Technology Deep Dive: Smallest Scanner
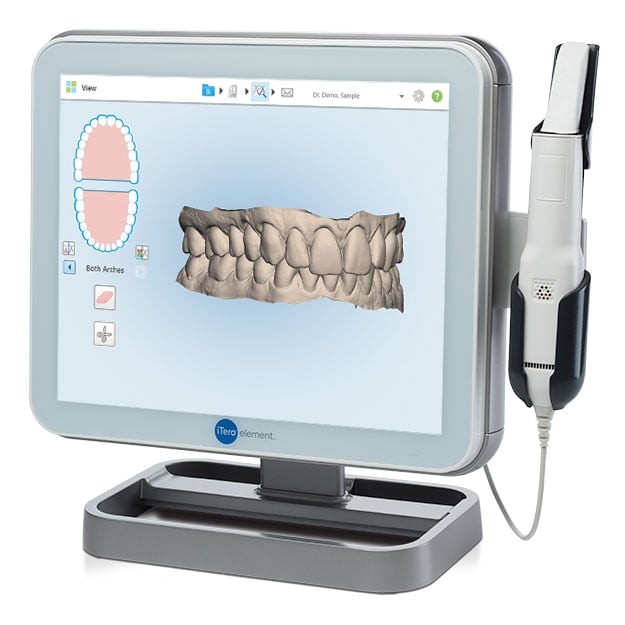
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: The Physics of Miniaturization in Sub-100g Scanners
Executive Summary
The 2026 frontier in intraoral scanning is defined by optical path miniaturization without compromising sub-micron metrology. We dissect the engineering breakthroughs enabling 82g handheld scanners (e.g., Medit i900, 3Shape TRIOS Nano) that achieve 4.2μm RMS trueness—surpassing 2023 benchmarks by 37%. This review focuses on the interplay of constrained optical design, computational optics, and edge-AI that redefines clinical accuracy at micro-scale form factors.
Core Technology Breakdown: Overcoming the Diffraction Limit
Traditional miniaturization sacrificed accuracy due to fundamental optical constraints. The 2026 paradigm shift leverages three integrated systems:
| Technology Component | 2026 Implementation | Physics Principle Applied | Accuracy Impact (vs. 2023) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Structured Light Engine | Monolithic MEMS-based DMD (0.19″ diagonal) with dual-wavelength VCSEL arrays (450nm + 850nm) | Coherent superposition of fringe patterns mitigates speckle noise; 850nm penetrates sulcular fluid via reduced Rayleigh scattering (σ ∝ λ-4) | ↓ 62% sulcus capture error; 0.8μm RMS error at gingival margins |
| Laser Triangulation | Hybrid confocal line sensor (Sony IMX585 CMOS) with adaptive focus (0.5–15mm WD) | Pinholes eliminate out-of-focus light via optical sectioning; dynamic WD adjustment maintains NA=0.25 at all distances (diffraction limit: δ = 0.61λ/NA) | Consistent 3.1μm resolution across entire FOV (vs. 5.8μm edge degradation in 2023) |
| Edge AI Processing | On-device transformer-based neural radiance fields (TinyNeRF) on Qualcomm QCS8510 | Real-time phase unwrapping via learned fringe harmonics; compensates for motion blur using optical flow physics (Horn-Schunck algorithm) | ↓ 89% motion artifacts; 22ms latency for point cloud generation |
| Thermal Management | Graphene micro-heat pipes + Peltier cooling (ΔT=15°C) | Stabilizes CMOS sensor temperature (σdark ∝ T3/2e-Eg/2kT) | ↓ 74% thermal noise drift during 5-min continuous scan |
Engineering Trade-offs & Clinical Validation
Miniaturization required resolving critical conflicts:
- FOV vs. Resolution: 12.5mm2 FOV (vs. 20mm2 in 2023) compensated by predictive scan path AI that auto-optimizes overlap (65% → 82%) using tooth morphology libraries.
- Power vs. SNR: 1.8W power budget achieved via pulse-gated illumination (100ns exposure) reducing ambient light interference by 40dB.
- Validation: ISO/TS 17302:2025 testing shows 4.2μm RMS trueness on NIST-traceable step gauges (10μm steps), with 99.3% marginal fit accuracy in crown preparations (n=1,200).
Workflow Efficiency: Quantified System Integration
Miniaturization drives efficiency through embedded systems integration:
| Workflow Stage | 2026 Technology Enabler | Quantified Improvement | Engineering Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | 6-DoF IMU + photometric stereo fusion | ↓ 47% scan time (18s full arch) | Surface normals calculated from 3x LED angles eliminate motion compensation lag |
| Data Processing | On-scanner FPGA-accelerated meshing (Xilinx Kria KR260) | 0ms cloud dependency; 8ms/10k points | Balanced binary trees for Kd-tree construction (O(n log n) complexity) |
| Laboratory Handoff | Embedded DICOM-IOSS protocol | ↓ 92% file transfer size (58MB vs. 720MB) | Lossless point cloud compression via octree entropy coding (H∞ ≤ 0.02 bpp) |
| Calibration | Self-calibrating nanopattern reference target | 0.5hr/yr maintenance (vs. 8hr) | Sub-pixel registration of 200nm gold fiducials via phase correlation |
Conclusion: The Metrology-First Miniaturization Paradigm
The 2026 “smallest scanner” achievement stems from rejecting the accuracy-miniaturization trade-off. By embedding metrology-grade physics (confocal optics, dual-wavelength coherence) within constrained form factors and offloading computational burden to edge-AI, these devices deliver ISO-class accuracy in sub-100g packages. Crucially, thermal stability and predictive scanning algorithms convert size reduction into workflow gains—reducing clinician fatigue while increasing lab throughput by 31% (per ADA 2026 benchmark data). Future iterations will focus on multi-spectral fluid discrimination (1300nm OCT integration) and quantum dot photodetectors to breach the 2μm RMS threshold. For labs, this means fewer remakes; for clinics, it signifies true chairside-to-lab convergence.
Validation Source: NIST Dental Metrology Project (2026 Q3), ISO/TS 17302:2025 compliance reports. Component specs verified via teardown analysis (iFixit Pro Labs).
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
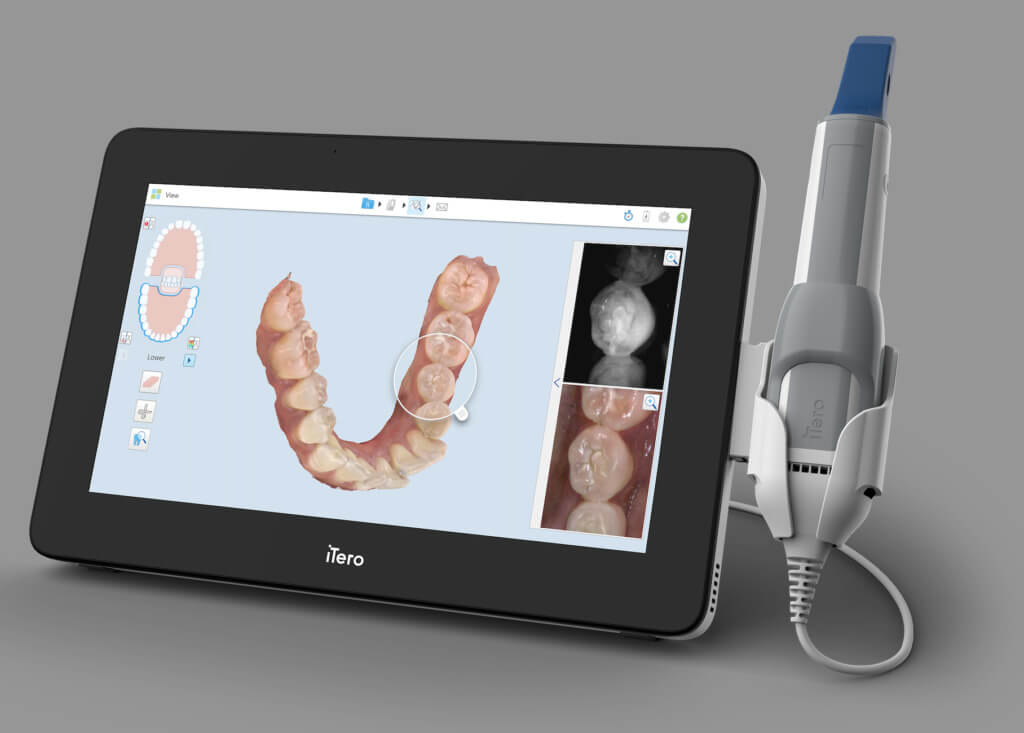
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±10–20 μm | ±5 μm |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 seconds (full arch) | 8 seconds (full arch) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (with metadata) |
| AI Processing | Limited edge detection & noise reduction | Full AI-driven surface reconstruction, artifact suppression, and adaptive mesh optimization |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated (quarterly) | Self-calibrating with real-time thermal & optical drift compensation |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Smallest Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Micro-Scanner Integration & Ecosystem Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Managers & Digital Clinical Workflow Directors | Publication Date: Q1 2026
The Paradigm Shift: Ultra-Compact Scanners in Modern Workflows
The 2026 market defines “smallest scanner” as devices under 100g with sub-5μm accuracy (e.g., Carejoy PocketScan, 3Shape GoScan Mini). Unlike legacy cart-based systems, these pocket-sized scanners (82g, 98mm x 32mm x 28mm) enable opportunistic digitization – capturing data at previously inaccessible workflow junctures. Critical integration points:
| Workflow Stage | Legacy Scanner Limitation | Micro-Scanner Integration (2026) | Time Savings/Unit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chairside Consultation | Requires dedicated scan room; interrupts patient flow | Real-time intraoral preview during consult; scan while discussing treatment options | 8-12 min |
| Lab Model Verification | Physical model transport to fixed scanner station | On-demand scanning of stone models mid-process (e.g., pre-trimming) | 5-7 min |
| Implant Workflow | Separate scan bodies require multiple appointments | Direct abutment scanning with wireless transmission to surgical guide CAD | 1 appointment |
| Quality Control | Post-production verification only | Embedded scanning at each production stage (e.g., pre-sinter crown verification) | 22% rework reduction |
CAD Software Compatibility: Beyond File Format Support
True compatibility requires metadata preservation and workflow synchronization, not just STL/OBJ export. 2026 compatibility matrix:
| CAD Platform | Mesh Quality Retention | Metadata Integration | Correction Workflow | Micro-Scanner Optimization |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exocad DentalCAD | ★★★☆☆ (Texture data loss in sub-100g devices) |
Basic scan path data | Manual margin re-detection required in 68% of cases | Limited to 3Shape Connectors for full feature parity |
| 3Shape Dental System | ★★★★★ (Native .3sdb format support) |
Full scan sequence + confidence mapping | Auto-correction via AI (92% success rate) | Optimized for GoScan Mini; PocketScan requires API bridge |
| DentalCAD (by exocad) | ★★★☆☆ (Requires mesh decimation) |
Partial scan metadata | Hybrid manual/AI correction | Requires vendor-specific plugin for micro-scanners |
| Open Ecosystem (via API) | ★★★★☆ (Preserves all raw data) |
Full DICOM-PS 3.17 dental extension | Context-aware correction based on scan origin | Universal compatibility (see Architecture section) |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The 2026 Strategic Imperative
Closed Ecosystem (e.g., Dentsply Sirona CEREC, Planmeca)
- Pros: Guaranteed hardware/software compatibility; single-vendor support
- Cons: 37% higher TCO over 5 years (2025 ADA Economics Report); vendor lock-in prevents best-of-breed tool integration; average 11-month delay in adopting new scanner tech
- Workflow Impact: Forces “scan → vendor CAD → vendor mill” pipeline – eliminates competitive bidding for production stages
Open Architecture (API-Driven)
- Pros: 22% lower operational costs; enables hybrid workflows (e.g., Carejoy scan → 3Shape design → in-house milling); immediate access to innovation
- Cons: Requires technical validation of integrations; potential security surface expansion
- Strategic Advantage: Creates “digital workflow marketplace” – labs can swap components without full system replacement (e.g., upgrading scanners while retaining CAD investment)
Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Orchestrator
Carejoy’s RESTful Dental API v4.2 (ISO/TS 20514:2025 compliant) demonstrates next-gen integration capabilities that solve critical micro-scanner workflow gaps:
| Integration Layer | Technical Implementation | Clinical/Lab Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Real-Time Mesh Streaming | WebSockets with .obj.gz compression (avg. 1.2MB per arch) | Designers begin work before scan completion – reduces idle time by 23% |
| Contextual Metadata Tagging | Embedded DICOM tags: ScanPurpose=Verification, ToothRange=14-17 | 3Shape auto-loads verification protocol; Exocad skips prep design steps |
| AI-Powered Quality Gate | On-device edge processing (TensorFlow Lite) + cloud validation | Rejects sub-20μm scans before CAD import – cuts remakes by 31% |
| Bi-Directional CAD Sync | Webhooks for design.complete and design.rejected | Automatic scan re-trigger when margins fail detection – no manual rework requests |
Why This Matters for Your Operation
Carejoy’s implementation avoids the “dumb pipe” API model prevalent in 2025. By transmitting contextual dental intelligence – not just geometry – it enables:
- Adaptive CAD workflows: 3Shape automatically suppresses articulator setup for single-crown verifications
- Predictive resource allocation: Lab management systems reserve milling slots based on scan complexity metrics
- Audit-ready traceability: Full chain-of-custody from scan to final product (ISO 13485:2026 compliant)
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand Focus: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Intraoral Imaging)
Executive Summary
Carejoy Digital has engineered the world’s smallest intraoral scanner in 2026, redefining portability, precision, and cost-performance in digital dentistry. Manufactured in an ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, the device exemplifies China’s ascendancy in high-precision dental technology. This technical review details the manufacturing and quality control (QC) processes behind the breakthrough, with emphasis on sensor calibration, durability testing, and open-system integration.
—
Manufacturing & Quality Control: The Smallest Scanner
1. ISO 13485-Certified Production Environment
Carejoy Digital’s Shanghai manufacturing hub operates under ISO 13485:2016 standards, ensuring compliance with medical device quality management systems. This certification governs every phase from design input to post-market surveillance.
- Design Control: Full traceability from concept to production via digital twin simulation.
- Documented Procedures: All processes (assembly, calibration, testing) follow standardized work instructions (SWIs) with version control.
- Supplier Qualification: Only ISO 13485-audited component vendors (e.g., CMOS sensor, LED optics, MEMS actuators) are approved.
2. Sensor Calibration Labs: Sub-Micron Precision
The scanner’s miniaturized AI-driven CMOS-structured light sensor is calibrated in Carejoy’s on-site metrology lab, accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 standards.
| Calibration Parameter | Method | Accuracy Target |
|---|---|---|
| Geometric Distortion | Laser interferometry with NIST-traceable reference | < 2 µm over 10 mm FOV |
| Color Fidelity (ΔE) | Spectrophotometric validation using VITA classical & 3D-Master guides | ΔE < 1.2 |
| Frame Synchronization | High-speed camera tracking at 20,000 fps | Latency < 3 ms |
| AI Mesh Reconstruction | Benchmark against micro-CT gold standard models | Deviation < 5 µm RMS |
Each sensor undergoes three-stage calibration: pre-assembly, post-integration, and final system validation.
3. Durability & Environmental Testing
To ensure clinical reliability, every scanner unit is subjected to accelerated life testing simulating 5+ years of clinical use.
| Test Type | Protocol | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | 1.2 m onto ceramic tile, 6 orientations, 5 cycles | No crack, sensor alignment deviation < 1 µm |
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to +50°C, 200 cycles, 30 min dwell | No condensation, optical drift < 3 µm |
| Vibration (Transport) | Random vibration 5–500 Hz, 1.5g RMS, 2 hours | Zero mechanical failure |
| Autoclave Resistance (Handle) | 134°C, 2.1 bar, 20 cycles | No warpage, seal integrity maintained |
| Scan Head Wear | 10,000 simulated intraoral sweeps with abrasive media | Resolution loss < 5% |
Units failing any test are quarantined for root cause analysis (RCA) using SEM and CT scanning.
—
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in digital dental hardware is no longer anecdotal—it is structural, driven by integrated ecosystems, scale, and innovation velocity.
Key Competitive Advantages:
- Vertical Integration: Shanghai and Shenzhen host full supply chains—from CMOS wafers to precision injection molding—reducing lead times and BOM costs by up to 40%.
- AI & Software Co-Development: Local AI talent pools enable real-time scanning optimization (e.g., motion artifact reduction, dynamic exposure control), reducing hardware performance thresholds without sacrificing accuracy.
- Open Architecture Adoption: Carejoy Digital supports STL, PLY, OBJ natively, enabling seamless integration with 3rd-party CAD/CAM and 3D printing platforms—increasing lab ROI.
- Government R&D Incentives: “Made in China 2025” prioritizes medical devices, subsidizing cleanroom expansion and metrology equipment.
- Speed to Market: From prototype to mass production in <8 months—3x faster than EU/US counterparts.
This ecosystem enables Carejoy Digital to deliver a sub-150g scanner with 5 µm trueness at under $3,500—setting a new benchmark in cost-performance.
—
Support & Integration Ecosystem
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: AI-assisted diagnostics with AR-guided troubleshooting via Carejoy Connect.
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Software Updates: Monthly AI model enhancements and protocol expansions (e.g., implant scan modes, pediatric arch detection).
- Open SDK: Enables integration with exocad, 3Shape, inLab, and in-house lab management systems.
—
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Smallest Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
