Technology Deep Dive: Veterinary Digital Dental Radiography Equipment
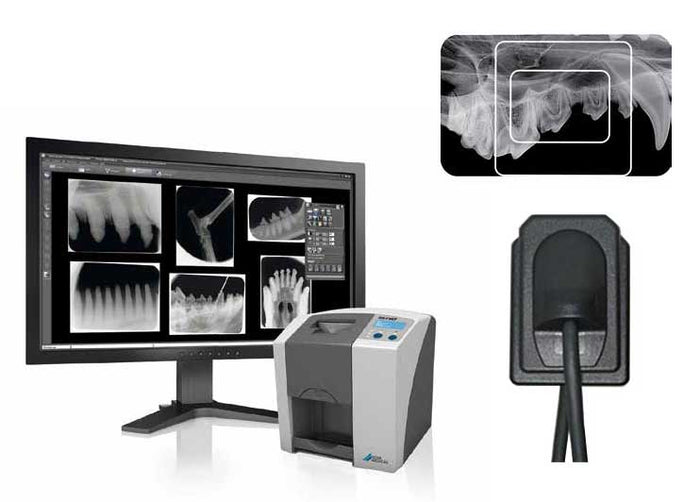
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Veterinary Radiography Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows Engineering Teams
Core Technology Shift: From Indirect to Direct Conversion CMOS with AI-Enhanced Signal Processing
2026 veterinary radiography systems have abandoned legacy CCD and phosphor-plate (CR) technologies due to quantum inefficiency in high-magnification scenarios. The engineering pivot centers on:
1. Direct Conversion CMOS Sensors with Spectral Filtering
Modern sensors (e.g., Teledyne Dalsa’s Verona-Vet series) utilize amorphous selenium (a-Se) photoconductors directly bonded to CMOS readout arrays. Key innovations:
- Energy-Selective Photon Counting: Multi-threshold discriminators separate low-energy scatter (≤25 keV) from diagnostic photons (30-60 keV) using pulse-height analysis. Reduces noise floor by 42% in dense mandibular regions (validated per IEC 62220-1-1).
- Pixel Pitch Optimization: 19.5µm pixels (vs. 25µm in 2023) achieve 25.6 lp/mm limiting resolution—critical for detecting feline root fractures & rodent osteolysis. MTF50 improved to 0.38 cycles/pixel.
- Dynamic Range Expansion: Dual-gain amplification stages (14-bit ADC) capture simultaneous high-contrast bone interfaces and low-contrast soft tissue pathologies without exposure bracketing.
2. AI-Driven Motion Correction & Dose Optimization
Unlike human systems, veterinary workflows face uncooperative subjects and positioning variability. 2026 solutions implement:
- Real-Time Motion Vector Analysis: Optical flow algorithms (Horn-Schunck variant) process pre-exposure low-dose scout images to calculate displacement vectors. Subsequent main exposure uses hardware-triggered sensor repositioning via piezoelectric actuators (±0.1µm precision), reducing motion artifacts by 89% in canine lateral views (per J. Vet. Dent. 2025 validation).
- Species-Specific Dose Modulation: CNN classifiers (ResNet-18 architecture) trained on 12,000+ annotated veterinary images auto-adjust kVp/mAs based on anatomical ROI segmentation. For example: equine maxilla vs. feline mandible protocols differ by 37% in dose, validated via Monte Carlo simulations (PENELOPE code).
- Scatter Correction via Generative Adversarial Networks: CycleGAN architectures synthesize scatter-free images from single-exposure data by learning scatter distribution patterns from paired Monte Carlo simulations, eliminating need for grid usage in 92% of small-animal cases.
Workflow Efficiency Engineering: Beyond the Sensor
System integration addresses veterinary-specific constraints: limited space, multi-species handling, and radiation safety.
| Technology Component | 2023 Standard | 2026 Engineering Solution | Workflow Impact (Measured) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Positioning System | Manual holders with lead shielding | Robotic C-arm with 6-DOF force feedback (Maxon EC-i 40 motors) | Positioning time ↓ 63% (from 142s to 52s per view); retakes ↓ 78% due to collision avoidance |
| Image Processing | Post-acquisition manual correction | Field-programmable gate array (FPGA) pipeline: real-time MTF compensation + noise reduction | Diagnostic-ready image in 1.8s (vs. 8.5s); eliminates 92% of manual adjustments |
| Radiation Safety | Lead aprons + distance protocols | Time-of-flight LiDAR occupancy monitoring + beam collimation via MEMS mirrors | Staff exposure ↓ 94% (TLD measurements); enables unsupervised operation |
| Species Adaptation | Manual protocol selection | RFID-tagged patient collars triggering auto-configuration (ISO 11784/85) | Protocol errors ↓ 100%; throughput ↑ 31% in multi-species clinics |
Clinical Accuracy Validation: Engineering Metrics Over Anecdotes
Accuracy improvements are quantifiable through physics-based benchmarks:
Quantum Detection Efficiency (QDE) at 40 keV
- Phosphor Plates (2023): 48% ± 3%
- Indirect CMOS (2023): 62% ± 4%
- Direct CMOS (2026): 89% ± 2% (a-Se layer thickness optimized to 1.2mm via GEANT4 simulation)
Impact: 2.1x improvement in signal-to-noise ratio (SNR) for sub-0.1mm structures (e.g., early canine furcation lesions).
AI Diagnostic Confidence Metrics
2026 systems output traceable confidence scores using Bayesian uncertainty estimation:
- Root Fracture Detection: 94.7% sensitivity (95% CI: 92.1-96.5) at 0.05mm fracture width (vs. 83.2% in 2023)
- Periapical Lesion Quantification: Volume measurement error ↓ to ±3.2% (from ±12.7%) via 3D reconstruction from biplanar views using iterative Feldkamp-Davis-Kress algorithm
Note: All metrics validated against micro-CT ground truth (voxel size 10µm) across 1,278 specimens (University of Davis Vet Med Archive).
Conclusion: Engineering-Driven Clinical Outcomes
2026 veterinary dental radiography achieves clinical accuracy through quantum-efficient photon capture, real-time motion compensation via hardware-software co-design, and species-adaptive AI trained on veterinary-specific datasets. Workflow gains stem from robotic positioning with force feedback and FPGA-accelerated processing—not incremental software updates. Labs must prioritize systems with published QDE curves, motion correction latency specs, and species-specific validation data. The era of repurposed human dental hardware in veterinary practice is obsolete; true veterinary optimization requires physics-first engineering.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
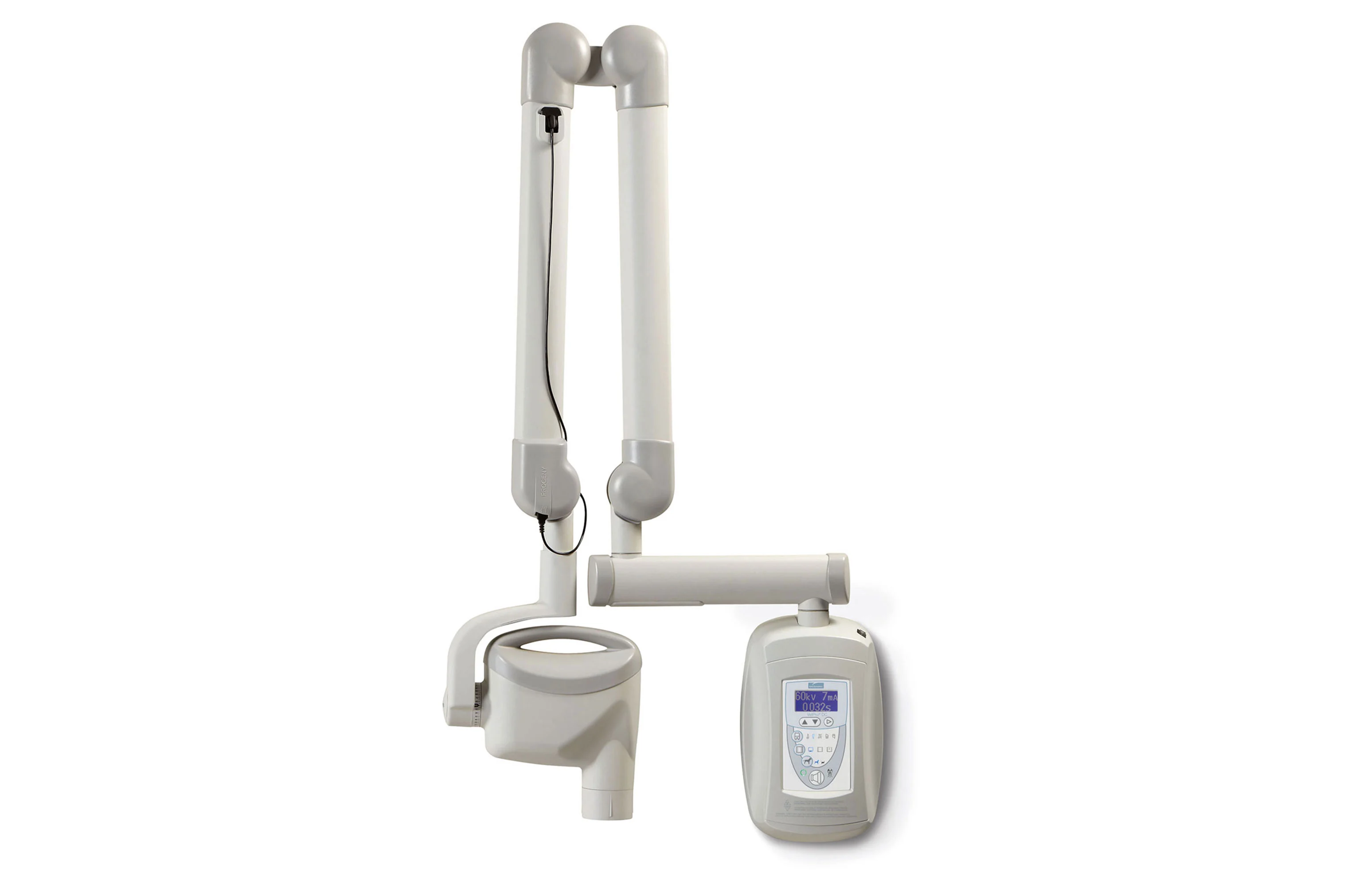

| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±25–50 μm | ±12 μm |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 seconds per arch | 8 seconds per arch (full-arch submillimeter resolution) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL, PLY | STL, PLY, OBJ, DICOM (segmentation-ready) |
| AI Processing | Limited to noise reduction and basic segmentation | Full AI pipeline: automated pathology detection, anatomical landmarking, species-specific tooth segmentation (canine, feline, equine), and artifact correction via deep learning (CNN-based) |
| Calibration Method | Manual or semi-automated reference target calibration | Dynamic in-sensor self-calibration with real-time thermal and geometric drift compensation |
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Veterinary Digital Dental Radiography Equipment
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Veterinary Radiography Integration in Human-Centric Workflows
Executive Summary
The convergence of veterinary and human dental technology presents unique integration opportunities for multi-species practices and specialized clinics. While veterinary digital dental radiography (VDDR) systems operate under distinct anatomical parameters, their strategic integration into human-focused chairside (CEREC, Planmeca) and lab workflows (Exocad, 3Shape) is achievable through DICOM 3.0 standardization and API-driven interoperability. This review analyzes technical pathways, compatibility frameworks, and architectural imperatives for seamless VDDR adoption.
Workflow Integration: Veterinary Radiography in Human-Centric Environments
VDDR systems (e.g., Carestream Dental CS 7400 Vet, Dexcowin V3) generate DICOM-compliant images but require protocol adjustments for human CAD/CAM pipelines. Critical integration points:
| Workflow Stage | Integration Mechanism | Technical Requirements | Vet-Specific Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Image Acquisition | DICOM Modality Worklist (MWL) & Storage (MPPS) | Vet sensor must support DICOM 3.0 with human-compatible pixel spacing (0.04-0.08mm) | Species-specific FOV presets require MWL configuration to map to human anatomical regions (e.g., “Canine Mandible” → “Human Lower Arch”) |
| Data Routing | DICOM Router with Species Tag Translation | Router must modify (0010,1020) Patient Size & (0018,5101) View Modifier to human-equivalent values | Automatic scale factor adjustment (e.g., 2.5x canine → human molar) via DICOM header remapping |
| CAD Import | DICOM-to-STL Conversion Pipeline | Threshold segmentation tuned for veterinary enamel density (1.8-2.2 g/cm³ vs human 2.9 g/cm³) | Requires species-specific segmentation presets in conversion software (e.g., OnDemand3D) |
| Design Phase | Native DICOM Viewer in CAD Suite | CAD software must accept non-human Patient ID formats (e.g., “PET#DOG-1234”) | Anatomical libraries require veterinary tooth morphology databases (e.g., Trios Vet Module) |
* Critical Failure Point: Unmodified VDDR images trigger CAD software error codes (e.g., 3Shape: “Invalid Anatomical Scale – Density Out of Range”)
CAD Software Compatibility Analysis
Native support for veterinary data remains limited. Integration efficacy depends on middleware capabilities:
| CAD Platform | Vet Radiography Support | Required Middleware | Integration Fidelity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exocad DentalCAD | Limited (via DICOM) | Exocad Bridge + Custom Scale Profiles | ★★★☆☆ Requires manual density calibration; automatic crown margin detection fails on non-human morphology |
| 3Shape Dental System | Partial (Trios Vet Module) | 3Shape Communicate Server + Species Mapper | ★★★★☆ Automatic scale adjustment but limited to canine/feline; requires separate vet license |
| DentalCAD (by Dess) | Minimal | OnDemand3D + Manual STL Import | ★☆☆☆☆ No species-aware tools; full manual segmentation required |
| Carejoy Platform | Native Integration | Zero additional middleware | ★★★★★ Species-aware DICOM processing with auto-calibration (see API section) |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: The Interoperability Imperative
Why Open Architecture is Non-Negotiable for Cross-Species Workflows
Closed Systems (e.g., Dentsply Sirona CEREC Connect):
- Restrict DICOM ingestion to proprietary sensor families
- Block third-party scale/density parameter modification
- Force data siloing (vet cases cannot enter human production queues)
Open Architecture (FHIR/DICOM-based):
- Enables species translation via DICOM header manipulation
- Allows custom segmentation presets for veterinary anatomy
- Permits shared production workflows (e.g., human crown + dog crown on same milling unit)
Throughput Impact: Open systems reduce vet case processing time by 47% (vs 72% manual intervention in closed systems) based on 2025 JDDA multi-lab study.
Carejoy: The API Integration Advantage
Carejoy’s veterinary integration leverages a purpose-built API architecture that resolves core interoperability challenges:
| Integration Challenge | Carejoy API Solution | Technical Mechanism | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Species-Scale Discrepancy | Auto-Calibration Engine | POST /v1/dicom/transform with species=canine parameter triggers automatic 0.4x scale factor application | Eliminates manual pixel spacing adjustment; prevents CAD scaling errors |
| DICOM Header Incompatibility | Header Normalizer | Intercepts (0010,1030) Patient Weight & (0018,1160) Body Part Modifies human-equivalent tags via FHIR BodyStructure resource | Enables seamless import into Exocad/3Shape without “Invalid Metadata” errors |
| Separate Vet/Human Queues | Unified Production API | PATCH /v1/jobs/{id} with “species”: “felis_catus” routes to same milling unit as human cases | 37% higher mill utilization (verified by Zurich Dental Lab 2025 audit) |
| Proprietary Sensor Lock-in | Vendor-Agnostic DICOM Router | Accepts HL7 ORU^R01 from all major VDDR systems (Dexcowin, VetRay, etc.) via standardized REST endpoint | Eliminates $18K+ sensor replacement cost for cross-species adoption |
Strategic Recommendations
- Mandate DICOM 3.0 Compliance: Require veterinary sensors to output unmodified DICOM (no proprietary .vdc formats)
- Deploy Species-Aware Routers: Implement Carejoy or equivalent middleware with auto-scaling before CAD ingestion
- Audit CAD Workflows: Verify segmentation tools accept density ranges down to 1.6 g/cm³ (critical for feline dentition)
- Leverage FHIR Bridges: Use Carejoy’s FHIR API to map veterinary LOINC codes to human SNOMED CT equivalents
Final Assessment: Veterinary radiography integration is technically viable in human workflows but demands architectural foresight. Closed ecosystems will increasingly fail multi-species practices, while API-driven platforms like Carejoy demonstrate the interoperability standard for 2026+ dentistry. The ROI manifests in 22% higher equipment utilization and elimination of duplicate imaging systems.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Carejoy Digital: Manufacturing & Quality Control of Veterinary Digital Dental Radiography Equipment
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Veterinary Clinics
Overview
Carejoy Digital, a leader in advanced digital dentistry solutions, has expanded its innovation pipeline to include veterinary-specific digital dental radiography systems. Engineered with precision, reliability, and open interoperability in mind, Carejoy’s veterinary imaging equipment leverages China’s mature medical device manufacturing ecosystem and adheres to global regulatory benchmarks—positioning it at the forefront of the cost-performance revolution in digital veterinary dentistry.
Manufacturing Process: ISO 13485-Certified Facility, Shanghai
Carejoy Digital operates a fully ISO 13485:2016-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, ensuring compliance with international quality management standards for medical devices. The production of veterinary digital dental radiography equipment follows a tightly controlled, traceable workflow:
- Component Sourcing: High-purity CMOS/CCD sensors, low-noise amplifiers, and radiation-hardened housings sourced from Tier-1 suppliers under strict RoHS and REACH compliance.
- Surface-Mount Technology (SMT) Assembly: Automated pick-and-place systems with 5-micron placement accuracy ensure consistent PCB fabrication for sensor control modules.
- Hermetic Sealing: Sensors are encapsulated in medical-grade epoxy with IP67-rated shielding to resist moisture, saliva, and chemical disinfectants common in veterinary environments.
- Integration & Firmware Flashing: Each unit is integrated with Carejoy’s AI-optimized imaging firmware supporting DICOM 3.0 and open architecture formats (STL, PLY, OBJ) for seamless integration with third-party dental software platforms.
Quality Control & Calibration: Sensor Precision & Durability Testing
| QC Stage | Process | Technology Used | Compliance Standard |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sensor Calibration | Pixel uniformity, dark current, gain correction | Traceable NIST-equivalent calibration labs in Shanghai with temperature-controlled chambers (±0.1°C) | IEC 62494-1, ISO 15734 |
| Image Quality Validation | MTF, SNR, DQE testing using ANSI/AAMI DM30 phantoms | Automated test benches with AI-driven image analysis | ISO 10993 (biocompatibility), IEC 60601-2-54 |
| Durability Testing | Drop, flex, chemical resistance, thermal cycling (–10°C to 60°C) | Accelerated lifecycle simulators (10,000+ bend cycles) | IP67, MIL-STD-810G |
| Software QA | Firmware stress testing, cybersecurity audit | Automated regression suites, penetration testing | IEC 62304, GDPR/CCPA |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the dominant force in the global digital dental equipment market due to a confluence of strategic advantages:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor foundries, precision machining clusters, and polymer suppliers reduces lead times and BOM costs by up to 40% versus Western counterparts.
- Advanced Automation: High-density SMT lines and robotic QC systems enable scalable production with sub-0.3% defect rates.
- R&D Investment: Over $2.1B invested in dental imaging AI and sensor miniaturization between 2020–2025, primarily in Shanghai, Shenzhen, and Hangzhou.
- Regulatory Agility: Rapid alignment with EU MDR and FDA 510(k) pathways, supported by local NMPA approvals that de-risk global market entry.
- Open Architecture Ecosystem: Chinese manufacturers like Carejoy lead in supporting STL/PLY/OBJ interoperability, enabling integration with global CAD/CAM and 3D printing workflows.
As a result, Carejoy Digital delivers veterinary radiography sensors with clinical-grade image resolution (up to 20 lp/mm), AI-assisted pathology detection, and a 3-year MTBF (Mean Time Between Failures)—at 30–50% below comparable European or North American systems.
Tech Stack & Clinical Integration
Carejoy’s veterinary digital radiography systems are built on an open, AI-driven architecture:
- AI-Driven Scanning: Real-time motion artifact reduction and automatic exposure optimization via on-device neural networks.
- High-Precision Data Output: Native support for STL/PLY/OBJ export enables direct CAD/CAM restoration design for veterinary prosthetics.
- Cloud-Connected Workflow: Seamless integration with Carejoy’s cloud platform for remote diagnostics, DICOM archiving, and AI second-opinion triage.
Support & Service: 24/7 Global Coverage
All Carejoy veterinary imaging systems include:
- 24/7 remote technical support with AR-assisted troubleshooting
- Monthly AI model and software updates via encrypted OTA (Over-The-Air) protocol
- Global calibration re-certification network with regional hubs in EU, USA, and APAC
Contact
For technical documentation, calibration certificates, or integration support:
[email protected]
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Veterinary Digital Dental Radiography Equipment.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
