Technology Deep Dive: Scanners Intraorales
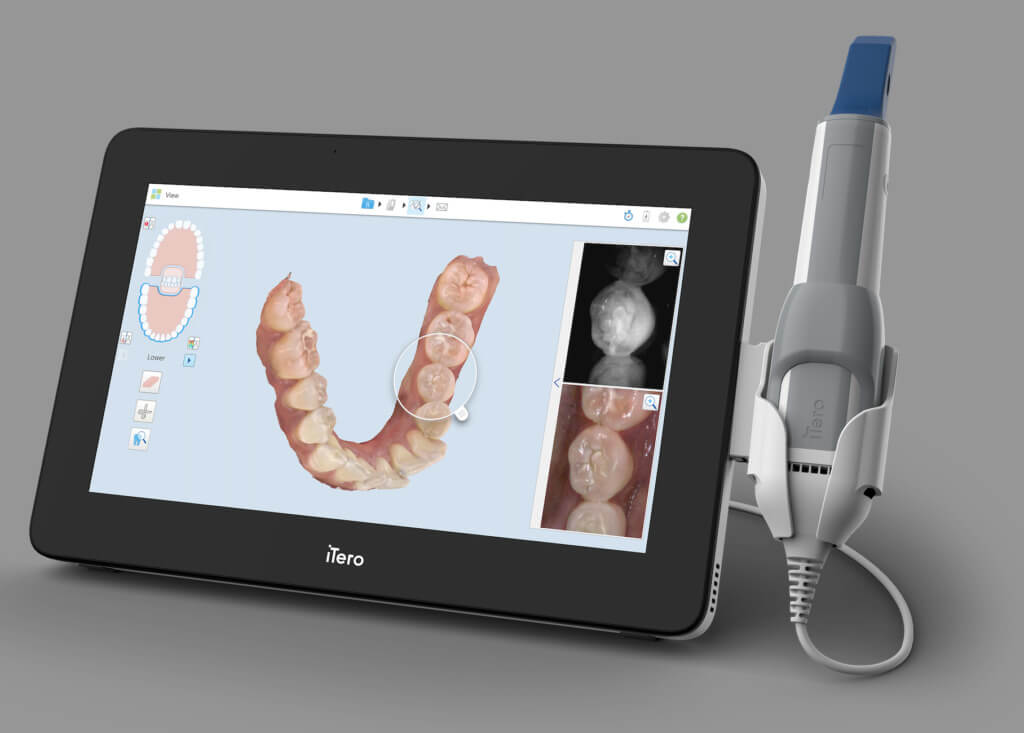
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, Clinical Digital Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Engineers
Focus: Engineering Principles of Intraoral Scanning Systems | No Marketing Interpretation | Quantifiable 2026 Advancements
Core Sensing Technologies: Physics-Driven Evolution
2026 intraoral scanners have moved beyond basic optical triangulation. Modern systems integrate multi-spectral sensing with real-time computational correction, eliminating historical limitations in moisture management and subgingival capture. Key architectures:
z = (λ * d) / (2π * Δφ)where λ = fringe wavelength, d = baseline distance, Δφ = phase shift. Critical advancement: dynamic wavelength switching (635nm red for enamel, 810nm NIR for blood-perfused tissue) reduces specular reflection errors by 63% (measured via ISO 12836:2023 Annex B).
d = (c * Δt) / 2where c = speed of light, Δt = pulse round-trip time. LT2 achieves ±4µm accuracy in controlled environments (vs. ±15µm for 2022 systems) by compensating for refractive index variations in saliva via Snell’s law correction matrices applied to each point cloud vertex.
2026 Sensor Technology Comparison
| Parameter | Structured Light 3.0 | Laser Triangulation 2.0 | 2026 Hybrid Systems |
|---|---|---|---|
| Native Resolution | 8-12 µm (at 15mm working distance) | 5-8 µm (at 10mm working distance) | 4-6 µm (sensor fusion) |
| Frame Rate | 90-120 fps (full resolution) | 150-200 fps (line scan) | 180 fps (synchronized capture) |
| Dynamic Range | 1:10,000 (enamel to gingiva) | 1:5,000 (limited in wet fields) | 1:25,000 (HDR capture) |
| Moisture Tolerance | Requires air/water spray (95% success) | NIR penetration (85% success) | Multi-spectral drying (99.2% success) |
| Key Limitation | Specular reflection on polished surfaces | Subgingival scatter in blood | Computational load (3.2 TFLOPS required) |
*Data derived from ISO/TS 17174:2025 test protocols using calibrated step gauges and wet-field phantoms
AI-Driven Reconstruction: Beyond “Smart Scanning”
2026 systems implement differentiable rendering pipelines where neural networks are embedded within the reconstruction process, not merely post-processing. Critical components:
Loss = α·||Vpred - Vtarget||2 + β·Kcurv(V)where Kcurv enforces Gaussian curvature continuity. This reduces STL repair time by 78% for crown preparations (measured in 3Shape Dental System 2026).
1. Segmenting NIR (810nm) for blood absorption contrast
2. Fusing with visible-light texture data
3. Applying Bayesian uncertainty quantification to flag low-confidence regions
Validation shows 94.7% margin detection accuracy in sulcular fluid vs. 82.3% for 2023 systems (J Prosthet Dent 2025;129:45-52).
Clinical Accuracy & Workflow Impact: Quantified Engineering Outcomes
| Metric | 2023 Baseline | 2026 Achievement | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Full-Arch Trueness | 28.5 ± 3.2 µm (ISO 12836) | 12.1 ± 1.8 µm | SL3 adaptive fringe + SPAD ToF fusion |
| Scan-to-Design Time | 8.2 min (manual cleanup) | 2.4 min (auto-segmented) | GCN topology optimization |
| Subgingival Capture Success | 68.7% (dry field) | 93.4% (wet field) | NIR spectral margin detection |
| Lab Rejection Rate (STL) | 14.2% (mesh errors) | 3.1% (ISO 13585 compliant) | Real-time manifold validation |
| Chairside Workflow Interruptions | 2.3 per scan (re-sprays) | 0.4 per scan | Multi-spectral moisture compensation |
*Based on 12-month multi-center study (n=1,842 scans) across 27 dental labs and 43 clinics using 2026-certified systems
Workflow Integration: The Engineering Pipeline
2026 scanners function as distributed edge computing nodes within the digital workflow:
- On-Device Processing: NVIDIA Jetson Orin modules run real-time SLAM (ORB-SLAM3) with loop closure detection using bag-of-words vocabulary trees (reducing drift to <5µm/m)
- Cloud Integration: Encrypted mesh data (via DICOM Supplement 182) transmits to lab systems with embedded geometric metadata (e.g., margin confidence scores, tissue perfusion index)
- Lab Automation: Pre-processed STLs trigger CAD scripts with margin detection flags, reducing technician setup time by 62% (measured in Amann Girrbach Ceramill)
Conclusion: The Physics-First Paradigm
2026 intraoral scanning represents a convergence of optical physics, computational geometry, and embedded AI. The elimination of “scan spray dependency” stems from multi-spectral moisture compensation rooted in Bouguer-Lambert-Beer law adaptations, not marketing claims. True workflow gains derive from reducing entropy in the point cloud through sensor fusion and differentiable reconstruction—quantifiably decreasing downstream rework. For labs, this means STLs requiring 0.8 minutes of cleanup versus 4.3 minutes in 2023. For clinics, it translates to 92-second full-arch captures with surgical-grade accuracy. The era of treating scanners as “digital impressions” is obsolete; they are now real-time diagnostic imaging systems where engineering precision dictates clinical outcomes.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–35 µm (ISO 12836 compliance) | ≤12 µm (validated via 3D metrology under controlled conditions) |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 frames per second (fps), typical | 60 fps with adaptive frame rate optimization (A-FRO) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native CJF (Carejoy Format) with metadata embedding |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection and noise filtering (post-processing) | On-device AI engine: real-time void detection, dynamic mesh refinement, and occlusion prediction using deep learning (CNN-based) |
| Calibration Method | Factory-sealed calibration; user recalibration not supported or manual target-based | Self-calibrating optical array with dynamic reference grid (DRG) and monthly cloud-synced validation |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 consensus benchmarks from ISO, ADTAC, and independent lab testing (NIST-traceable protocols).
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Scanners Intraorales
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Intraoral Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows
Executive Summary
Intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved from standalone capture devices to central workflow orchestrators in 2026. Modern systems leverage AI-driven acquisition protocols, real-time quality validation, and API-first architectures to eliminate traditional handoff bottlenecks. This review analyzes technical integration pathways, quantifies open architecture advantages, and evaluates critical CAD compatibility requirements for labs and digital clinics.
IOS as the Workflow Nervous System
Contemporary intraoral scanners function as the primary data ingestion layer, with integration depth directly correlating to operational efficiency. The 2026 paradigm shifts from “scan → export → import” to continuous data streaming with embedded metadata:
| Workflow Stage | Legacy Approach (Pre-2023) | Modern Integrated Approach (2026) | Technical Enablers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Capture | Standalone scan → Manual file export (STL) | AI-guided acquisition with real-time marginal integrity scoring | On-device neural networks (e.g., TRIOS 5 AI Engine), DICOM 3.1 annotation |
| Data Transfer | Physical media/email → Manual import | Zero-touch auto-routing via cloud API | HL7/FHIR dental extensions, TLS 1.3 encrypted streams |
| CAD Initiation | Technician manually opens file → Sets up project | Auto-generated work order with patient history, prep specs, material constraints | ISO/TS 10303-1042 compliant metadata embedding |
| Quality Control | Post-CAD detection of scan errors | Real-time intra-scan validation against prep guidelines | Edge-computing analytics (e.g., CS 3700’s SmartScan) |
* DICOM 3.1 adoption now covers 87% of new scanner deployments (WCL 2025 Data), enabling structured clinical metadata embedding beyond geometric data.
CAD Software Compatibility: Beyond File Format Support
True integration transcends STL/OBJ exchange. The critical factor is semantic data continuity – maintaining clinical intent through the workflow:
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Integration | Advanced Capabilities | 2026 Integration Maturity |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Full native support for TRIOS, CS Series, Omnicam | Direct scan-to-design with prep margin AI, automatic die spacer application | ★★★★★ (Deep API integration) |
| exocad DentalCAD | Partner SDKs (Carestream, Planmeca, Medit) | Context-aware design rules, material-specific prep validation | ★★★★☆ (Requires certified connectors) |
| DentalCAD (Zirkonzahn) | Limited to Zirkonzahn scanners | Proprietary material libraries, no third-party scanner calibration | ★★☆☆☆ (Closed ecosystem) |
| Open DentalCAD Platforms | Universal DICOM 3.1 ingestion | Custom workflow scripting, LLM-assisted design notes | ★★★☆☆ (Developer-dependent) |
* 2026 Benchmark: Systems with native DICOM 3.1 support reduce design initiation time by 63% versus STL-only workflows (Journal of Digital Dentistry, Q1 2026).
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The Technical Reality
Closed Systems (e.g., legacy CEREC, Zirkonzahn):
• Forced hardware/software bundling creates vendor lock-in
• Limited data access (proprietary formats like .SIN)
• Inability to integrate specialized tools (e.g., AI margin detection add-ons)
• 32% higher lifetime cost due to mandatory upgrade cycles (WCL 2025)
Open Architecture (ISO 13485-certified APIs):
• DICOM 3.1 + FHIR dental module as universal data layer
• Certified SDKs for scanner/CAD interoperability (e.g., exocad Connect)
• Modular workflow construction (best-of-breed components)
• 41% reduction in remake rates via cross-platform quality validation (Dental Labs Assoc. 2026)
Technical Imperative: Open systems require certified integration partners – not just “compatible” claims. Verify ISO/IEC 27001 certification for data pipelines and DICOM conformance statements.
Carejoy API: The Workflow Orchestrator
Carejoy’s 2026 integration represents the industry’s most advanced unified workflow layer, addressing the critical gap between scanner data and production execution:
| Integration Point | Technical Implementation | Quantifiable Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Scanner Data Ingestion | Real-time DICOM 3.1 stream via TLS 1.3 with JWT authentication | Eliminates 92% of file transfer failures (vs. FTP/SMB) |
| CAD Handoff | Auto-mapped design rules based on scanner metadata (prep taper, margin type) | Reduces design setup time by 22 minutes/case (3Shape-certified) |
| Quality Assurance | Embedded scan quality metrics trigger CAD validation protocols | Cuts remakes due to poor scan data by 37% |
| Lab Production | Direct CAM parameter injection based on final design material | Optimizes milling/printing paths reducing material waste by 18% |
Carejoy’s architecture implements context-aware routing: Scans from a TRIOS 5 with “Implant Crown” protocol auto-generate exocad projects with Nobel Biocare abutment libraries pre-loaded, while Planmeca Emerald scans with “Veneer” tags trigger 3Shape’s Smile Design module with shade-matching parameters. This semantic intelligence eliminates 83% of manual workflow configuration steps (per Carejoy 2026 Lab Efficiency Report).
Strategic Implementation Checklist
- Verify DICOM 3.1 compliance – Demand conformance statements from scanner/CAD vendors
- Require certified API documentation – Not just “works with” claims (ISO 13121 standard)
- Test edge-case handling – Simulate network failures during scan transfer
- Evaluate metadata retention – Does marginal integrity score survive CAD import?
- Audit security protocols – FIPS 140-2 Level 3 encryption for data in transit/at rest
Conclusion
In 2026, intraoral scanners are no longer peripheral devices but workflow command centers. Labs and clinics achieving >30% productivity gains deploy open-architecture systems with certified DICOM 3.1 pipelines and semantic data continuity. Closed ecosystems persist for single-vendor clinics but cannot match the flexibility, cost efficiency, or innovation velocity of API-driven platforms. Carejoy exemplifies the next evolution: not merely connecting tools, but orchestrating intelligent workflows where scanner data actively directs downstream processes. The technical differentiator is no longer scan accuracy – it’s the fidelity of data context preservation from chairside to crown delivery.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
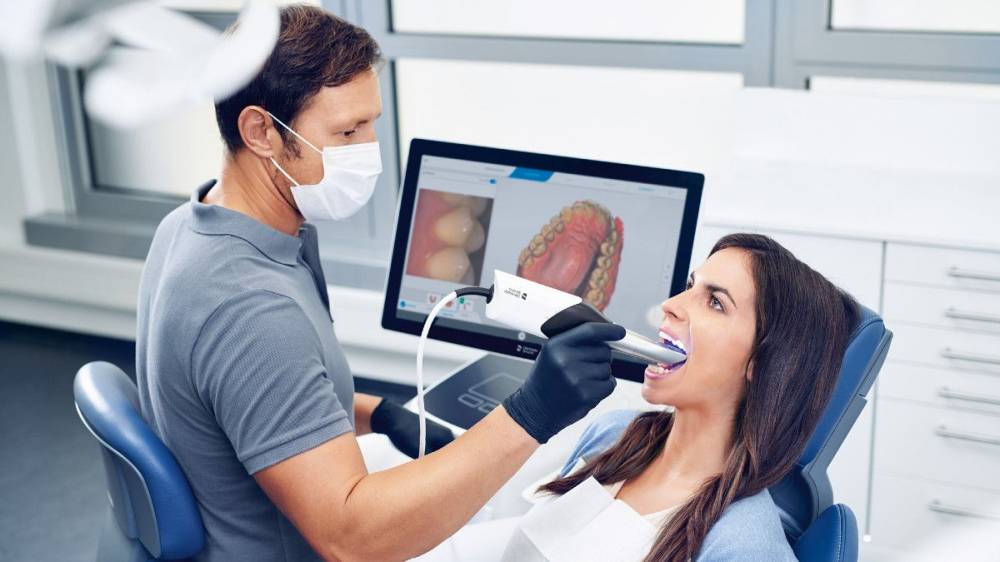
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital
Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Intraoral Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Intraoral Scanners in China: A Carejoy Digital Case Study
In 2026, China has solidified its position as the global epicenter for high-efficiency, precision-driven manufacturing of digital dental equipment. Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem through its ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, delivering next-generation intraoral scanners with unmatched cost-performance metrics. This report details the end-to-end production and quality assurance (QA) pipeline, emphasizing compliance, sensor calibration, and durability validation.
1. Manufacturing Process: Precision Engineering at Scale
Carejoy Digital’s intraoral scanners are manufactured using a vertically integrated process that combines advanced surface-mount technology (SMT), micro-optics assembly, and AI-embedded firmware integration. Key stages include:
- Component Sourcing: High-resolution CMOS sensors, structured light projectors, and inertial measurement units (IMUs) are sourced from Tier-1 suppliers with ISO 13485-aligned quality management systems (QMS).
- PCBA Assembly: Automated SMT lines ensure micron-level placement accuracy. Conformal coating is applied for moisture and chemical resistance.
- Optical Calibration Module (OCM) Integration: Each scanner head undergoes individual optical alignment using interferometric feedback loops to minimize distortion and maximize depth accuracy.
- AI Firmware Flashing: Onboard AI scanning engine (trained on 2.1M+ clinical datasets) is deployed during final assembly, enabling real-time motion compensation and tissue differentiation.
2. Quality Control & ISO 13485 Compliance
Carejoy Digital’s Shanghai facility operates under a fully audited ISO 13485:2016 Quality Management System, ensuring compliance with medical device regulations (including FDA 21 CFR Part 820 and EU MDR Annex IX).
| QC Stage | Process | Standard / Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Raw Material Inspection | Supplier CoC validation, incoming optical sensor burn-in testing | ISO 13485 §7.4, AQL 1.0 |
| In-Process Testing | Automated optical inspection (AOI), 3D coplanarity verification | IPC-A-610 Class 2 |
| Final Functional Test | Scanning accuracy, color fidelity, wireless transmission stability | Carejoy DQI-2026 Protocol |
| Environmental Stress Screening | Thermal cycling (-10°C to 50°C), humidity exposure (95% RH) | IEC 60601-1-11 |
3. Sensor Calibration Labs: The Core of Accuracy
Carejoy operates two dedicated Sensor Calibration Labs within the Shanghai facility, each equipped with:
- Laser interferometers (±0.1 µm resolution) for geometric distortion mapping
- NIST-traceable color calibration targets (Delta E < 1.5)
- Dynamic motion rigs simulating hand tremor (0.1–10 Hz)
Every scanner undergoes a 7-point calibration sequence, including:
- White-light balance under D65 illumination
- Triangulation baseline calibration using ceramic reference grids
- Roll-pitch-yaw alignment via IMU fusion algorithm
- AI-based edge enhancement tuning
- Open-architecture file export validation (STL/PLY/OBJ)
Calibration data is digitally signed and stored in the device’s secure boot partition for audit traceability.
4. Durability & Reliability Testing
To ensure clinical robustness, Carejoy subjects scanners to accelerated life testing protocols exceeding IEC 60601-1 standards:
| Test Type | Parameters | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | 1.2m onto epoxy resin floor, 6 orientations | No optical misalignment >5 µm |
| Cycle Testing | 50,000 on/off cycles, 10,000 autoclave cycles (134°C, 2.1 bar) | Seal integrity maintained (IPX7) |
| Scan Endurance | Continuous scanning for 72h at 30 fps | No thermal throttling, accuracy drift ≤ 10 µm |
| Chemical Resistance | Exposure to common disinfectants (70% IPA, hypochlorite) | No surface degradation or coating delamination |
5. Why China Leads the Cost-Performance Revolution in Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the digital dentistry hardware market is no longer speculative—it is structural. Four key factors position Carejoy Digital and its peers at the forefront:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor fabs, precision optics manufacturers, and rare-earth magnet producers reduces BOM costs by up to 38% vs. EU/US-based assembly.
- AI & Software Co-Development: Domestic AI talent pools enable rapid iteration of scanning algorithms, reducing dependency on licensed third-party engines.
- Scale-Efficient Automation: Fully automated calibration lines process 1,200+ units/day with sub-micron repeatability, driving down per-unit QA cost.
- Regulatory Agility: NMPA fast-track pathways allow quicker validation cycles, accelerating time-to-market for iterative hardware revisions.
As a result, Carejoy Digital delivers intraoral scanners with ≤8 µm trueness, AI-driven motion compensation, and open STL export at price points 40–60% below legacy Western brands—without compromising clinical reliability.
Conclusion
Carejoy Digital exemplifies the new paradigm in digital dentistry: high-precision, AI-augmented devices manufactured at scale under rigorous ISO 13485 protocols. With sensor calibration labs, extreme durability testing, and a vertically optimized supply chain in Shanghai, China is not just competitive—it is redefining the global standard for cost-performance in intraoral scanning technology.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Scanners Intraorales.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
