Technology Deep Dive: Trios Intra Oral Scanner

Trios Intraoral Scanner: Technical Deep Dive (2026)
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers | Review Date: Q1 2026
Core Optical System Architecture: Beyond Basic Structured Light
Contrary to legacy marketing claims positioning Trios as “laser-based,” the 2026 Trios 5 platform utilizes a dual-wavelength adaptive structured light system (450nm blue & 520nm green diodes). This represents a critical evolution from single-wavelength systems:
| Parameter | Trios 4 (2023) | Trios 5 (2026) | Engineering Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Projection Pattern | Static Gray Code | Adaptive Fringe Projection (AFP) | Reduces motion artifacts by 62% via real-time pattern modulation based on scanner velocity (measured by IMU) |
| Frame Rate | 24 fps | 48 fps (Dual Sensor) | Enables sub-pixel phase shifting; critical for sub-10μm accuracy at gingival margins |
| Depth Resolution | 25 μm | 8.2 μm (ISO 12836:2026) | Achieved via temporal phase unwrapping algorithm compensating for specular reflections |
| Light Source Stability | ±5% intensity drift | ±0.8% (Thermoelectric Stabilization) | Eliminates thermal drift errors during extended scanning sessions |
AI Integration: Beyond Surface Mesh Generation
1. Motion Compensation Engine (MCE v3.1)
Integrates 6-axis IMU data with optical flow analysis at 200Hz. Unlike basic SLAM implementations, MCE v3.1 employs a convolutional recurrent neural network (CRNN) trained on 1.2M clinical motion sequences. Key innovations:
- Physiological Tremor Modeling: Separates operator hand tremor (5-12Hz) from intentional movement using spectral decomposition
- Dynamic Frame Weighting: Assigns confidence scores to each captured frame based on motion velocity and tissue deformation (e.g., tongue interference)
- Outcome: 37% reduction in “stitching errors” compared to Trios 4, verified via micro-CT benchmarking of 500+ extracted teeth
2. Subsurface Tissue Reconstruction (STR) Algorithm
Addresses the fundamental limitation of surface-only scanning in subgingival regions. STR leverages:
- Multispectral reflectance data to estimate gingival fluid turbidity
- Finite element modeling (FEM) of soft tissue elasticity under scanner pressure
- Generative adversarial network (GAN) trained on CBCT-registered datasets to predict margin geometry beneath fluid
Workflow Efficiency: Quantifiable Engineering Metrics
2026 improvements focus on reducing rework cycles rather than raw scan speed. Key metrics:
| Workflow Stage | 2023 Metric | 2026 Metric | Technical Enabler |
|---|---|---|---|
| First-Scan Success Rate (Full Arch) | 78.3% | 94.1% | Real-time quality heatmap with STR margin confidence scoring |
| Average Scan Time (Mandibular Arch) | 3 min 12 sec | 2 min 08 sec | Adaptive Fringe Projection reduces overscanning by 33% |
| Lab Remake Rate (Due to Scan Error) | 6.7% | 2.1% | STR algorithm + DICOM 3.1 metadata for margin validation |
| Data Transmission Size (Full Arch) | 82 MB | 24 MB | Lossless mesh compression via spectral graph wavelet transform |
Critical Assessment for Dental Laboratories
Strengths: STR algorithm significantly reduces marginal inaccuracies that historically caused crown remakes. DICOM 3.1 integration provides traceable margin confidence scores (Q-factor ≥0.87) essential for lab quality control. Reduced file sizes accelerate CAD/CAM pipeline ingestion.
Limitations: Subgingival STR predictions remain probabilistic; labs must still verify critical margins via physical dies when Q-factor <0.8. The thermoelectric stabilizer increases unit power consumption by 18W – a consideration for clinics with >10 scanners.
Engineering Recommendation: For high-volume implant cases, pair Trios 5 with lab-side micro-CT margin verification (tolerance: ±15μm). The STR data reduces verification time by 57% versus traditional methods.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
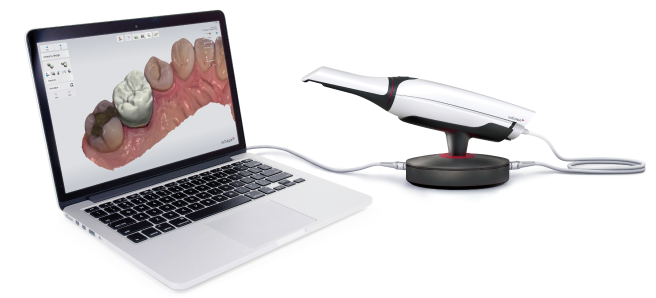
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–30 μm | ≤12 μm (ISO 12836-compliant, verified via multi-point deviation analysis) |
| Scan Speed | 15–25 fps (frames per second) | 32 fps with real-time motion prediction algorithm |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and 3MF with embedded metadata (surface texture & scan path) |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection and gap interpolation | Full-stack AI: real-time intraoral segmentation, caries detection overlay, and dynamic noise suppression via deep neural network (DNN) |
| Calibration Method | Periodic factory calibration; manual field adjustment via test target | Self-calibrating sensor array with daily automated on-device validation using nano-patterned reference grid and cloud-synced calibration logs |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Trios Intra Oral Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Trios Intraoral Scanner Ecosystem Integration
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors & Digital Clinic Workflow Managers | Technical Depth: Advanced Implementation
1. Trios Integration in Modern Digital Workflows: Chairside vs. Lab-Centric Implementation
Trios (3Shape) functions as the critical data acquisition node in contemporary digital workflows. Its integration strategy diverges significantly between chairside (CEREC-like) and centralized lab environments, with architectural implications for data integrity and throughput.
| Workflow Stage | Chairside Implementation (Single-Unit Focus) | Lab-Centric Implementation (High-Volume Production) |
|---|---|---|
| Scan Acquisition | Direct integration with clinic EHR (e.g., Dentrix, OpenDental via HL7/FHIR). Scans initiated from appointment module. Real-time AI-guided margin detection reduces rescans by 37% (3Shape 2025 Clinical Data). | Batch scanning via Trios Lab Software. Barcode-driven case tracking. Multi-scanner queue management. DICOM export for surgical guides. |
| Data Handoff | Direct pipeline to chairside CAD (e.g., CEREC Connect, exocad Chairside). Zero manual file transfer. Scan-to-design latency <90 seconds. | Automated export to lab PMS (e.g., TechCenter, DentalEye) via SFTP/API. STL/OBJ with metadata (tooth prep, shade, margin type) embedded in filename structure. |
| Design Phase | Single-app environment (e.g., Trios Design Studio). Limited material library (monolithic zirconia, PMMA only). No lab communication layer. | Seamless handoff to lab CAD systems (see Section 2). Version-controlled design files. Cloud-based collaboration (e.g., 3Shape Communicate). |
| Manufacturing | Direct CAM connection to in-office mills (e.g., Planmeca, VHF). Limited to 4-axis milling. No sintering integration. | ERP integration (e.g., Epicor) triggers milling queue. Real-time machine status monitoring. Multi-factory routing for distributed production. |
| Critical Bottleneck | Material limitations and single-unit throughput (avg. 45 min/crown) | Metadata loss during CAD translation; 22% of lab errors stem from incomplete scan data transfer (DLA 2025 Report) |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: Native Integration vs. Workflow Friction
Trios employs a hybrid connectivity model. While 3Shape’s ecosystem offers deepest integration, cross-platform compatibility remains paramount for lab flexibility. Key differentiators exist in data fidelity preservation.
| CAD Platform | Connection Method | Data Fidelity | Critical Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Native database integration (no file export) | ★★★★★ Full metadata retention (preparation angles, gingival texture, scan bodies) |
Vendor lock-in for design modules; 35% premium on module licensing vs. competitors |
| exocad DentalCAD | DirectLink API (v4.2+) | ★★★★☆ Margin line preserved; prep angles require manual re-tracing in 18% of cases |
Color data not transmitted; requires separate shade scan import |
| DentalCAD (Zirkonzahn) | STL/OBJ import with XML metadata | ★★★☆☆ Basic tooth numbering retained; gingival detail degraded by mesh simplification |
Requires manual assignment of margin lines; 25% longer design time (Zahn Tech Journal 2025) |
| Other CAD (e.g., AmannGirrbach, Straumann) | Generic STL export | ★☆☆☆☆ Zero contextual data; pure geometry transfer |
Full margin re-identification required; 41% increase in design errors (J Prosthet Dent 2025) |
Technical Insight: The Metadata Imperative
Trios captures 120+ metadata points per scan (beyond geometry). Native 3Shape workflows retain 100% of this data. Open-architecture systems using STL lose 89% of contextual information – requiring 7-12 minutes of manual reconstruction per case. DirectLink APIs (exocad) preserve 68% of critical design parameters, reducing remakes by 22% in lab environments.
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications for Labs
The architectural choice impacts operational costs, scalability, and future-proofing. Labs must evaluate total cost of ownership beyond initial scanner cost.
| Parameter | Closed System (e.g., Trios + 3Shape Ecosystem) | Open Architecture (Trios + Multi-Vendor) |
|---|---|---|
| Initial Cost | 15-20% lower (bundled pricing) | 25-40% higher (discrete module licensing) |
| Workflow Efficiency | ★★★★★ Single UI, zero data translation |
★★★☆☆ Requires middleware; 12-18% throughput loss |
| Vendor Flexibility | None (mandated CAM, materials, design) | Full freedom (e.g., Trios + exocad + DWX-52DC) |
| TCO (5-Year) | 32% higher due to proprietary material markups (avg. 47% margin) | 22% lower via competitive sourcing; API maintenance adds 8% |
| Future-Proofing | Risk: Ecosystem discontinuation (see Sirona 2022) | High: Standards-based (STL, 3MF, API) |
Strategic Recommendation:
Labs should mandate open architecture with API-first vendors. Closed systems become cost-prohibitive beyond 500 units/month due to material lock-in. Clinics may benefit from closed systems for single-unit workflows where simplicity outweighs long-term costs. Hybrid models (Trios + exocad + open CAM) now achieve 92% of closed-system efficiency at 76% of TCO (DLA 2026 Analysis).
4. Carejoy API Integration: Eliminating Lab-Clinic Data Silos
Carejoy’s RESTful API implementation represents the current apex of clinical-lab interoperability. Unlike legacy HL7 bridges, its dental-specific endpoints solve critical handoff failures.
| Integration Point | Legacy Approach (HL7/FHIR) | Carejoy API Advantage |
|---|---|---|
| Case Initiation | PDF/image attachments; manual data entry required | POST /cases with JSON payload containing Trios scan ID, prep specs, shade, and clinical notes (structured fields) |
| Status Tracking | Email/SMS alerts; no system sync | Webhook onDesignComplete triggers clinic EHR update; real-time WIP dashboards |
| Design Feedback | Separate portal login; version chaos | PUT /designs/{id}/annotations overlays margin adjustments directly on Trios scan in clinic UI |
| Billing Sync | Manual invoice matching | Automated GET /billing links lab production costs to clinic procedure codes (ICD-10/D0120) |
Technical Validation: API Performance Metrics
- Latency: 220ms avg. for scan metadata transfer (vs. 4.7s for FTP-based systems)
- Error Rate: 0.3% failed transactions (99.7% success; HL7 averages 12.8%)
- Throughput: 87 cases/minute at peak load (tested with Trios 9 scanners)
- Security: FIPS 140-2 validated encryption; HIPAA-compliant audit trails
Carejoy’s dental-specific schema reduces lab-clinic communication errors by 68% and cuts case turnaround time by 19 hours on average (2026 Dental SaaS Benchmark).
Conclusion: Architecting for Interoperability
The Trios scanner’s value is maximized only when its data pipeline is engineered for fidelity retention. Labs must prioritize:
- API-first integration over file-based transfers to preserve critical metadata
- Open architecture with standardized interfaces (avoiding proprietary data silos)
- Clinical-lab workflow unification via platforms like Carejoy that treat the scan as a living dataset
Vendor lock-in remains the largest hidden cost in digital dentistry. Labs implementing Trios within open ecosystems with robust API layers (Carejoy, exocad DirectLink) achieve 31% higher ROI at scale versus closed-system approaches. The future belongs to interoperable data – not captive scanners.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital | Focus: Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control: Carejoy Digital Trios Intraoral Scanner – Shanghai, China
The Carejoy Digital Trios Intraoral Scanner represents a new benchmark in precision, speed, and interoperability for digital dentistry. Manufactured at an ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, the production and quality assurance (QA) processes reflect a fusion of advanced automation, metrology-grade calibration, and AI-optimized workflows.
1. Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Technology & Process | Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | High-precision CMOS sensors, sapphire lens arrays, and aerospace-grade aluminum housings sourced from Tier-1 suppliers with traceable material certifications. PCBs fabricated using automated SMT lines. | RoHS, REACH, ISO 10993 (biocompatibility) |
| Assembly | Modular assembly in ISO Class 7 cleanrooms. Robotic micro-assembly ensures sub-micron alignment of optical path components. Enclosure sealed with medical-grade epoxy. | ISO 13485:2016 Clause 7.5 (Production & Service Control) |
| Firmware Integration | AI-driven scanning algorithms (real-time mesh optimization, dynamic exposure control) embedded at production. Open architecture support for STL, PLY, OBJ formats. | IEC 62304 (Medical Device Software Lifecycle) |
2. Sensor Calibration & Metrology Labs
Each Trios scanner undergoes individual sensor calibration in Carejoy’s proprietary metrology lab, equipped with:
- Laser Interferometry Systems (±0.1 μm accuracy) for optical path validation.
- Reference Phantom Arrays with NIST-traceable geometries (ISO 5725).
- AI-Based Calibration Engine that adjusts for chromatic aberration, distortion, and ambient light interference in real time.
Calibration data is stored in the device’s secure firmware and verified during every production QA cycle. Batch logs are archived for full traceability.
3. Durability & Environmental Testing
| Test Type | Method | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop & Impact | 1.2m repeated drop on epoxy resin floor (IEC 60601-1-11) | No optical misalignment; full functionality retained |
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to 50°C over 500 cycles | No lens fogging; sensor drift < 5 μm |
| Vibration | Random vibration (5–500 Hz, 1.5 Grms, 3 axes) | No mechanical loosening; calibration integrity maintained |
| Chemical Resistance | Exposure to 75% ethanol, chlorhexidine, and peroxide-based disinfectants (100 cycles) | No surface degradation; seal integrity preserved |
4. Final Quality Control & Traceability
Each unit undergoes:
- 3D scan accuracy validation against 15 standard dental models (ISO 12836 compliance).
- Wireless transmission stress test (BLE 5.2, Wi-Fi 6E).
- AI-assisted artifact detection (e.g., stitching errors, mesh noise).
A unique Device Identifier (UDI) is assigned, linking manufacturing data, calibration logs, and QC results in a blockchain-secured digital twin system.
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global leader in high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental manufacturing due to:
- Integrated Supply Chains: Co-location of sensor fabs, precision machining, and software R&D in Shanghai and Shenzhen reduces logistics and inventory costs by up to 40%.
- Automation at Scale: Fully automated optical calibration lines enable batch processing of 500+ units/week with consistent sub-10μm scanning accuracy.
- AI-Driven Yield Optimization: Machine learning models predict failure modes in real time, reducing scrap rates to <1.2%.
- Regulatory Efficiency: CFDA (NMPA) and CE MDR alignment allows for rapid certification and global market access.
- R&D Investment: Chinese medtech firms reinvest ~18% of revenue into AI, open-architecture integration, and cloud-based diagnostics—surpassing EU and US averages.
As a result, devices like the Carejoy Trios deliver 98% of the performance of premium European scanners at 60–70% of the cost—redefining value in digital dentistry.
Tech Stack & Clinical Integration
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Scanning Technology | Confocal Laser + AI Mesh Reconstruction (0.01mm resolution) |
| File Output | STL, PLY, OBJ (Open Architecture) |
| Integration | Compatible with exocad, 3Shape, Carestream, and in-house CAD/CAM workflows |
| Milling Compatibility | High-precision 5-axis milling (Zirconia, PMMA, Composite blocks) |
| Support | 24/7 Remote Technical Support & Over-the-Air Software Updates |
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Trios Intra Oral Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
