Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for disadvantages of dental implants
In the rapidly evolving landscape of dental solutions, understanding the disadvantages of dental implants is crucial for international B2B buyers seeking to make informed procurement decisions. While dental implants offer a multitude of benefits, including improved aesthetics and functionality, they also come with notable drawbacks that can affect patient satisfaction and operational efficiency. For buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, recognizing these limitations is essential to ensure that the products they source align with their market needs and patient expectations.
This guide delves into the critical aspects of dental implants, covering a wide array of topics such as types of implants, materials used, manufacturing and quality control processes, supplier options, and cost considerations. Each section is designed to provide actionable insights that empower buyers to navigate the complexities of the global dental implant market. By understanding the potential challenges—ranging from surgical complications to long-term maintenance issues—buyers can better evaluate suppliers and choose products that enhance their service offerings while minimizing risks.
Furthermore, the guide addresses frequently asked questions, providing clarity on common concerns that may arise during the sourcing process. With a comprehensive understanding of the disadvantages of dental implants, B2B buyers can confidently engage with suppliers, ensuring that their choices not only meet regulatory standards but also resonate with the unique demands of their regional markets.
Understanding disadvantages of dental implants Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Surgical Risks | Potential complications during surgery, including infections. | Dental clinics, oral surgery centers | Pros: High success rate; Cons: Risk of complications can deter patients. |
| Cost Considerations | High initial investment for materials and procedures. | Dental supply companies, insurance providers | Pros: Long-term investment; Cons: Upfront costs can limit accessibility. |
| Time Commitment | Extended treatment duration involving multiple visits. | Dental practices, orthodontic services | Pros: Comprehensive treatment; Cons: Time-intensive, affecting patient flow. |
| Bone Quality Dependency | Success relies on sufficient bone density for placement. | Implant manufacturers, dental restoration firms | Pros: Customizable solutions; Cons: Not suitable for all patients, limiting market. |
| Maintenance Requirements | Ongoing care needed to ensure longevity and prevent issues. | Dental hygiene products, maintenance services | Pros: Encourages long-term relationships; Cons: Additional costs for patients. |
Surgical Risks
Surgical risks associated with dental implants encompass complications that may arise during the implantation procedure. These include infections, nerve damage, and sinus issues, which can lead to patient dissatisfaction or additional corrective procedures. For B2B buyers, understanding these risks is crucial when selecting implant systems and surgical techniques. Emphasizing training and certifications for dental professionals can mitigate these risks, ensuring a safer environment for patients.
Cost Considerations
The financial aspect of dental implants can be a significant barrier for both providers and patients. The initial costs include not only the implants themselves but also surgical fees, anesthesia, and follow-up care. For B2B buyers, aligning with manufacturers that offer competitive pricing or financing options can enhance accessibility. Additionally, providing patients with clear information about the long-term value of implants can help justify the upfront investment.
Time Commitment
Dental implants often require several appointments, including consultations, surgical procedures, and follow-ups. This time commitment can be a deterrent for potential patients who seek quicker solutions. B2B buyers should consider the implications of treatment duration on patient satisfaction and clinic workflow. Investing in technologies that streamline the process, such as digital planning tools, can help reduce the overall time commitment and improve patient experience.
Bone Quality Dependency
The success of dental implants heavily relies on the quality and density of the patient’s bone structure. In cases where bone density is insufficient, additional procedures such as bone grafting may be necessary. This dependency can limit the market for implants among certain populations. B2B buyers should focus on sourcing implants that offer solutions for varying bone conditions, thus expanding their potential customer base and enhancing treatment options.
Maintenance Requirements
Dental implants require ongoing maintenance to ensure their longevity and functionality. This includes regular check-ups and professional cleanings, which can incur additional costs for patients. For B2B buyers, offering maintenance packages or partnering with dental hygiene product suppliers can create a value-added service for clinics. Educating patients about the importance of maintenance will foster long-term relationships and enhance patient retention.
Related Video: 3 Types of Dental Implants and Surface treatments explained!
Key Industrial Applications of disadvantages of dental implants
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of disadvantages of dental implants | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Understanding patient rejection rates | Improves patient care and satisfaction | Need for reliable data on implant success rates |
| Dental Manufacturing | Development of alternative solutions | Diversifies product offerings | Focus on innovation and regulatory compliance |
| Insurance | Risk assessment for coverage policies | Enhances risk management strategies | Accurate data on complications and treatment costs |
| Research & Development | Clinical studies on implant failures | Supports evidence-based advancements in dentistry | Collaboration with dental institutions for data access |
| Training & Education | Curriculum development for dental professionals | Ensures well-informed practitioners | Access to up-to-date research and case studies |
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, understanding the disadvantages of dental implants, such as patient rejection rates and complications, is critical for enhancing patient care. By analyzing these factors, healthcare providers can develop tailored treatment plans that minimize risks and improve outcomes. For international B2B buyers in regions like Africa and South America, sourcing reliable data on implant success rates and patient experiences is vital. This allows healthcare providers to make informed decisions, ultimately leading to higher patient satisfaction and retention.
Dental Manufacturing
The dental manufacturing industry can leverage insights into the disadvantages of dental implants to innovate and develop alternative solutions. By identifying the common issues associated with traditional implants, manufacturers can create products that address these shortcomings, such as biocompatible materials or designs that reduce the likelihood of complications. For buyers in Europe and the Middle East, focusing on innovation and regulatory compliance in manufacturing processes is essential to meet local market demands and standards, ensuring a competitive edge.
Insurance
In the insurance sector, understanding the disadvantages of dental implants is crucial for developing comprehensive risk assessment models for coverage policies. By analyzing complications and treatment costs associated with dental implants, insurers can enhance their risk management strategies, ensuring they offer competitive and fair coverage options. For B2B buyers in regions like Turkey and Poland, accurate data on complications will facilitate the development of policies that align with market needs, ultimately leading to improved profitability.
Research & Development
Clinical studies on implant failures and their disadvantages play a significant role in the research and development sector. By focusing on these aspects, R&D teams can support evidence-based advancements in dentistry, leading to the development of safer and more effective dental solutions. For international buyers, especially from Africa and South America, collaborating with dental institutions for data access is crucial. This collaboration can drive innovation while addressing the specific challenges faced in their local markets.
Training & Education
The training and education sector can utilize the disadvantages of dental implants to develop comprehensive curricula for dental professionals. By incorporating the challenges and limitations of dental implants into training programs, educators can ensure that future practitioners are well-informed about potential complications and patient management strategies. For B2B buyers in Europe and the Middle East, access to up-to-date research and case studies is essential for creating relevant educational content that prepares dental professionals for real-world challenges.
Related Video: Dental Implants vs Bridges for a Missing Tooth
Strategic Material Selection Guide for disadvantages of dental implants
When selecting materials for dental implants, understanding their properties, advantages, and limitations is crucial for B2B buyers, especially in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here, we analyze four common materials used in dental implants: titanium, zirconia, stainless steel, and polymer-based composites. Each material presents unique characteristics that can significantly impact the performance and suitability of dental implants.
Titanium
Key Properties: Titanium is well-known for its excellent biocompatibility, strength-to-weight ratio, and corrosion resistance. It can withstand the pressures of chewing and is highly resistant to oxidation, making it suitable for long-term use in the oral environment.
Pros & Cons: Titanium implants are durable and have a long history of successful use in dentistry. However, they can be more expensive than other materials, and the manufacturing process can be complex due to the need for precision machining. Additionally, some patients may have allergies to titanium, which can limit its applicability.
Impact on Application: Titanium is compatible with various media, including saliva and oral bacteria, which is critical for the success of dental implants. Its ability to osseointegrate—bonding directly with bone—enhances stability and longevity.
Considerations for Buyers: For international buyers, compliance with standards such as ASTM F136 for titanium alloys is essential. Understanding regional regulations and patient preferences is also critical, as some markets may prefer non-metal options.
Zirconia
Key Properties: Zirconia is a ceramic material known for its aesthetic appeal, high strength, and excellent biocompatibility. It is resistant to wear and has a lower thermal conductivity than metals, which can enhance patient comfort.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of zirconia is its tooth-like appearance, making it a preferred choice for anterior implants. However, it is more brittle than titanium, which can lead to fracture under excessive stress. Additionally, zirconia implants typically have a higher manufacturing cost due to the complexity of the sintering process.
Impact on Application: Zirconia is suitable for patients looking for aesthetic solutions, particularly in visible areas. However, its brittleness may limit its use in posterior applications where higher chewing forces are present.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers must ensure that zirconia implants comply with relevant standards, such as ISO 6872 for dental ceramics. Market preferences may vary, with some regions favoring metal implants for their proven track record.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its strength, corrosion resistance, and cost-effectiveness. It is often used in temporary dental implants or in pediatric dentistry due to its durability.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of stainless steel is its affordability and ease of manufacturing. However, it is less biocompatible than titanium and zirconia, which can lead to complications in some patients. Additionally, stainless steel does not offer the same aesthetic benefits as other materials.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for short-term applications or as a transitional solution. Its mechanical properties make it a good choice for temporary restorations but less ideal for long-term use.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should be aware of compliance with standards such as ASTM F899 for stainless steel used in dental applications. The choice of stainless steel may be influenced by cost considerations in regions with budget constraints.
Polymer-Based Composites
Key Properties: Polymer-based composites are lightweight, flexible, and can be engineered for specific mechanical properties. They are often used in combination with other materials to enhance performance.
Pros & Cons: These materials can be designed for specific applications, providing versatility and customization. However, they typically have lower mechanical strength compared to metals and ceramics, which can limit their use in load-bearing applications.
Impact on Application: Polymer composites are suitable for specific applications where flexibility and patient comfort are prioritized, such as in temporary implants or for patients with special needs.
Considerations for Buyers: Buyers should evaluate the regulatory compliance of polymer composites with standards like ISO 10993 for biocompatibility. Awareness of regional preferences for materials is also important, as some markets may prioritize traditional materials over newer composites.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for disadvantages of dental implants | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium | Permanent dental implants | Excellent biocompatibility | Potential allergies, high cost | High |
| Zirconia | Aesthetic anterior implants | Tooth-like appearance | Brittle, higher manufacturing cost | High |
| Stainless Steel | Temporary or pediatric implants | Cost-effective, durable | Less biocompatible, aesthetic issues | Low |
| Polymer-Based Composites | Temporary implants or special needs applications | Customizable, lightweight | Lower mechanical strength | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of the advantages and limitations of various materials used in dental implants, enabling B2B buyers to make informed decisions based on their specific market needs and patient preferences.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for disadvantages of dental implants
Manufacturing Processes for Dental Implants
The manufacturing of dental implants involves several critical stages, each contributing to the final product’s quality and performance. Understanding these stages can help international B2B buyers make informed decisions when sourcing dental implants.
Main Stages of Manufacturing
-
Material Preparation
The first step in the manufacturing process is the selection and preparation of materials. Titanium and zirconia are the most common materials used due to their biocompatibility and strength. Suppliers must ensure that these materials meet specific chemical and physical standards, which often involves sourcing from certified suppliers. Additionally, pre-processing techniques such as cleaning and surface treatment are essential to enhance adhesion and osseointegration. -
Forming
After material preparation, the forming process begins. This can include techniques such as forging, casting, or machining. Each method has its benefits:
– Forging offers superior mechanical properties and consistency.
– Casting allows for complex geometries.
– Machining provides precision and surface finish.
B2B buyers should consider suppliers that use advanced forming techniques, as these will likely yield higher-quality implants.
-
Assembly
In this stage, components of the implant system (such as abutments and screws) are assembled. This process requires meticulous attention to detail, as any misalignment can lead to implant failure. Automation in assembly can enhance precision and reduce human error, which is a crucial factor for buyers focused on reliability. -
Finishing
The finishing process includes surface treatments that improve the implant’s interaction with bone. Techniques such as sandblasting, acid etching, or coating with bioactive materials are common. The choice of finishing technique can significantly impact the implant’s performance, particularly in terms of osseointegration and longevity.
Quality Assurance Practices
Quality assurance (QA) in the manufacturing of dental implants is paramount to ensure safety and efficacy. International standards and industry-specific certifications play a crucial role in establishing a reliable QA framework.
Relevant International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system (QMS). Suppliers adhering to ISO 9001 demonstrate their commitment to quality and customer satisfaction.
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking signifies compliance with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
- API Certification: Particularly relevant for implant manufacturers, API (American Petroleum Institute) certification ensures that products meet rigorous quality standards.
QC Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are integral throughout the manufacturing process:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
This stage involves inspecting raw materials upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards. B2B buyers should request IQC reports from suppliers to verify compliance. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process helps identify defects early. Techniques such as statistical process control (SPC) can be employed. Buyers should inquire about the IPQC measures their suppliers implement. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
After manufacturing, a comprehensive inspection of the final product is conducted. FQC includes functional testing, dimensional checks, and surface integrity assessments. Buyers should ensure that suppliers provide detailed FQC reports.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are commonly employed to ensure the quality of dental implants:
- Mechanical Testing: Evaluates the strength and durability of implants under stress.
- Corrosion Resistance Testing: Assesses how implants withstand bodily fluids over time.
- Biocompatibility Testing: Ensures that materials do not elicit an adverse reaction in the body.
B2B buyers should ask suppliers about their testing protocols and results to ensure the implants meet necessary safety standards.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international buyers, verifying a supplier’s quality control practices is essential to mitigate risks associated with dental implants.
- Audits: Conducting regular audits of suppliers can help buyers assess compliance with quality standards. This may include reviewing documentation and inspecting manufacturing processes firsthand.
- Quality Reports: Requesting quality assurance reports can provide insights into a supplier’s adherence to standards and any corrective actions taken in response to previous issues.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of a supplier’s manufacturing practices. This is especially important for buyers from regions with varying regulatory standards.
QC and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
International B2B buyers should be aware of the nuances in quality control and certification when sourcing dental implants. Different regions may have varying standards, which can complicate the procurement process. Buyers should:
- Understand Regional Regulations: Familiarize themselves with the regulatory landscape in their respective regions. For example, the Middle East may have different requirements compared to Europe.
- Evaluate Certification Validity: Ensure that the certifications held by suppliers are recognized in their target market. This is crucial for compliance and can affect importation processes.
- Build Relationships with Local Partners: Collaborating with local distributors or regulatory experts can aid in navigating the complexities of certification and compliance.
By being proactive in understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices of dental implants, international B2B buyers can make informed decisions that ensure the safety, efficacy, and success of their dental implant procurement strategies.
Related Video: What I Wish I Knew About the Downsides Before Getting Dental Implants…
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for disadvantages of dental implants Sourcing
Understanding the Cost Structure of Dental Implants
When evaluating the sourcing of dental implants, it is essential to dissect the various cost components that contribute to the final pricing. The primary cost elements include:
-
Materials: The quality of materials used in dental implants, such as titanium or zirconia, significantly affects the cost. High-quality materials often come with a premium price but are crucial for durability and biocompatibility.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is necessary for both manufacturing the implants and for the surgical procedures involved. Labor costs can vary significantly depending on the region, with higher rates typically found in developed countries.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all indirect costs associated with production, including utilities, facility rent, and equipment maintenance. Efficient manufacturing processes can help mitigate these costs.
-
Tooling: Specialized tools and molds are required for implant production. The initial investment in tooling can be substantial, impacting the overall cost structure.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing rigorous QC procedures ensures the implants meet necessary standards, which can add to costs but is vital for patient safety and regulatory compliance.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs vary based on distance, shipping method, and any tariffs or customs duties applicable to international shipments. These costs are particularly relevant for buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically include a profit margin in their pricing. Understanding the margin can provide insight into the competitiveness of the pricing.
Factors Influencing Pricing
Several key factors can influence the pricing of dental implants:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchasing often leads to discounted pricing. Buyers should consider negotiating minimum order quantities (MOQs) to achieve better pricing.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom implants or those with specific design features may incur additional costs. Buyers need to balance customization with budget constraints.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Implants that meet international quality certifications (like ISO or CE marks) may cost more but provide assurance of reliability and safety.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of the supplier can influence pricing. Established suppliers with proven track records may charge higher prices but offer better guarantees and support.
-
Incoterms: The terms of delivery can affect the total cost. Understanding Incoterms (like FOB, CIF) is essential for estimating shipping costs and responsibilities.
Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficiency
To navigate the complexities of dental implant sourcing effectively, international buyers should consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiate: Engage in discussions with suppliers to negotiate better terms, especially when placing large orders. Leverage competition among suppliers to secure advantageous pricing.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Evaluate the TCO, which includes initial costs, maintenance, and potential replacement costs over time. This holistic view can help in making informed purchasing decisions.
-
Evaluate Regional Suppliers: For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, exploring local suppliers can reduce logistics costs and lead times. However, assess their quality and compliance with international standards.
-
Stay Informed about Pricing Trends: Keep abreast of market trends that may affect material costs, such as fluctuations in raw material prices or changes in labor costs due to economic conditions.
-
Understand Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have varying pricing structures based on local demand, competition, and economic conditions. Conducting thorough market research can yield valuable insights.
Disclaimer
The prices mentioned in this analysis are indicative and subject to change based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. It is advisable for buyers to conduct their due diligence and obtain quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential disadvantages of dental implants Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘disadvantages of dental implants’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for disadvantages of dental implants
Understanding the technical properties and trade terminology associated with dental implants is crucial for international B2B buyers. This knowledge not only aids in assessing the disadvantages of dental implants but also informs purchasing decisions and negotiations. Below, we explore essential specifications and terminology that can significantly influence your procurement strategy.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The classification of materials based on their composition and quality. Common materials for dental implants include titanium and zirconia.
– B2B Importance: Understanding the material grade is essential, as it affects the implant’s biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and overall longevity. Buyers should prioritize high-grade materials to minimize the risk of implant failure and ensure patient safety. -
Surface Roughness
– Definition: A measurement of the texture of the implant surface, which influences osseointegration—the process by which the implant fuses with the jawbone.
– B2B Importance: Implants with optimized surface roughness promote better bone attachment. Buyers should seek products with proven surface treatments that enhance integration, thereby reducing the risk of complications and improving patient outcomes. -
Tolerance
– Definition: The permissible limit of variation in a physical dimension or measurement, critical for fitting components precisely.
– B2B Importance: Tolerance levels are vital in ensuring that implants fit accurately within the oral cavity. High precision reduces the likelihood of complications, such as misalignment or infection, making it a critical factor for buyers looking for quality assurance. -
Mechanical Strength
– Definition: The ability of the implant to withstand forces without fracturing, typically measured in terms of yield strength and tensile strength.
– B2B Importance: Implants must endure significant chewing forces. Buyers should assess the mechanical strength of implants to ensure they can withstand the demands of daily use, thereby reducing the risk of breakage and the need for replacements. -
Corrosion Resistance
– Definition: The ability of the implant material to resist degradation due to chemical reactions with the environment, particularly bodily fluids.
– B2B Importance: Corrosion resistance is crucial for the longevity and safety of dental implants. Buyers should prioritize implants that demonstrate high resistance to corrosion, as this can prevent premature failure and the need for costly replacements.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Explanation: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– B2B Insight: When sourcing dental implants, understanding whether a supplier is an OEM can indicate the quality and reliability of the products. OEMs often adhere to higher standards and provide better warranties. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Explanation: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– B2B Insight: Knowing the MOQ is critical for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers from Africa and South America, for instance, may need to negotiate lower MOQs to align with their purchasing capabilities. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Explanation: A document sent to suppliers requesting a price quote for specific products or services.
– B2B Insight: Utilizing RFQs can streamline the procurement process. Buyers should prepare detailed RFQs to ensure they receive accurate quotes that reflect their needs, including specifications and delivery timelines. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Explanation: A series of pre-defined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce, used in international sales contracts.
– B2B Insight: Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for understanding shipping responsibilities and costs. This knowledge helps buyers negotiate better terms and avoid unexpected expenses. -
Lead Time
– Explanation: The amount of time between the initiation of an order and its completion.
– B2B Insight: Understanding lead times is essential for effective supply chain management. Buyers should inquire about lead times to ensure timely delivery of dental implants, which can impact patient care and practice scheduling.
By familiarizing themselves with these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make informed decisions that mitigate the disadvantages associated with dental implants, ultimately enhancing patient care and operational efficiency.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the disadvantages of dental implants Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global dental implants market is evolving rapidly, driven by increasing demand for advanced dental solutions and a rising awareness of oral health. Factors such as the aging population, higher disposable incomes, and a growing inclination towards cosmetic dentistry are propelling market growth. However, international B2B buyers must navigate several challenges related to the disadvantages of dental implants, including high costs, potential complications, and the need for skilled professionals.
Emerging technologies are reshaping the sourcing landscape, with innovations like 3D printing and computer-aided design (CAD) enhancing the precision and customization of dental implants. As a result, suppliers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe (notably Poland and Turkey) are increasingly adopting these technologies to streamline production and reduce costs. Additionally, there is a notable shift towards digital platforms for procurement, allowing buyers to access a wider range of suppliers and compare offerings effectively.
Another key trend is the growing focus on implant materials. Biocompatibility and long-term durability are paramount, prompting suppliers to explore alternative materials that might mitigate disadvantages, such as allergic reactions or implant failure. Furthermore, the market is witnessing an increase in collaborative partnerships between dental professionals and manufacturers, fostering innovation and addressing the specific needs of various regions, especially in emerging markets.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the dental implants sector, as environmental concerns gain prominence among international buyers. The production of dental implants often involves processes that can lead to significant waste and resource depletion. B2B buyers are increasingly seeking suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and minimizing their carbon footprint.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Ethical sourcing is equally important, as buyers are now more informed about the impacts of their purchasing decisions. A transparent supply chain is crucial for ensuring that materials are obtained responsibly and that labor practices meet ethical standards. Certifications like ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and Fair Trade can provide assurance regarding the sustainability and ethical practices of suppliers. Buyers should actively seek out suppliers that hold these certifications to align with their corporate social responsibility goals.
Moreover, the trend towards green materials, such as biocompatible polymers and sustainably sourced titanium, is gaining traction. These materials not only reduce environmental impact but also address some disadvantages associated with traditional implants, such as rejection or inflammation. By prioritizing suppliers that invest in sustainable and ethical practices, B2B buyers can enhance their brand reputation and meet the growing consumer demand for responsible products.
Brief Evolution/History
The dental implants sector has undergone significant transformations since its inception in the mid-20th century. Initially, dental implants were rudimentary and often faced high failure rates. However, advancements in materials science, surgical techniques, and digital technologies have dramatically improved outcomes and patient satisfaction.
In recent decades, the introduction of osseointegration—the process by which bone attaches to the implant—has been a game changer. This has led to higher success rates and longer-lasting solutions, but it also introduced new challenges such as the need for thorough patient evaluations and post-operative care. As the market continues to evolve, B2B buyers must remain cognizant of these historical trends to make informed sourcing decisions and anticipate future developments.
Related Video: Full Mouth Dental Implants: Everything You Need to Know and Cost
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of disadvantages of dental implants
-
What are the main disadvantages of dental implants that B2B buyers should be aware of?
B2B buyers should be cognizant of several disadvantages associated with dental implants, including the potential for complications such as infection, nerve damage, or sinus issues. Additionally, the high upfront costs and the need for multiple procedures can be prohibitive, especially for markets in Africa and South America where budget constraints may exist. Understanding these factors can aid in better supplier negotiations and product selection. -
How can I vet suppliers to ensure they provide quality dental implants?
Conduct thorough due diligence when vetting suppliers by checking certifications, such as ISO or CE marks, which indicate compliance with international safety standards. Request product samples for evaluation and verify the supplier’s reputation through industry references and reviews. Additionally, consider visiting manufacturing facilities if feasible, especially in regions like Turkey or Poland, to assess production processes firsthand. -
What customization options should I look for when sourcing dental implants?
Many suppliers offer customization options tailored to specific market needs, including different sizes, materials, and designs. It’s crucial to discuss your requirements upfront to ensure that the supplier can accommodate them. Additionally, inquire about their capacity to produce customized implants in response to changing market demands, which can be particularly beneficial in regions with diverse patient needs. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for dental implants?
MOQs for dental implants can vary significantly based on the supplier and the complexity of the product. Typically, suppliers may require orders ranging from 50 to 200 units. Lead times can also fluctuate based on the supplier’s location and production capacity; however, it’s common for lead times to be between 4 to 12 weeks. Establishing clear communication about your needs can help negotiate favorable terms. -
What payment terms are generally acceptable when sourcing dental implants internationally?
Payment terms can vary widely by supplier and region. Common practices include upfront payment, partial payment upon order confirmation, and balance upon delivery. For international transactions, consider secure payment methods like letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks. Understanding local customs and practices in regions like the Middle East or Africa can further enhance transaction security.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
What quality assurance (QA) certifications should I look for in dental implants?
Essential QA certifications include ISO 13485 for medical devices and CE marking for compliance with European health and safety standards. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s quality control processes, including testing protocols and product traceability. Ensuring that a supplier has robust QA measures in place can significantly reduce the risk of complications associated with dental implants. -
How can I handle logistics and shipping when importing dental implants?
Efficient logistics management is critical for timely delivery of dental implants. Collaborate with suppliers to understand their shipping capabilities and preferred logistics partners. When importing, consider factors such as customs regulations, tariffs, and potential delays. It is advisable to work with a logistics provider experienced in medical device transportation to navigate these complexities effectively. -
What steps should I take if a dispute arises with a supplier regarding dental implants?
In the event of a dispute, first attempt to resolve the issue through direct communication with the supplier. Keep detailed records of all transactions and communications to support your case. If resolution fails, consider mediation or arbitration as stipulated in your contract. Understanding local laws and international trade agreements can also provide guidance in navigating disputes effectively, ensuring that your interests are protected.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for disadvantages of dental implants
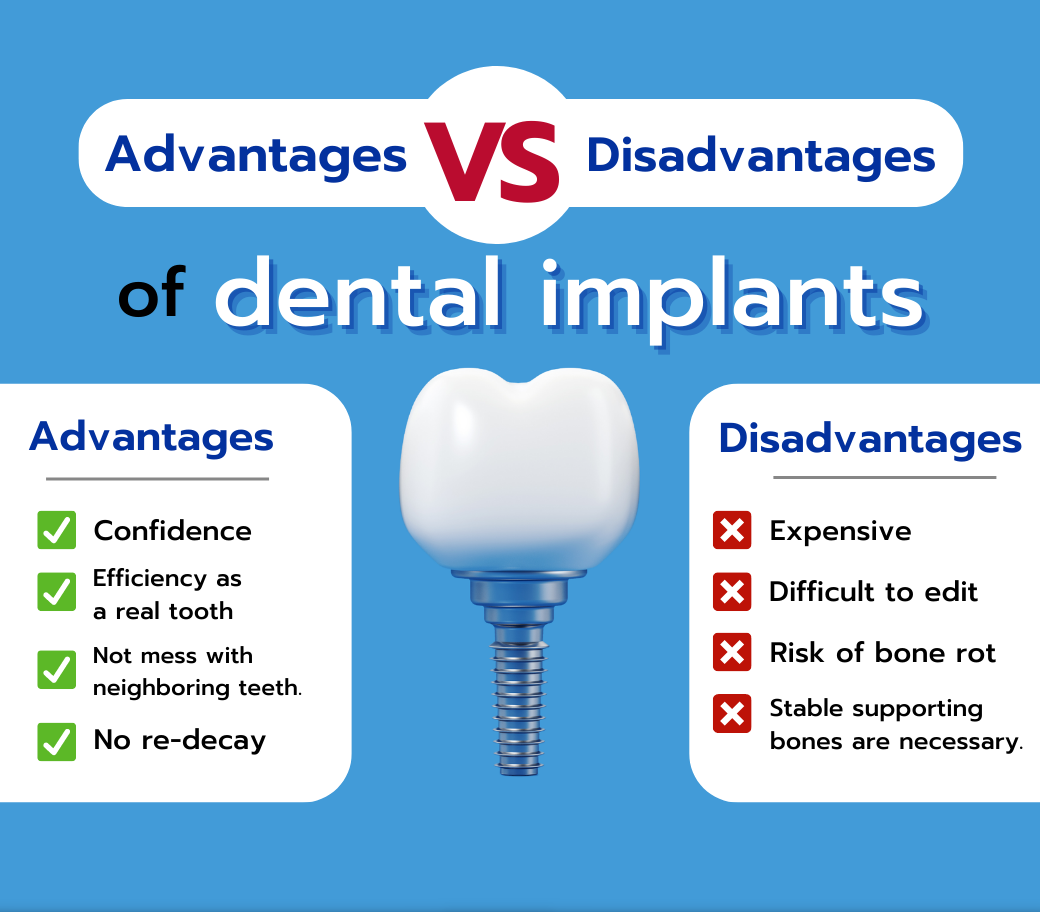
In conclusion, understanding the disadvantages of dental implants is crucial for international B2B buyers who are considering investment in this sector. Key takeaways include recognizing potential complications such as surgical risks, the need for adequate bone density, and the long-term maintenance required. Additionally, the higher upfront costs and the necessity for skilled professionals can impact the overall feasibility and return on investment.
Strategic sourcing plays a vital role in mitigating these disadvantages. By partnering with reliable suppliers, buyers can ensure the procurement of high-quality materials and advanced technology, reducing the likelihood of complications and enhancing patient outcomes. Furthermore, establishing relationships with experienced dental practitioners can aid in streamlining the implementation process, ultimately leading to a more successful integration of dental implants into practices.
As we look to the future, it is essential for B2B buyers in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe to remain informed about advancements in dental implant technology and best practices. By proactively engaging with suppliers and industry experts, businesses can position themselves advantageously in a competitive market. Embrace this opportunity to enhance your offerings and meet the growing demand for effective dental solutions.
