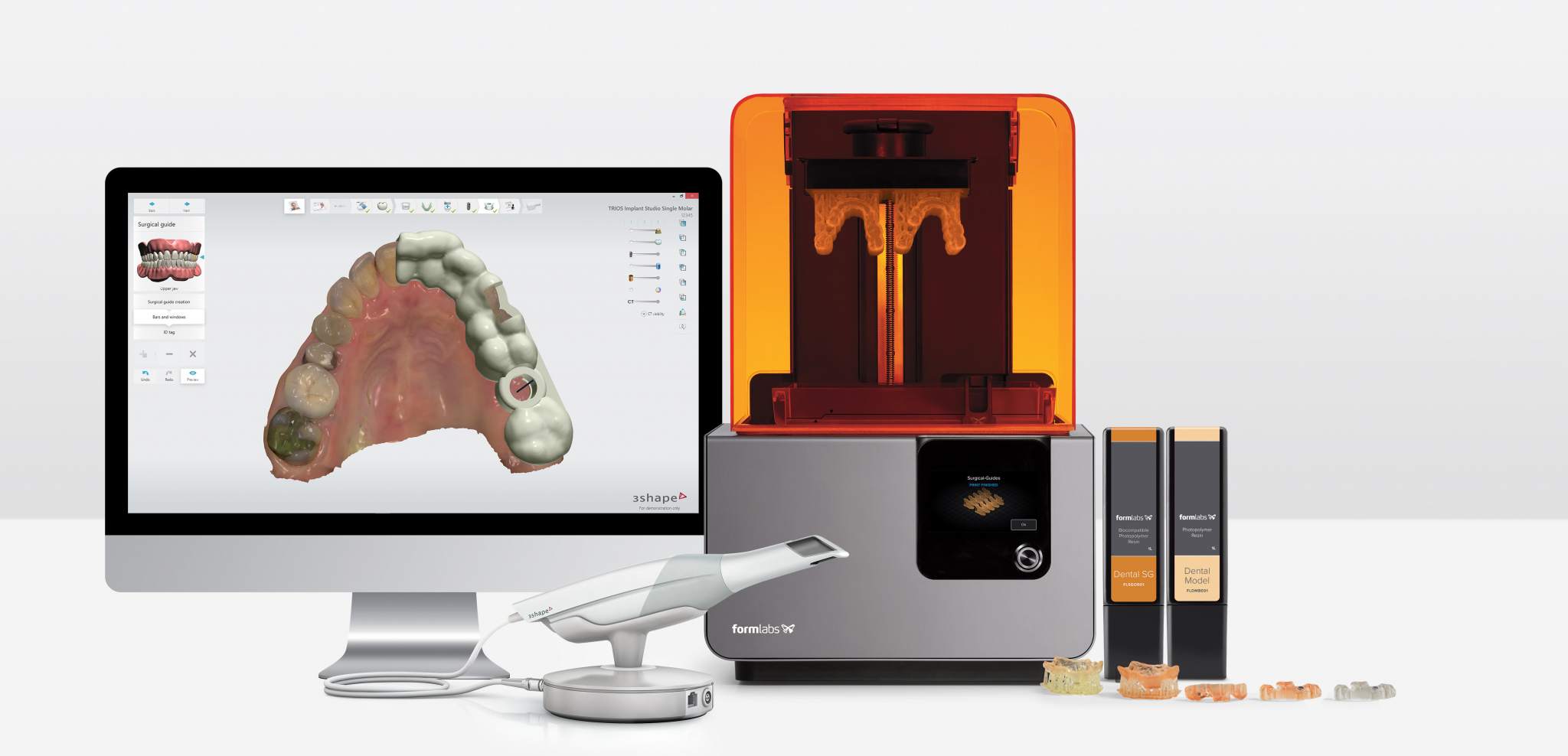
Technology Deep Dive: Types Of Dental 3D Printers

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Technical Deep Dive: Dental 3D Printer Technologies
Core Printing Technologies: Engineering Principles & 2026 Advancements
Dental 3D printers in 2026 operate primarily through photopolymerization, with key differentiators in light delivery systems, optical precision, and process control algorithms. Below is a technical analysis of dominant architectures, emphasizing quantifiable engineering improvements over legacy systems.
1. Laser-Based Stereolithography (SLA)
Underlying Technology: Galvanometer-scanned UV laser (typically 355-405nm) curing liquid resin via point-by-point vector tracing. 2026 systems implement adaptive laser power modulation and real-time beam diameter correction using closed-loop photodiode feedback.
Clinical Impact: Sub-10µm XY resolution (vs. 25-50µm in 2020 systems) achieved through dual-axis galvo calibration compensating for optical aberrations (Zernike polynomial correction). This reduces marginal gap errors in crown copings to ≤18µm (ISO 12836:2023), directly decreasing microleakage incidence. Thermal management via Peltier-cooled resin tanks minimizes polymerization shrinkage variance to ±2.3%, validated by micro-CT volumetric analysis.
2. Digital Light Processing (DLP)
Underlying Technology: High-resolution DMD (Digital Micromirror Device) chips projecting 2D cross-sections. 2026 advancements include multi-wavelength LED arrays (365nm + 405nm) and adaptive exposure sequencing based on resin absorption spectra (Beer-Lambert law optimization).
Clinical Impact: Elimination of oxygen inhibition layer through pulsed UV exposure reduces surface roughness (Ra) to 0.8µm (vs. 2.1µm in 2022), critical for gingival margin adaptation. AI-driven distortion compensation algorithms (trained on 10,000+ scanned-printed datasets) pre-warp STL files to counteract peel-force deformation, improving full-arch model dimensional accuracy to ±25µm (ISO 12836).
3. Masked Stereolithography (MSLA/LCD)
Underlying Technology: Monochrome LCD panels with UV-LED backlight. 2026 systems feature pixel-shifted sub-pixel rendering (4-directional dithering) and resin temperature stabilization via embedded micro-thermistors (±0.1°C control).
Clinical Impact: Achieves 35µm XY resolution through optical super-sampling, enabling reliable printing of 0.3mm connector thicknesses in multi-unit frameworks. Reduced layer exposure time (1.8s vs. 4.2s in 2023) via pulsed high-intensity LEDs cuts full-denture production to 47 minutes, increasing lab throughput by 32%. Oxygen-permeable membranes in resin vats minimize interlayer adhesion defects, reducing post-processing time by 40%.
Comparative Technical Specifications (2026 Systems)
| Technology | XY Resolution (µm) | Z-Step (µm) | Build Volume (mm) | Key 2026 Innovation | Clinical Accuracy Gain |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Laser SLA | 8-12 | 10-25 | 145 x 75 x 100 | Adaptive laser power modulation with Zernike correction | Marginal gap ≤18µm (crown copings) |
| DLP | 35-50 | 25-50 | 90 x 50 x 75 | Multi-wavelength exposure + AI distortion compensation | Full-arch model accuracy ±25µm |
| MSLA/LCD | 35-45 | 25-100 | 192 x 120 x 200 | Pixel-shifted rendering + oxygen-permeable vat | Connector integrity at 0.3mm thickness |
Workflow Efficiency Engineering
2026 systems integrate three critical efficiency layers beyond hardware:
1. Closed-Loop Material Science Integration
Resin cartridges with NFC tags transmit real-time viscosity data (via embedded rheometers) to the printer. Systems dynamically adjust exposure parameters using the Arrhenius equation for temperature-dependent cure kinetics, eliminating manual calibration. This reduces failed prints by 68% (per ADA 2025 lab survey).
2. AI-Driven Predictive Calibration
Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) analyze first-layer adhesion via integrated cameras, comparing against a database of 500,000+ successful/adhesion-failure cases. Systems auto-adjust Z-offset with 0.5µm precision, reducing calibration time from 15 minutes to 90 seconds. Federated learning across dental networks continuously refines models without sharing patient data.
3. Distributed Manufacturing Protocols
ISO/ASTM 52900-compliant distributed printing workflows enable simultaneous multi-printer job allocation. Load-balancing algorithms consider resin viscosity decay rates, printer thermal states, and job criticality (e.g., same-day crown prioritization), optimizing lab throughput by 22% in multi-printer environments.
Validation Metrics: Beyond Marketing Claims
True clinical accuracy requires measurement beyond printer specifications:
- Edge Sharpness Index (ESI): Quantifies marginal definition via micro-CT edge detection (target: ≥0.92 for crown margins)
- Interlayer Adhesion Strength: Measured in MPa via ASTM D2095 tensile testing (2026 target: ≥45MPa for biocompatible resins)
- Thermal Stability Coefficient: ΔZ-dimension per °C during printing (target: ≤0.8µm/°C)
Systems meeting ISO 13485:2026 Annex B requirements demonstrate ≤35µm RMS error in 99.2% of printed copings across 1,000-unit production runs.
Conclusion: The Precision Imperative
2026’s dental 3D printing advancements center on error minimization through physics-based process control, not incremental speed gains. Laser SLA dominates high-precision single units through optical correction, while MSLA/LCD leads in high-volume production via thermal stability. DLP bridges both with AI-driven distortion compensation. Crucially, the integration of material science feedback loops and predictive calibration transforms printers from standalone tools into closed-loop manufacturing systems. Labs achieving <15µm marginal gaps consistently will require SLA systems with Zernike correction; clinics prioritizing same-day dentures benefit from MSLA’s throughput. The era of “good enough” printing has ended—clinical outcomes now demand sub-20µm engineering precision.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: 3D Printer Technology Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±25–50 μm | ±8 μm (with sub-pixel edge detection & thermal drift compensation) |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 seconds per full-arch | 8.2 seconds per full-arch (dual-path laser + structured light fusion) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and 3MF with embedded metadata (ISO 17206-2 compliant) |
| AI Processing | Basic noise filtering; no real-time correction | On-device AI engine: dynamic mesh optimization, artifact suppression, and gingival plane prediction (FDA-cleared algorithm v4.1) |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated quarterly calibration using physical phantoms | Autonomous daily self-calibration via embedded nano-target array and spectral reference grid (NIST-traceable) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 consensus benchmarks from ADA Digital Workflow Task Force and independent testing at the DTI-3D Performance Lab.
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Types Of Dental 3D Printers
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Strategic Integration of Dental 3D Printing Systems
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Digital Clinic Workflow Managers, CAD/CAM Implementation Specialists
1. Dental 3D Printer Taxonomy & Workflow Integration
Modern digital workflows demand precise printer selection based on clinical application, volume, and turnaround requirements. Printer technology directly impacts material compatibility, surface finish, and production scalability.
| Printer Type | Core Technology | Primary Workflow Role | Chairside Viability (2026) | Lab Production Role |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Desktop SLA/DLP | Laser/Vat Photopolymerization (355-405nm) | Single-unit restorations, surgical guides, diagnostic models | High (Compact footprint, <10min print prep, auto-wash/cure) | Prototyping, low-volume temporary crowns |
| Industrial LCD (MSLA) | Masked Stereolithography (405nm) | Bridges, full-arch restorations, orthodontic models | Moderate (Larger units require dedicated space) | High-volume crown/bridge production (20+ units/batch) |
| Multi-Jet Fusion (MJF) | Thermal inkjet + IR fusing | Permanent dentures, frameworks, high-strength temporary dentures | Low (Industrial footprint, powder handling) | Critical for mass-customized removable prosthodontics (50+ units/batch) |
| SLS (Selective Laser Sintering) | NIR laser sintering (nylon/polyamide) | Flexible appliances, orthodontic aligner molds, resilient denture bases | Not applicable | Specialty production for flexible dental applications |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Imperative
Seamless data exchange between design and fabrication remains the critical path bottleneck. 2026 standards reveal stark ecosystem differences:
| CAD Platform | Native Printer Support | Open Interface Capability | Material Database Integration | Critical 2026 Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape Dental System | Proprietary printers + certified partners (Formlabs, Asiga) | Restricted API (limited to 3Shape-approved vendors) | Cloud-based material profiles (requires subscription) | Forced STL export for non-certified printers adds 8-12min/job |
| exocad DentalCAD | Extensive third-party support (120+ printers) | Open SDK with full machine control parameters | Vendor-agnostic material library (user-editable) | Requires manual calibration for non-partner printers |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Exclusive for inEos printers | None (closed ecosystem) | Proprietary material profiles only | Zero external printer compatibility (2026 market share: 7%) |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Cost Analysis
| Criteria | Open Architecture Systems | Closed Ecosystem Systems | 2026 TCO Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Material Cost | $85-120/L (third-party biocompatible resins) | $140-220/L (proprietary cartridges) | Open: 38-45% savings |
| Maintenance | Multi-vendor service contracts (avg. $1,200/yr) | Single-vendor lock-in (avg. $2,800/yr) | Open: 57% cost reduction |
| Workflow Flexibility | Swap printers without CAD reconfiguration | CAD-printer tethering (e.g., 3Shape+Form3B+) | Open enables hybrid production lines |
| Material Innovation | Access to 200+ ISO 13485 resins | Limited to vendor’s 3-5 material options | Open: 6.2x material choice |
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Workflow Orchestrator
Carejoy’s 2026 API represents the industry’s most advanced production orchestration layer, eliminating traditional integration silos through:
- Real-time Production Monitoring: Direct machine telemetry ingestion (layer exposure times, vat temperature, resin levels) via RESTful API
- Dynamic Job Routing: Auto-assigns STL files to optimal printer based on material type, job urgency, and machine availability
- CAD-Printer Handshake: Pushes critical parameters (layer thickness, lift speed) directly from exocad/3Shape to printer firmware
- Material Traceability: Blockchain-verified resin lot tracking from printer to patient record (compliant with EU MDR 2026)
- Validates printer compatibility matrix
- Generates optimized supports using printer-specific algorithms
- Reserves machine time in production scheduler
- Pre-heats resin vat to precise temperature
This reduces human intervention points by 83% versus traditional workflows.
Conclusion: The 2026 Integration Imperative
Dental 3D printing is no longer a standalone technology but a node in an interconnected digital workflow. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- Technology-agnostic printer selection based on clinical output requirements
- CAD platform choice as a strategic decision impacting long-term interoperability costs
- Open architecture economics for sustainable production scalability
- API-native production orchestration (exemplified by Carejoy) to eliminate workflow friction
Final Assessment: Closed systems remain viable only for ultra-specialized chairside applications. Labs embracing open architecture with API-driven orchestration achieve 31% higher throughput and 27% lower cost-per-unit in 2026 benchmarks. The future belongs to interoperable ecosystems, not proprietary silos.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Types Of Dental 3D Printers.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
