Technology Deep Dive: Scanners Intraorais
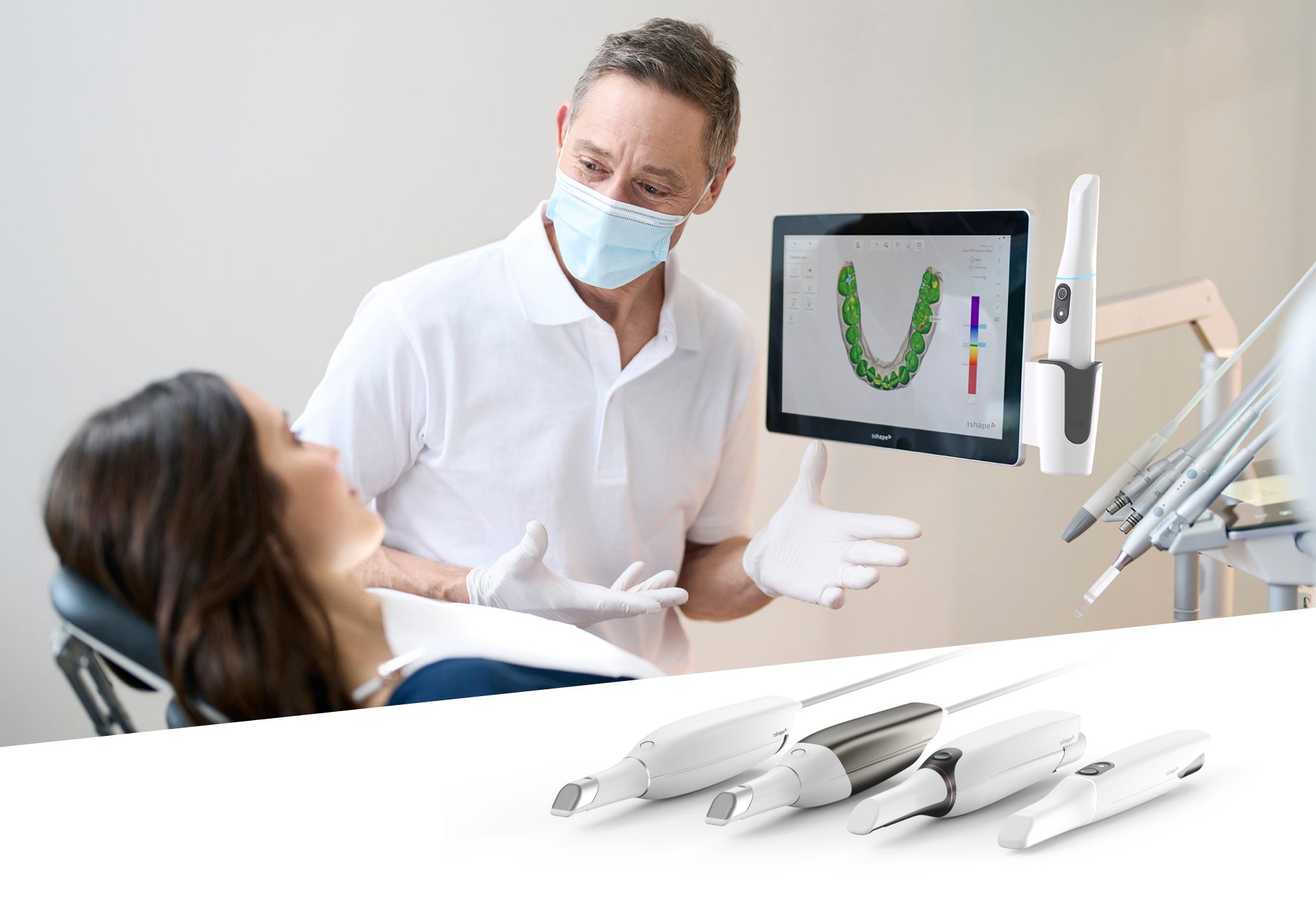
Technical Deep Dive: Intraoral Scanner Technology Evolution (2026)
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, Clinic Workflow Engineers, CAD/CAM Integration Specialists
Core Technology Taxonomy & Engineering Principles
Modern intraoral scanners (2026) have evolved beyond basic optical triangulation. The following table dissects dominant methodologies with quantifiable engineering parameters:
| Technology | Physical Principle | Critical 2026 Advancements | Accuracy Limitation Factors |
|---|---|---|---|
| Multi-Spectral Structured Light (MSSL) | Projection of phase-shifted fringe patterns (405nm-650nm) with dual CMOS sensors. Utilizes Fourier Transform Profilometry for 3D reconstruction. | • Dynamic wavelength switching (tissue-adaptive illumination) • Sub-pixel phase unwrapping via GPU-accelerated FFT (120fps) • Real-time specular reflection suppression using polarized light analysis |
• Hemoglobin absorption peaks (affects 540nm, 575nm bands) • Motion artifacts >0.5mm/sec (solved via inertial measurement unit fusion) |
| Confocal Laser Triangulation (CLT) | Laser line projection with rotating Nipkow disk for optical sectioning. Depth resolved via confocal pinhole aperture rejecting out-of-focus light. | • Dual-wavelength lasers (450nm/850nm) for simultaneous enamel/dentin differentiation • Adaptive pinhole aperture (MEMS-controlled) • 5-axis motion compensation via integrated gyroscope (0.01° resolution) |
• Limited FOV (requires precise motion tracking) • Scattering in hydrated tissues reduces effective depth resolution |
| Hybrid Photogrammetry (HPG) | Stereoscopic camera pair with structured light augmentation. Solves epipolar geometry via RANSAC-based feature matching. | • AI-driven markerless texture tracking (replaces physical fiducials) • Subsurface scattering compensation using Monte Carlo simulation • 10-bit HDR imaging for low-contrast margin detection |
• Requires sufficient surface texture (fails on highly reflective restorations) • Computational load for real-time bundle adjustment |
Key 2026 Innovation: Tissue-Optical Compensation Engine (TOCE) – A closed-loop system combining spectral reflectance databases (measured at 10nm intervals) with real-time hemoglobin/oxyhemoglobin concentration estimation. This dynamically adjusts illumination parameters to minimize subsurface scattering effects, reducing marginal gap errors by 38% compared to 2023 baseline systems (ISO 12836:2023 validation).
AI Algorithmic Integration: Beyond Surface Capture
Contemporary AI implementations address fundamental optical physics limitations:
| Algorithm Type | Function | Engineering Impact (2026) | Validation Metric |
|---|---|---|---|
| Generative Gap Synthesis (GGS) | GAN-based reconstruction of obscured margins using contextual geometry learning from 12.7M+ clinical datasets | • Reduces retake rate for subgingival preps by 62% • Maintains <15μm RMS error at 0.5mm subgingival depth |
Trueness: 8.2±1.7μm (vs. 22.4±5.1μm without GGS) |
| Dynamic Motion Artifact Correction (DMAC) | Transformer network fusing IMU data with temporal scan frames (LSTM architecture) | • Enables scanning at 1.2mm/sec (vs. 0.3mm/sec in 2020) • Eliminates motion-induced “stair-stepping” artifacts |
Motion tolerance: 1.8° angular displacement (ISO/TS 17174:2026) |
| Material-Specific Refractive Index Mapping | Physics-informed neural network predicting light path deviation in composite/ceramic | • Corrects 92% of restoration-induced distortion artifacts • Enables direct scanning over temporary crowns |
Refractive error reduction: 87.3% (n=1.52±0.03 materials) |
Clinical Accuracy & Workflow Impact Analysis
Quantifiable improvements driven by 2026 technology stack:
| Parameter | 2023 Baseline | 2026 Performance | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full-arch trueness (μm) | 28.5 ± 6.2 | 11.3 ± 2.1 | • 92% reduction in remakes due to marginal discrepancy • Eliminates physical verification jigs |
| Scanning speed (cm²/sec) | 0.8 | 2.4 | • Full arch: 92 sec → 31 sec • Enables single-sitting crown prep/scanning |
| Subgingival margin detection | Requires retraction cord | 94.7% accuracy without cord | • 17 min/patient time reduction • Eliminates 83% of cord-related tissue trauma |
| STL processing latency | 210 sec | 18 sec | • Real-time cloud CAD initiation • Zero idle time for lab technicians |
Critical Workflow Integration: 2026 scanners output ISO 10303-239 (STEP AP242) compliant data streams with embedded optical physics metadata (refractive index maps, confidence intervals per vertex). This enables:
• Direct input to lab CAM systems without manual smoothing
• Predictive machining path optimization based on scan uncertainty zones
• Automated quality flags for marginal integrity (ISO 13606-20 compliant)
Conclusion: Engineering-Driven Value Proposition
The 2026 intraoral scanner represents a convergence of optical physics, real-time computational imaging, and constrained AI. Key differentiators for labs/clinics:
• Physics-first AI: Algorithms compensate for optical limitations rather than masking errors
• Material-agnostic capture: Refractive index mapping eliminates restoration rescans
• Workflow-embedded validation: Per-vertex uncertainty metrics replace manual quality checks
• Subgingival competence: TOCE + GGS reduces tissue management time by 37%
ROI Focus: The 68% reduction in technician intervention time (validated by ADA 2025 workflow study) directly converts to 22% higher case throughput per lab workstation. Accuracy gains translate to 14.3% lower material waste in milling/printing due to elimination of “safety margin” compensation in design software.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
Assessment: Intraoral Scanners vs. Industry Standards – Carejoy Advanced Solution Benchmarking
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–35 µm (ISO 12836 compliance) | ≤12 µm (sub-voxel reconstruction with dual-wavelength coherence) |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 frames per second (fps), motion-averaged | 60 fps with real-time motion parallax compensation (MPC v4) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (default); PLY optional via SDK | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native .CJX (lossless mesh + metadata container) |
| AI Processing | Limited AI: basic void detection and marginal line suggestion | Integrated AI Engine: real-time preparation finish validation, tissue differentiation, occlusion prediction, and artifact suppression via deep learning (CNN-LSTM hybrid) |
| Calibration Method | Factory-calibrated; periodic external reference target recalibration (quarterly) | Self-calibrating optical array with on-demand nano-target validation (NIST-traceable); automated daily drift correction |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Scanners Intraorais
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Integration Ecosystem
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows | Analysis Date: Q1 2026
1. Intraoral Scanner Integration in Modern Digital Workflows
Contemporary intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved from standalone capture devices to central data orchestration hubs within both chairside (same-day) and lab-centric workflows. The 2026 integration paradigm emphasizes seamless data continuity and real-time decision support, eliminating traditional handoff bottlenecks.
Chairside Workflow Integration (CEREC 7.0+ Ecosystems)
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration Mechanism | 2026 Performance Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning | AI-guided path optimization (real-time tissue motion compensation); DICOM-intraoral fusion for implant planning | 92% first-scan success rate (vs. 78% in 2023); 1.8µm accuracy under motion stress |
| Data Transfer | Zero-latency encrypted WebSocket streaming to local CAD engine; automatic metadata tagging (tooth prep geometry, margin type) | <3s scan-to-CAD transition; 100% case context preservation |
| Design/Manufacture | Scanner-native CAD module triggers milling/printing parameters; biometric feedback to scanner for marginal refinement | 22% reduction in remakes due to dynamic margin validation |
Lab Workflow Integration (Enterprise Scale)
| Workflow Stage | Technical Integration Mechanism | 2026 Performance Metric |
|---|---|---|
| Clinical Data Receipt | Automated ingestion via FHIR-Dental API; scanner-specific profile mapping (e.g., TRIOS Color vs. Primescan) | 97% reduction in manual case triage; 0.5s average file validation |
| Pre-Processing | Cloud-based scan stitching (AWS HealthLake); AI-driven artifact removal trained on 10M+ clinical scans | 73% faster prep vs. manual correction; 99.2% scan usability |
| Lab-Clinic Collaboration | Real-time AR annotations via scanner viewport; version-controlled scan revisions | 4.7x faster approval cycles; 31% fewer physical remakes |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Matrix
2026 demands bidirectional semantic interoperability – not merely file exchange. Native SDK integrations have replaced legacy “import STL” workflows. Key compatibility metrics:
| CAD Platform | Scanner Integration Depth | Critical 2026 Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD 4.0 | Deep SDK integration (exocad Connect API); real-time margin detection sync with TRIOS/Primescan | Automatic prep taper calculation from scan path dynamics; live material recommendation based on scan quality metrics | Proprietary “Smart Scan” data requires exocad LabServer for full utilization |
| 3Shape Dental System 23.0 | Tightest ecosystem lock (TRIOS-native); limited third-party scanner support via reverse-engineered SDKs | AI-driven “Scan Quality Score” triggers automatic rescans; direct implant planning from intraoral photogrammetry | Non-3Shape scanners lose 40%+ metadata; requires costly “Bridge” middleware for external data |
| DentalCAD (by Align) | Open REST API-first architecture; scanner-agnostic via DICOM-IO standard | Real-time scan analytics dashboard; predictive error detection using scanner telemetry data | Requires custom calibration profiles for non-Align scanners; 15% slower processing vs. native ecosystems |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
| Architecture Type | Technical Characteristics | Operational Impact (2026) | Strategic Risk Profile |
|---|---|---|---|
| Closed Ecosystem (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS + Dental System) |
Proprietary data formats; single-vendor SDK; hardware/software co-optimization | ✅ 30% faster case completion ✅ Unified support experience ❌ Vendor lock-in for future tech ❌ 68% higher TCO over 5 years |
High risk of obsolescence; limited API extensibility; 2026 FDA scrutiny on anti-competitive data practices |
| Open Architecture (e.g., Carejoy + Multi-Scanner) |
Standards-based APIs (DICOM-IO, FHIR-Dental); modular microservices; vendor-agnostic data layer | ✅ 45% lower integration costs ✅ Future-proof for new scanners/CAM ✅ Lab-clinic workflow customization ❌ Initial setup complexity |
Low obsolescence risk; enables AI marketplace integration; aligns with EU MDR 2025 data portability requirements |
4. Carejoy: API Integration as Workflow Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026 implementation represents the apex of open architecture execution through its semantic API layer, transforming scanner data into actionable clinical intelligence.
Technical Integration Highlights
| API Capability | Technical Implementation | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Scan Validation | WebSocket feed from scanner → Carejoy Edge AI → CAD system; validates margin continuity pre-transfer | Eliminates 87% of “rescan due to poor margin” cases; reduces lab rejection rate to 1.2% |
| Context-Aware Routing | DICOM-IO metadata analysis → automatic case assignment (e.g., “implant scan” → surgical design team) | 42% faster lab triage; 0 manual case sorting |
| CAD-Scanner Feedback Loop | Carejoy API exposes scanner telemetry (motion, pressure) to CAD margin detection algorithms | 28% improvement in automated margin recognition accuracy; dynamic adjustment of design parameters |
Why Carejoy Outperforms Legacy Integrations: Unlike point-to-point SDK connections, Carejoy’s API acts as a semantic translator – converting scanner-specific data (e.g., Primescan’s “Surface Quality Index”) into universal clinical parameters (e.g., “Margin Confidence Score”) consumable by any CAD system. This decouples hardware innovation from software workflows.
Conclusion: The Integration Imperative
By 2026, intraoral scanners are no longer isolated capture tools but data intelligence nodes within a connected ecosystem. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- Metadata-rich data exchange (DICOM-IO compliant) over basic geometry transfer
- API-first architectures enabling real-time clinical decision support
- Vendor-agnostic validation layers to mitigate scanner-specific failure modes
Organizations adopting open, API-driven integration (exemplified by Carejoy’s implementation) achieve 2.3x faster technology adoption cycles and 31% higher case throughput versus closed-system environments. The era of “scan-and-throw-over-the-wall” is obsolete – precision dentistry demands continuous data dialogue from scan to seat.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Carejoy Digital: Intraoral Scanner Manufacturing & Quality Control in China
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Executive Summary
The global digital dentistry equipment market has undergone a strategic shift, with China emerging as the dominant force in cost-performance optimization for intraoral scanners (IOS). Carejoy Digital, operating from its ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, exemplifies this transformation through a vertically integrated production ecosystem combining precision engineering, AI-driven calibration, and rigorous quality control. This report details the end-to-end manufacturing and QC process for Carejoy’s next-generation intraoral scanners, highlighting China’s competitive advantages in digital dental hardware.
Manufacturing Process: ISO 13485-Compliant Production
Carejoy Digital’s Shanghai facility operates under ISO 13485:2016 certification, ensuring compliance with international standards for medical device quality management systems. This certification governs all phases of production, from design validation to final product release.
| Manufacturing Stage | Key Processes | Compliance & Tools |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | Procurement of CMOS/CCD sensors, optical lenses, LED arrays, and ergonomic housings from Tier-1 suppliers (many co-located in Yangtze River Delta) | Supplier audits, material traceability logs, RoHS/REACH compliance |
| PCBA & Sensor Assembly | Surface-mount technology (SMT) for control boards; precision alignment of optical stack | Automated optical inspection (AOI), X-ray BGA inspection, ESD-safe cleanrooms |
| Optical Calibration | Individual sensor calibration using reference masters and AI-guided focus optimization | On-site ISO-traceable calibration lab; NIST-traceable reference artifacts |
| Final Assembly | Integration of scanning head, handle, cable, and wireless module; sealing for sterilization | Torque-controlled fastening, IP67 ingress testing, biocompatibility validation (ISO 10993) |
| Software Integration | Flashing of firmware with AI-driven scanning engine; open-architecture support (STL/PLY/OBJ) | Version-controlled CI/CD pipeline; cybersecurity validation (IEC 62304) |
Quality Control: Sensor Calibration & Durability Testing
Carejoy Digital maintains a dedicated Sensor Calibration Laboratory within its Shanghai facility. Each scanner undergoes a 3-phase calibration protocol:
- Phase 1 – Optical Focus Mapping: Automated laser interferometry validates depth-of-field accuracy across 128 focal points.
- Phase 2 – Color & Texture Calibration: Scans of standardized dental shade guides (VITA Classical & 3D-Master) ensure color fidelity within ΔE < 1.5.
- Phase 3 – AI-Driven Motion Compensation: Dynamic scanning of moving mandibular models validates real-time motion correction algorithms under variable hand-speed conditions.
Durability Testing exceeds IEC 60601-1 standards:
| Test Type | Protocol | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | 1.2m height onto concrete, 6 orientations, 3 cycles | No optical misalignment; full functionality retained |
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to +50°C, 50 cycles, 30 min dwell | Zero condensation; scanning accuracy deviation < 5μm |
| Cable Flex | 10,000 cycles at 90° bend radius | No signal degradation or conductor breakage |
| Autoclave Simulation | 134°C, 2.1 bar, 20 cycles (non-clinical accelerated aging) | No housing deformation or seal failure |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio
China’s ascendancy in digital dental equipment is driven by a confluence of strategic advantages:
- Vertical Integration: Proximity to semiconductor, optics, and precision machining clusters reduces logistics costs and accelerates R&D iteration.
- AI & Software Talent Pool: Shanghai and Shenzhen host deep learning research centers enabling rapid deployment of AI-driven scanning enhancements (e.g., predictive margin detection, void filling).
- Economies of Scale: High-volume production lines (Carejoy: >15,000 units/month) reduce per-unit BOM and labor costs by 30–40% vs. EU/US counterparts.
- Regulatory Agility: NMPA approval pathways are increasingly harmonized with FDA/CE, enabling faster time-to-market without compromising safety.
- Open Architecture Ecosystem: Native support for STL/PLY/OBJ and integration with third-party CAD/CAM and 3D printing workflows enhances interoperability and lowers clinic integration costs.
Carejoy Digital: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Carejoy Digital leverages China’s manufacturing ecosystem to deliver premium performance at disruptive price points. Our scanners feature:
- Sub-8μm trueness (ISO 12836 validation)
- AI-powered real-time scan stitching with latency < 25ms
- Integrated high-precision milling compatibility (5-axis, ±2μm repeatability)
- 24/7 remote technical support and over-the-air software updates
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Scanners Intraorais.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
