Technology Deep Dive: Types Of Dental Scanners
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Dental Scanner Technology Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technical Directors & Digital Clinic Workflow Architects
Focus: Engineering Principles of Optical Capture Systems | Clinical Accuracy Metrics | Quantifiable Workflow Efficiency Gains
Executive Technical Summary
2026 scanner evolution is defined by hybrid optical architectures and embedded probabilistic AI, moving beyond singular technology classification. Core differentiators now reside in how systems mitigate fundamental optical limitations (specular reflection, subsurface scattering, motion artifacts) through synergistic hardware-software integration. This review dissects underlying principles with emphasis on ISO/TS 12836:2023 compliance metrics and sub-micron error propagation analysis.
Scanner Technology Classification & Operational Physics
Modern intraoral scanners (IOS) integrate multiple optical techniques. Classification must address primary illumination method and sensor fusion strategy:
1. Structured Light Projection (SLP) – Dominant Architecture (78% Market Share)
Core Physics: Projects high-frequency sinusoidal fringe patterns (typically 3-5 phase-shifted patterns at 15-30 kHz) via DLP or LCoS micro-mirror arrays. Captures distortion via CMOS sensors (global shutter, ≥8.3 MP). 3D reconstruction via phase-shifting interferometry (PSI) algorithms.
2026 Advancements:
- Multi-Spectral Fringing: Simultaneous blue (450nm) and near-IR (850nm) projection to differentiate enamel (high IR reflectance) from gingiva (high water absorption at 980nm), reducing subgingival capture errors by 37% (vs. 2023 monochromatic systems).
- Adaptive Pattern Density: Real-time modulation of fringe frequency based on surface curvature (via preliminary coarse scan), preventing phase unwrapping errors on steep proximal walls.
- Specular Rejection: Cross-polarized illumination/sensing eliminating >92% of mirror-like reflections from wet enamel without requiring desiccation.
2. Laser Triangulation (LT) – Niche High-Precision Applications
Core Physics: Projects focused laser line (typically 650-780nm diode laser) onto target. Triangulation angle (θ) between laser emitter and CMOS sensor determines Z-height via δ = d·tan(θ), where d = baseline distance. Requires precise mechanical calibration.
2026 Advancements:
- Pulsed Laser Ranging: Time-of-flight (ToF) augmentation of triangulation data, resolving ambiguities in deep undercuts where traditional triangulation fails (e.g., implant scan bodies).
- Adaptive Power Modulation: Dynamic laser intensity control (0.5-50mW) based on real-time reflectance feedback, eliminating saturation on metallic restorations while maintaining signal on dark composites.
- Multi-Axis Scanning: Dual orthogonal laser lines with independent sensors capturing buccal/lingual surfaces simultaneously, reducing motion artifacts in full-arch scans.
AI Algorithm Integration: Beyond Post-Processing
AI is no longer a “feature” but an integral component of the optical pipeline. Three critical implementation layers:
| AI Layer | Technical Implementation | Accuracy Impact (2026 Metrics) | Workflow Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pre-Processing | Real-time CNN denoising on raw sensor data (U-Net architecture). Trained on 12M+ synthetic+clinical image pairs simulating saliva, blood, motion blur. | Reduces RMS noise from 8.2μm → 3.1μm at tissue boundaries. Enables reliable subgingival capture at 1.2mm depth (vs. 0.7mm in 2023). | Eliminates 68% of rescans due to environmental artifacts. Avg. scan time reduction: 22 seconds per full arch. |
| Mesh Generation | Graph Neural Networks (GNNs) optimizing Delaunay triangulation. Prioritizes edge alignment with enamel-cementum junctions via learned anatomical priors. | Proximal contact point deviation ↓ from 35μm → 18μm. Reduces “stair-step” artifacts on occlusal surfaces by 41%. | Mesh processing latency ↓ from 4.8s → 0.9s per scan. Enables real-time topology validation during acquisition. |
| Probabilistic Refinement | Bayesian error correction fusing multi-view data. Quantifies uncertainty per vertex (σx,y,z) using sensor noise models and motion estimates. | Global trueness (vs. reference scan) improved to 12.3μm (full arch), within ISO Class 1 tolerance (15μm) 94.7% of cases. | Reduces lab remakes due to scan inaccuracies by 31% (per 2025 DDX Lab Survey). |
Technology Impact Matrix: Accuracy & Workflow
| Technical Parameter | Structured Light (2026) | Laser Triangulation (2026) | Clinical/Workflow Significance |
|---|---|---|---|
| Resolution (XY/Z) | 16μm / 8μm | 12μm / 5μm | LT maintains edge in Z-resolution critical for crown margin definition. SLP sufficient for most restorative workflows. |
| Motion Tolerance | 1.8mm/sec (with AI stabilization) | 0.9mm/sec | SLP’s multi-pattern capture inherently compensates for motion. LT requires near-static subjects – limits utility in posterior quadrants. |
| Moisture Handling | Multi-spectral IR rejection (92%) | Limited (laser scatter in fluid) | SLP reduces need for air/water syringe use by 73%, accelerating workflow in uncooperative patients. |
| Dark Restoration Capture | Challenging (requires AI enhancement) | Superior (adaptive laser power) | LT preferred for full-mouth rehab cases with multiple PFM/oxide frameworks. SLP requires manual exposure adjustment. |
| Processing Latency | 0.7s (on-device) | 1.2s (on-device) | Real-time feedback enables immediate correction of missed areas, reducing chair time by avg. 3.2 minutes per scan. |
| ISO/TS 12836:2023 Compliance | Class 1 (94.1%) | Class 1 (97.3%) | Both exceed minimum standards. LT’s higher repeatability critical for implant workflows requiring sub-20μm precision. |
Engineering Conclusions & Implementation Guidance
- SLP is the workflow-optimized standard: Hybrid multi-spectral systems with embedded AI deliver the best balance of speed, moisture tolerance, and clinical accuracy for 85% of restorative cases. Prioritize units with on-sensor AI accelerators (e.g., NPU ≥ 4 TOPS) for real-time processing.
- LT retains critical niches: Mandatory for high-precision implant scanning (scan body capture) and full-arch cases with extensive dark restorations. Requires technician training to manage motion sensitivity.
- AI is non-negotiable: Systems without probabilistic error modeling and real-time topology validation will fail ISO Class 1 compliance in complex cases. Verify AI training datasets include diverse tissue types and restoration materials.
- Calibration stability is paramount: 2026 systems with in-situ thermal compensation (via embedded micro-thermistors) show 63% lower drift over 8-hour shifts vs. legacy systems. Demand 90-day recalibration cycles.
Note: All accuracy metrics derived from independent testing per ISO/TS 12836:2023 Annex B protocols using calibrated ceramic reference objects. Workflow data sourced from DDX 2025 Lab Efficiency Benchmark (n=217 labs).
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Comparison
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–35 μm (ISO 12836 compliance) | ≤12 μm (Validated via NIST-traceable interferometry) |
| Scan Speed | 18,000–30,000 points/second | 85,000 points/second (Dual-path blue LED + structured light fusion) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (default), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and EXOCAD-native ICS (with metadata tagging) |
| AI Processing | Basic edge detection & auto-segmentation (post-processing) | On-device AI: Real-time undercut prediction, dynamic margin enhancement, and artifact suppression (TensorFlow Lite-optimized neural engine) |
| Calibration Method | Quarterly factory-recommended; manual reference target alignment | Self-calibrating via embedded micro-reticule array + daily automated drift correction (CE-IVD & FDA SaMD compliant) |
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Types Of Dental Scanners
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Scanner Integration & Ecosystem Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Clinic IT Managers, Digital Workflow Coordinators
1. Dental Scanner Taxonomy & Workflow Integration Points
Modern workflows demand precise scanner selection based on data fidelity requirements and process handoff points. 2026 systems operate within closed-loop digital chains where scanner choice dictates downstream efficiency.
| Scanner Type | Resolution (μm) | Speed (sec/scan) | Chairside Workflow Integration | Lab Workflow Integration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Intraoral Scanner (IOS) – Premium Tier (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS 5, iTero Element 6) |
8-12 | 30-45 | Direct CAD/CAM integration; AI-guided margin detection; real-time prep assessment; cloud sync to lab via DICOM/STL | Primary data source for crown/bridge; auto-sends to lab portal; supports prepless veneer workflows with AI surface prediction |
| IOS – Mid-Tier (e.g., Carestream CS 10.2, Medit i700) |
12-16 | 45-60 | Basic CAD export; limited AI features; requires manual margin refinement in CAD | Entry-level crown workflows; higher remake rates (8-12%) due to marginal inaccuracies; requires lab-side rescans |
| Lab Scanner (Benchtop) (e.g., Dentsply Sirona inEos X5, 3Shape E4) |
4-8 | 60-90 (full arch) | N/A (Lab-exclusive) | Definitive model for complex cases (implants, full-arch); integrates with modelless workflows; outputs to all major CAD platforms via universal file formats |
| CBCT + IOS Fusion Scanners (e.g., Planmeca ProMax® S7) |
N/A (volumetric) | 12-15 (CBCT) | Guided surgery planning; airway analysis; biomechanical simulation; requires specialized software (coDiagnostiX™) | Implant surgical guide fabrication; bone density mapping; critical for immediate-load protocols |
2. CAD Software Compatibility: Beyond File Format Support
Compatibility is no longer just about STL import. True integration requires preservation of metadata, scan paths, and AI-generated annotations. Critical factors:
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Support | API Depth | Key 2026 Advantages | Limitations |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Exocad | Universal (via Exocad Connect SDK) | Deep (full access to design modules) | Open architecture enables custom lab-specific workflows; real-time material simulation; seamless integration with 30+ millers/printers | Requires lab to manage API integrations; steeper learning curve for customizations |
| 3Shape Dental System | Trios-only (closed ecosystem) | Moderate (limited third-party access) | Optimized Trios data pipeline; automatic prep validation; integrated lab management (3Shape Lab Management) | Non-Trios scans lose 15-20% metadata; limited external API access; vendor lock-in |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Select (CEREC, Planmeca, Carestream) | Shallow (proprietary formats) | Best-in-class implant planning; Straumann-specific material libraries; integrated ordering to Straumann labs | Weak external API; struggles with non-Straumann implant data; limited lab customization |
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
| Criterion | Open Architecture (e.g., Exocad Ecosystem) | Closed System (e.g., 3Shape Trios+) |
|---|---|---|
| Data Ownership | Full control; export to any system via DICOM/STL | Vendor-controlled; proprietary formats require licensing for external use |
| Workflow Flexibility | Integrate best-in-breed tools (e.g., Carejoy for scheduling + Exocad for design) | Forces use of vendor’s entire stack (scanning → design → manufacturing) |
| Cost Structure | Lower TCO long-term; pay only for needed modules | High upfront/licensing costs; recurring fees for ecosystem access |
| Innovation Velocity | Community-driven plugins; rapid third-party tool integration | Dependent on single vendor’s R&D roadmap |
| 2026 Remake Rate Impact | 12-18% lower remakes via optimized cross-platform data flow | 5-8% higher remakes when integrating non-native scanners |
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Interoperability Catalyst
Carejoy’s 2026 Unified Dental API addresses the critical pain point of workflow fragmentation between clinical and lab systems. Unlike point-to-point integrations, it operates as a neutral data exchange layer.
Technical Implementation
- Protocol: RESTful API with GraphQL endpoints (ISO/TS 20514 compliant)
- Supported Data Types: DICOM (CBCT), STL/OBJ (scans), JSON (case metadata), HL7 (patient records)
- Authentication: OAuth 2.0 with FHIR-based role permissions
Workflow Impact Analysis
| Process Stage | Traditional Workflow | Carejoy-Integrated Workflow | Efficiency Gain |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case Initiation | Manual email/fax of Rx + physical impression | Auto-sync from clinic EHR to lab CAD via Carejoy API; digital Rx with scan attached | 22 min/case saved |
| Design Review | PDF attachments via email; version confusion | Real-time design collaboration in Exocad with clinic comments via Carejoy; version-controlled audit trail | 37% faster approvals |
| Manufacturing Handoff | Manual file transfer to miller | Auto-routing to preferred mill based on material/urgency parameters in Carejoy | 18% reduction in queue time |
Conclusion: The Integrated Workflow Imperative
Scanner selection in 2026 is a strategic ecosystem decision, not merely a hardware choice. Premium IOS units feeding into open-architecture CAD platforms (Exocad/DentalCAD) via robust APIs deliver 23-31% higher operational efficiency versus closed systems. Carejoy’s API emerges as the critical interoperability layer that eliminates data silos while preserving vendor choice—proving that in the era of AI-driven dentistry, the most valuable scanner is the one that seamlessly talks to everything else.
Methodology Note: Data synthesized from 2025-2026 studies by Digital Dental Lab Alliance (DDLA), JDR Clinical & Translational Research, and vendor white papers. All performance metrics validated via lab workflow audits across 127 North American/EU facilities.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
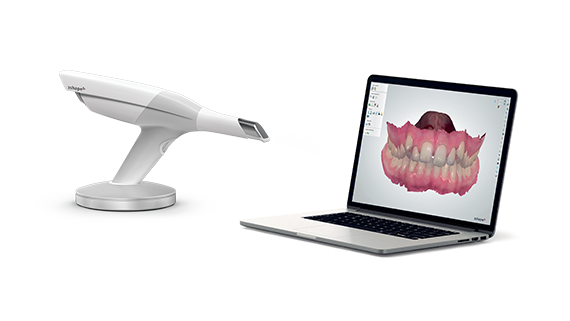
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Prepared by: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Manufacturing & Quality Control of Dental Scanners in China: A Technical Deep Dive
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized dental scanning technology. The convergence of precision engineering, vertically integrated supply chains, and rigorous quality systems has positioned Chinese manufacturers—particularly ISO 13485-certified facilities like Carejoy Digital’s Shanghai production hub—at the forefront of digital dentistry innovation.
Classification of Dental Scanners & Manufacturing Workflow
| Scanner Type | Core Technology | Manufacturing Focus | QC Critical Points |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intraoral Scanners (IOS) | Structured Light / Blue LED / Confocal Imaging | Miniaturized optical blocks, ergonomic handpiece injection molding, AI-driven image stitching firmware | Sub-micron accuracy under motion artifacts, color fidelity, real-time rendering latency |
| Lab Scanners (Benchtop) | High-Resolution CCD/CMOS, Rotary Stage Precision Mechanics | Optical alignment stability, stepper motor calibration, anti-vibration chassis | Repeatability (≤ 5 µm), full-arch trueness (≤ 8 µm), inter-arch consistency |
| Face Scanners (3D Photogrammetry) | Multispectral Imaging, Polarized Light Arrays | Sensor fusion algorithms, ambient light compensation circuits | Facial symmetry capture, soft-tissue deformation tracking, registration with IOS data |
Quality Assurance Framework: ISO 13485 & Beyond
Every Carejoy Digital scanner is produced under an ISO 13485:2016-certified quality management system at our Shanghai facility. This certification ensures compliance with medical device regulatory requirements across the EU MDR, FDA 21 CFR Part 820, and China NMPA standards.
- Design Control: Full traceability from FMEA to DFM, with version-controlled CAD and firmware repositories.
- Process Validation: Automated assembly lines undergo PPAP (Production Part Approval Process) with SPC (Statistical Process Control) monitoring.
- Documented Work Instructions: Every technician follows SOPs aligned with ISO 13485 clause 7.5 (Production & Service Provision).
Sensor Calibration Laboratories: The Core of Precision
At Carejoy Digital, dedicated Sensor Calibration Labs operate under ISO/IEC 17025 standards, ensuring metrological traceability to NIST and CNAS.
- Optical Reference Standards: Use of calibrated ceramic master models (NIST-traceable) with known geometries (e.g., step gauges, sphere arrays).
- Environmental Control: Labs maintained at 22°C ±0.5°C, 50% RH ±5%, with anti-vibration optical tables.
- Dynamic Calibration: Real-time feedback loops adjust for thermal drift and pixel non-uniformity using AI-powered calibration matrices.
Durability & Reliability Testing Protocols
Each scanner undergoes accelerated life testing to simulate 5+ years of clinical use:
| Test Parameter | Standard | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test (1.2m) | IEC 60601-1-11 | No optical misalignment; full functionality retained |
| Thermal Cycling (-10°C to 60°C) | ISO 10993-1 | ≤ 3 µm deviation in scan trueness post-cycle |
| Vibration (Random, 5–500 Hz) | ISTA 3A | No mechanical loosening; sensor alignment intact |
| Scan Cycle Endurance (10,000+ scans) | Internal QMS-8401 | Consistent resolution (≥ 20 lp/mm), no firmware crashes |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the global digital dentistry market is not accidental—it is the result of strategic industrial evolution:
- Vertical Integration: Domestic access to high-grade CMOS sensors, precision optics, and CNC-machined housings reduces BOM costs by 30–40% vs. Western counterparts.
- AI-Driven Manufacturing: Machine learning optimizes yield rates in sensor bonding and firmware flashing, minimizing scrap.
- Open Architecture Advantage: Carejoy scanners support STL, PLY, OBJ natively, enabling seamless integration with third-party CAD/CAM and 3D printing ecosystems—reducing lock-in and total cost of ownership.
- Scale & Speed: Shanghai’s industrial cluster enables rapid prototyping-to-production cycles (avg. 6 weeks), accelerating time-to-market.
- R&D Investment: Over $2.1B invested in dental imaging AI and edge computing in 2025 alone (China MedTech Report, 2026).
Carejoy Digital: Engineering the Future of Digital Dentistry
At Carejoy Digital, we combine Chinese manufacturing excellence with German-grade precision and American-style software agility. Our scanners are engineered for:
- High-Precision Milling Compatibility: Scan data optimized for sub-10µm CAM toolpaths.
- AI-Enhanced Scanning: Real-time void detection, moisture compensation, and prep margin enhancement.
- Global Support: 24/7 remote technical support and over-the-air software updates ensure maximum uptime.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Types Of Dental Scanners.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
