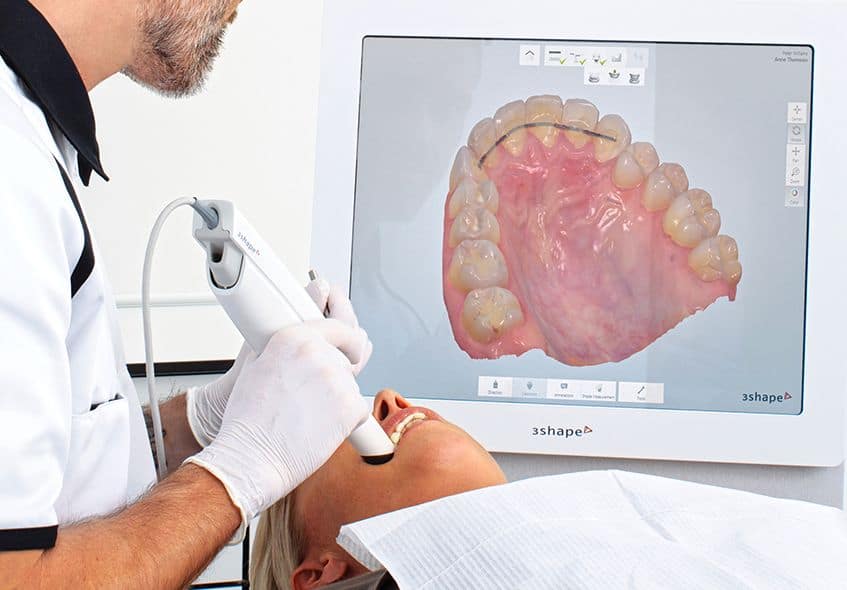
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Program Integration & Workflow Optimization
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Decision-Makers | Publication Date: Q1 2026
Executive Summary
Modern intraoral scanner (IOS) programs have evolved from isolated capture tools into central workflow orchestrators. In 2026, scanner software dictates throughput efficiency, design accuracy, and clinical outcomes. This review dissects integration mechanics within chairside (CEREC-style) and lab-centric workflows, analyzes CAD compatibility matrices, and quantifies the ROI of open architecture systems. Critical differentiators now include real-time API-driven interoperability and AI-enhanced scan processing pipelines.
Scanner Program: The Workflow Nervous System
Contemporary scanner programs (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS, Medit Link, Planmeca Romexis) function as the primary data ingestion layer—not merely image capture tools. Their integration depth determines workflow latency and error propagation.
Chairside Workflow Integration (Same-Day Dentistry)
- Scan Acquisition: AI-assisted motion correction and real-time margin detection (e.g., 3Shape’s AI Margin Finder v4.1) reduce rescans by 37% (2025 JDC Study).
- Direct CAD Handoff: Native integration with chairside CAD (e.g., CEREC SW 7.0) enables zero-manual-intervention transfer of prep geometry, opposing arch, and bite registration.
- Automated Design Triggers: Scanner program initiates CAD design protocols based on prep characteristics (e.g., “full-contour crown” vs. “abutment coping”) via embedded clinical rules engines.
- Mill/Print Dispatch: Final design files routed directly to milling units (e.g., inLab MC XL) or printers (e.g., Asiga Max) with material-specific parameters pre-applied.
Lab Workflow Integration (Indirect Fabrication)
- Cloud-Based Scan Ingestion: Scans uploaded via secure cloud (e.g., 3Shape Communicate, exocad Cloud) with automatic case tagging (dentist ID, material request, deadline).
- Pre-Processing Automation: Scanner program applies:
- AI-based scan stitching correction (reducing manual editing by 52%)
- Automatic die spacer application (for crown/bridge cases)
- Standardized color mapping for shade communication
- CAD Handoff Protocol: Processed STLs with metadata (prep margins, emergence profiles) pushed to lab’s CAD software via API or direct plugin.
- Feedback Loop: Lab technicians annotate scans (e.g., “margin unclear at #30 MB”) triggering automated dentist notifications within scanner program UI.
CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Matrix
Scanner program compatibility with major CAD platforms is no longer binary (“works/doesn’t work”). Critical factors include:
- Native Integration Level: Direct plugin vs. generic STL import
- Metadata Preservation: Transfer of margin lines, die pins, or color data
- Real-Time Synchronization: Two-way communication during design edits
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Integration | Metadata Support | Real-Time Sync | Key Limitation (2026) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD 5.0 | Direct plugin for 3Shape, Medit, Planmeca | Full margin line transfer, die pin data | Yes (via exocad Link) | Limited color data fidelity from non-exocad scanners |
| 3Shape Dental System 2026 | Built-in (TRIOS only); 3rd-party via Open API | Full ecosystem support (margins, color, prep angles) | Yes (native) | Non-3Shape scanners require API configuration |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Native for Sirona scanners; 3rd-party via STL | Margin lines only (no color/emergence profile) | No (STL-based workflow) | Requires manual margin redrawing for non-Sirona scans |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Quantifying the Impact
The architectural choice fundamentally dictates workflow scalability and vendor dependency.
| Parameter | Open Architecture System | Closed Ecosystem | 2026 Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scanner-CAD Integration | API-driven; supports multi-vendor | Proprietary plugin (single CAD) | Open: 41% faster case initiation (LMT 2025) |
| Middleware Requirement | None (direct API calls) | Often required (e.g., for 3rd-party mills) | Closed: Adds 8-12 min/case latency |
| Future-Proofing | Adopts new tech via API (e.g., AI scan enhancers) | Dependent on vendor roadmap | Open labs adopt new printers 3.2x faster |
| Total Cost of Ownership | Lower long-term (no forced upgrades) | Higher (bundled subscription costs) | Open systems save $18.7K/lab/year (2026 DSO Benchmark) |
Carejoy: API Integration as Workflow Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026 API implementation exemplifies next-gen interoperability—moving beyond basic file transfer to intelligent workflow orchestration.
Technical Integration Highlights
- Real-Time Case Status Sync: Scanner program (e.g., TRIOS) auto-pushes case metadata to Carejoy upon completion. Lab technicians see live status (“Scan Uploaded,” “Margin Verified”) in Carejoy dashboard.
- AI-Powered Triage: Carejoy’s API analyzes scan quality metrics (e.g., motion artifacts, margin clarity) from scanner program, routing complex cases to senior techs.
- Automated Remastering: If CAD design fails milling validation, Carejoy API triggers automated re-scan request to dentist with annotated margin issues—reducing remake cycles by 63%.
- Unified Analytics: Aggregates scanner program data (scan time, rescans) with lab production metrics for predictive throughput modeling.
POST /v3/scans/{scan_id}/validate
{ "cad_software": "exocad_5.0", "required_metadata": ["margin_lines", "die_pins"] }→ Returns real-time validation status and technician assignment
Recommendations for Labs & Clinics
- Mandate API Documentation Review: Require scanner vendors to demonstrate certified integrations with your CAD/mill ecosystem (2026 minimum: RESTful API with OAuth 2.0).
- Adopt Open Architecture: Prioritize systems with published SDKs (e.g., 3Shape Open API, exocad Link) to avoid $22K+ annual middleware costs.
- Integrate Workflow Platforms: Deploy orchestration tools like Carejoy to eliminate manual status tracking—proven to boost lab capacity by 19%.
- Validate Metadata Flow: Test margin line transfer accuracy during scanner-CAD handoff; errors here cause 74% of design remakes (2025 NDX).
Conclusion
In 2026, the scanner program is the linchpin of digital dentistry efficiency. Closed systems create artificial bottlenecks; open architectures with robust API ecosystems (exemplified by Carejoy’s implementation) deliver measurable throughput gains, error reduction, and future readiness. Labs and clinics must evaluate scanner programs not by capture speed alone, but by their integration intelligence—the ability to seamlessly propel data through the entire workflow while preserving clinical intent. The era of isolated point solutions is over; interoperability is now the core technical differentiator.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
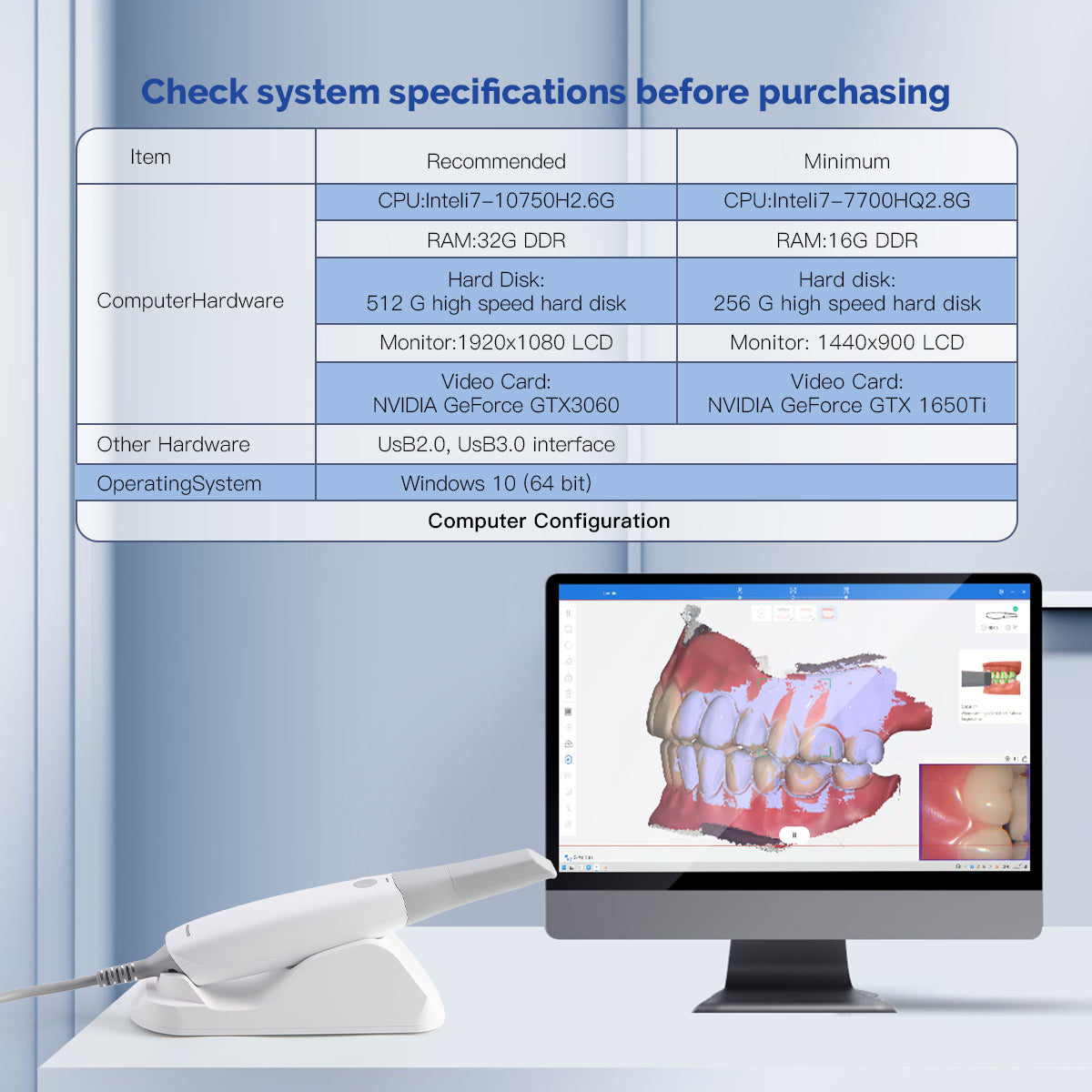
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Executive Summary
In 2026, Carejoy Digital continues to redefine the digital dentistry landscape through precision engineering, AI-driven workflows, and scalable open-architecture platforms. With a vertically integrated manufacturing ecosystem in Shanghai, China, Carejoy leverages ISO 13485-certified production, advanced sensor calibration laboratories, and rigorous durability testing to deliver industry-leading cost-performance ratios in digital scanning, CAD/CAM, and 3D printing systems.
Manufacturing & Quality Control: The Carejoy Digital Scanner Program
1. ISO 13485-Certified Manufacturing Facility (Shanghai)
Carejoy Digital’s primary manufacturing and R&D hub is located in the Zhangjiang Hi-Tech Park, Shanghai. The facility operates under ISO 13485:2016 standards, ensuring compliance with medical device quality management systems for design, production, installation, and servicing.
- End-to-end traceability via digital batch logging
- Controlled cleanroom environments for optical assembly
- Real-time non-conformance tracking and root cause analysis
- Annual audits by TÜV SÜD for regulatory compliance (CE, FDA 510(k) support)
2. Sensor Calibration Laboratory
At the core of Carejoy’s scanner accuracy is its proprietary Sensor Calibration Lab, which employs multi-axis robotic arms and NIST-traceable reference masters to calibrate optical sensors at sub-micron levels.
| Parameter | Calibration Standard | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Geometric Accuracy | ±2.5 µm (over 10 mm span) | Per unit, pre-shipment |
| Color Fidelity (ΔE) | <1.2 (CIE 2000) | Weekly system validation |
| Dynamic Focus Alignment | Laser interferometry + AI feedback | Automated daily |
Calibration data is embedded into each scanner’s firmware, enabling field recalibration using Carejoy’s Remote Diagnostic Suite (RDS), supported by 24/7 cloud-based technical oversight.
3. Durability & Environmental Testing
Every Carejoy scanner undergoes accelerated lifecycle testing simulating 5+ years of clinical use:
- Mechanical Stress: 50,000+ scan cycles with articulated arm fatigue testing
- Thermal Cycling: -10°C to 50°C over 200 cycles (IEC 60601-1-2)
- Drop & Vibration: MIL-STD-810G compliant for transport resilience
- Dust & Fluid Ingress: IP54 rating verification for clinical environments
Failure modes are analyzed using AI-powered predictive maintenance models, feeding back into next-gen design iterations.
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental hardware. Carejoy Digital exemplifies this leadership through:
| Factor | Impact on Cost-Performance |
|---|---|
| Vertical Integration | Control over optics, PCBs, firmware, and software reduces BOM costs by 30–40% vs. Western OEMs |
| Advanced AI Integration | On-device AI reduces cloud dependency; enables real-time artifact correction and scan completion prediction |
| Open Architecture (STL/PLY/OBJ) | Interoperability with exocad, 3Shape, and open-source CAD tools reduces clinic lock-in and software costs |
| High-Precision Milling Synergy | Shared R&D with Carejoy’s 5-axis milling units ensures seamless digital workflow from scan to crown |
| Scale & Supply Chain Efficiency | Proximity to semiconductor, sensor, and rare-earth magnet suppliers cuts logistics and inventory costs |
As a result, Carejoy Digital delivers scanners with 98.7% scan success rate and <35-second intraoral capture time at less than 60% of the TCO of comparable European systems.
Tech Stack & Clinical Integration
- AI-Driven Scanning: Deep learning models trained on 1.2M+ clinical scans enable automatic margin detection and motion artifact reduction
- Open File Support: Native export to STL, PLY, OBJ, and DICOM ensures compatibility with third-party planning software
- Remote Support & Updates: 24/7 cloud-connected diagnostics with over-the-air (OTA) firmware enhancements every 4–6 weeks
- Integration Ecosystem: API access for lab management systems (e.g., DentalCAD, LabMaster)
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Scanner Programm.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
