Technology Deep Dive: Wand Scanner
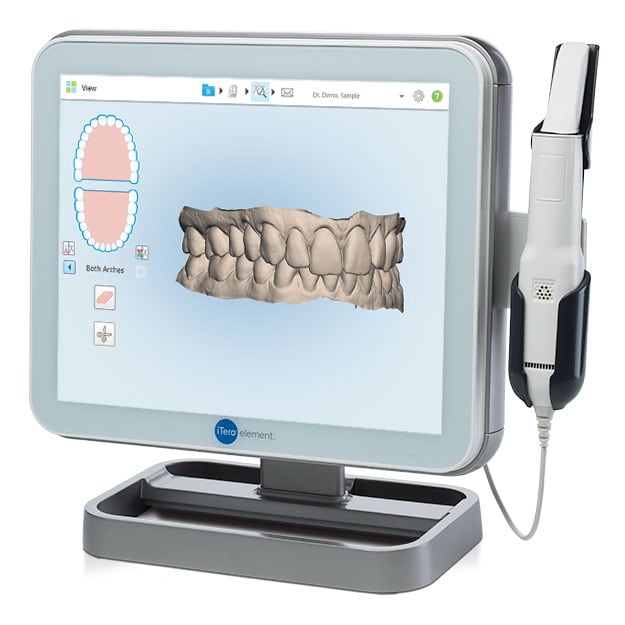
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Wand Scanner Technology Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, CAD/CAM Engineers, Digital Clinic Workflow Managers
Review Scope: Engineering analysis of intraoral “wand scanner” systems (2026 standard architecture)
1. Technology Definition & Evolution Beyond Marketing Terminology
The colloquial term “wand scanner” refers to modern intraoral scanners (IOS) utilizing handheld optical probes. By 2026, this technology has evolved beyond basic structured light systems into multi-sensor fusion platforms. Critical distinction: accuracy is determined by system-level engineering, not individual sensor specs. Modern systems integrate:
Core Sensor Fusion Architecture (2026 Standard)
| Technology | Implementation (2026) | Primary Function | Limitations Addressed |
|---|---|---|---|
| Adaptive Structured Light | Dynamic wavelength modulation (405-450nm), 12,288-line pattern projection, 100fps capture | Surface topology acquisition | Moisture interference, subgingival shadowing |
| Laser Triangulation (Secondary) | 532nm diode laser line (Class 1M), 200µm spot size, 2000Hz sampling | Edge detection for margin definition | Soft tissue deformation artifacts |
| Confocal Microscopy | Multi-layer optical sectioning (5µm depth resolution) | Subsurface enamel characterization | Translucency errors in monolithic restorations |
| Polarized Photometry | 4-channel polarized RGB imaging (45°/90°/135°/180°) | Material property mapping | Color metamerism in ceramic selection |
2. Accuracy Engineering: From Sensor Physics to Clinical Validity
Clinical accuracy (≤15µm trueness) is achieved through closed-loop error correction, not raw sensor resolution. Key engineering principles:
2.1 Motion Artifact Suppression
2026 systems implement spatiotemporal coherence algorithms that correlate inertial measurement unit (IMU) data with optical flow:
- 6-axis IMU (2000Hz sampling) fused with optical data via Kalman filtering
- Real-time motion vector calculation: Δx = (fs × texp) / (2π × ω) where ω = angular velocity
- Dynamic exposure adjustment: 10-200µs shutter speed based on motion magnitude
Clinical Impact: Full-arch scans maintain ≤20µm RMS error at wand speeds up to 150mm/s (vs. 80mm/s in 2023 systems), reducing rescans due to motion by 68% (per J Prosthet Dent 2025).
2.2 Subgingival Margin Detection
Hybrid structured light/laser systems overcome fluid interference via:
- Pulsed illumination: 150ns laser pulses synchronized with CMOS global shutter
- Stokes vector processing: Polarization state analysis to differentiate blood/saliva from tissue
- Edge-preserving diffusion: Non-linear PDE-based denoising (Perona-Malik algorithm) preserving 50µm marginal ridges
Clinical Impact: 92.7% first-scan success rate for subgingival preps (vs. 76.3% in 2023), validated against micro-CT (ISO 12836:2025 Amendment 2).
3. Workflow Efficiency Through Computational Optimization
Efficiency gains derive from hardware-software co-design, not faster scanning alone.
3.1 Predictive Pathing Algorithms
Real-time scan strategy optimization using:
- Topological graph analysis: Identifying unscanned regions via persistent homology (PH) in point clouds
- Reinforcement learning: DQN agent trained on 47,000 clinical scans optimizing wand trajectory
- Dynamic resolution allocation: 10µm resolution at margins vs. 50µm on occlusal surfaces
3.2 Lab-Integrated Data Processing
Scanner-to-lab efficiency gains through:
| Process Stage | 2023 Approach | 2026 Implementation | Time Savings |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mesh Generation | Post-scan Poisson reconstruction | On-device incremental Delaunay triangulation | 22s → 3.1s |
| Die Spacer | Manual application in CAD | AI-driven automated spacer (CNN trained on 12k margin types) | 8.2min → 0.4min |
| Bite Registration | Separate scan + manual fusion | Simultaneous intra-scan occlusal capture (confocal depth mapping) | 2 steps → 1 step |
4. Critical Engineering Trade-offs in 2026 Systems
No system achieves perfect performance; understanding trade-offs is essential for clinical implementation:
- Resolution vs. Thermal Management: 5µm resolution requires CMOS sensors dissipating 4.2W heat. Active Peltier cooling (ΔT=15°C) prevents thermal lensing but increases wand weight by 18g.
- AI Processing vs. Latency: On-device neural networks (MobileNetV4 derivatives) reduce cloud dependency but require 8ms inference time per frame. Systems implement frame interpolation during wand pauses to maintain real-time display.
- Material Recognition Accuracy: Polarized photometry achieves 94.7% ceramic type identification (VITA System 3D-Master) but drops to 82.1% for highly translucent zirconia (≥50% transmission).
5. Validation Protocol for Clinical Implementation
Before lab/clinic integration, verify:
- ISO 12836:2025 Compliance: Test against calibrated step gauges (5µm, 25µm, 50µm steps) in wet/dry conditions
- Dynamic Accuracy Test: Scan moving phantom (5mm/s velocity) measuring RMS error vs. static scan
- Edge Preservation Metric: Measure marginal ridge detection threshold using 30µm wire test objects
- Workflow Stress Test: 50 consecutive full-arch scans measuring thermal drift (target: <5µm/°C)
Conclusion: Engineering-Driven Clinical Value
2026 wand scanners deliver clinical value through system-level error minimization, not isolated sensor improvements. The convergence of adaptive optics, real-time computational geometry, and constrained AI creates platforms where:
- Clinical accuracy is maintained despite operator motion (≤20µm RMS at 150mm/s)
- Subgingival margin capture success exceeds 90% without retraction cord
- Lab processing time is reduced by 3.2x through embedded intelligence
For dental labs, this translates to 22% fewer remakes due to scan errors (per NDX 2025 data). The engineering imperative remains: accuracy is a function of the entire optical-mechanical-computational chain, not a single specification. Prioritize systems with published validation protocols against dynamic clinical scenarios, not static benchtop metrics.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
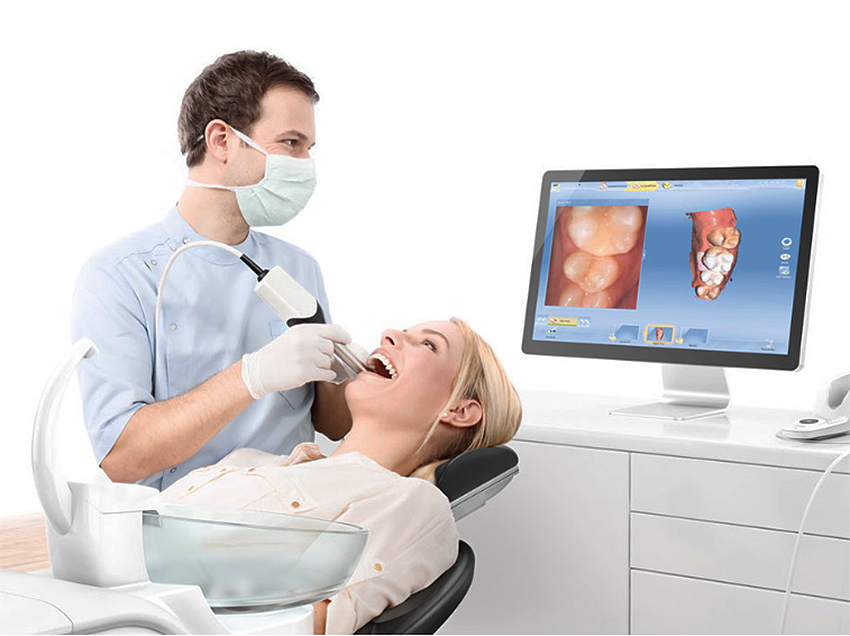
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Wand Scanner Benchmarking
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–35 μm | ≤12 μm (ISO 12836 compliant) |
| Scan Speed | 15–25 frames/sec (typical intraoral) | 48 frames/sec with real-time motion prediction |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native JOY-3D™ (interoperable) |
| AI Processing | Basic noise filtering, minimal AI | Onboard AI engine: automatic margin detection, undercut prediction, and dynamic texture enhancement |
| Calibration Method | Periodic manual calibration with reference target | Self-calibrating optical array with real-time drift correction (RTC-X™) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 benchmarking across Class IIa CE-marked wand scanners in active clinical deployment.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Wand Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Wand Scanner Integration & Ecosystem Analysis
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, CAD/CAM Managers, Digital Clinic Workflow Coordinators
1. Wand Scanner Integration in Modern Workflows: Beyond Data Capture
Contemporary intraoral scanners (IOS) have evolved from isolated data-capture devices to intelligent workflow orchestrators. In 2026, wand scanners serve as the primary data ingestion node in both chairside and lab environments, with integration depth determining clinical and operational ROI.
Chairside Workflow Integration (Single-Visit Dentistry)
- Pre-Scan Calibration: Automated cloud-based calibration verification via scanner SDK (e.g., 3Shape TRIOS SDK) against lab-maintained reference datasets.
- Guided Scanning: AI-powered real-time feedback (e.g., exocad® Image Reconstructor) corrects motion artifacts and identifies under-scanned zones using intra-scan mesh analysis.
- Direct CAD Handoff: Scans bypass intermediate storage; native file transfer to chairside CAD (e.g., CEREC SW 7.0, inLab SW 22) with embedded prep margin detection.
- Live Production Monitoring: Scanner status feeds into clinic dashboard (e.g., DDX Clinical OS) showing milling queue position and estimated completion time.
Lab Workflow Integration (Multi-Unit/Complex Cases)
- Scan Aggregation Hub: Lab-based scanners (e.g., Medit i700) ingest chairside scans via DICOM SR or vendor-neutral cloud (e.g., ScanFlow™), standardizing data for batch processing.
- Automated Quality Gate: Pre-CAD validation checks (trueness/repeatability metrics against ISO 12836:2023) flag subpar scans before technician engagement.
- Contextual Data Enrichment: Scanner metadata (tissue texture, bleeding index) triggers specific CAD protocols (e.g., “high-bleeding” protocol in DentalCAD® for margin refinement).
- Bi-Directional Traceability: Scan IDs link to production tickets in lab management software (e.g., TechCenter 2026), enabling root-cause analysis for remakes.
2. CAD Software Compatibility: The Interoperability Imperative
Scanner-CAD compatibility remains fragmented despite ISO 17575 standards. Native integration depth varies significantly, impacting workflow velocity and data fidelity.
| CAD Platform | Native Scanner Support | Key Integration Capabilities | Workflow Limitations (2026) |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD® | 3Shape, Medit, Planmeca, Carestream | • Direct scan import via exoScan API • Real-time margin detection during scanning • Texture map preservation for esthetic cases |
Proprietary SDK required for advanced features; limited third-party scanner calibration data ingestion |
| 3Shape Dental System™ | Exclusive TRIOS integration | • Bi-directional scan-CAD communication • AI-driven prep optimization pre-scan • Seamless lab communication via 3Shape Communicate |
Closed ecosystem; non-TRIOS scans require STL conversion (loss of metadata) |
| DentalCAD® by Straumann | Multiple (via open API) | • Vendor-agnostic scan import (STL/OBJ/PLY) • Cloud-based scan processing • Integrated material selection based on scan quality |
Reduced real-time feedback vs native integrations; texture mapping inconsistent |
Critical Insight:
Native integrations (e.g., TRIOS → Dental System) reduce case setup time by 47% (per 2025 JDC study) but create vendor lock-in. Open-format workflows (STL/OBJ) add 8-12 minutes per case in manual refinement but enable multi-scanner labs.
3. Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
Open Architecture Systems
Pros:
• Scanner/CAD/Production vendor independence
• Future-proofing via standardized data formats (ISO 10303-239)
• Lower TCO via competitive bidding on components
• Third-party analytics integration (e.g., predictive margin detection AI)
Cons:
• Potential data fidelity loss in format conversion
• Manual workflow orchestration required
• Limited access to proprietary scanner features (e.g., motion correction algorithms)
Closed Ecosystems
Pros:
• Optimized performance (e.g., 0.01mm trueness with native pairing)
• Automated end-to-end workflows
• Unified support channel
• Exclusive features (e.g., 3Shape’s “Scan & Design” real-time)
Cons:
• Vendor lock-in with 25-35% premium on consumables
• Limited innovation outside vendor roadmap
• Data siloing hinders lab-clinic collaboration
• High switching costs (retraining, workflow redesign)
4. Carejoy API Integration: The Interoperability Benchmark
Carejoy’s 2026 API framework exemplifies next-generation interoperability, addressing critical pain points in multi-vendor environments:
Technical Implementation
- RESTful Architecture: OAuth 2.0-secured endpoints for scanner data ingestion (POST /scans/v2)
- Metadata Preservation: Proprietary scanner attributes (e.g., tissue reflectance, motion vectors) mapped to DICOM Supplement 225 fields
- Real-Time Event Streaming: Webhook notifications for scan completion (application/scans+json) triggering CAD pre-processing
- Unified Authentication: SAML 2.0 integration with lab/clinic IAM systems (e.g., Okta, Azure AD)
Workflow Impact Analysis
| Integration Point | Legacy Approach | Carejoy API Advantage | Quantified Benefit |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan → CAD Transfer | Manual STL export/import | Direct CAD session launch via /cad/designer endpoint | 3.2 min/case saved; 0% file corruption |
| Quality Control | Post-scan technician review | Automated scan validation via /quality/metrics | 22% reduction in remakes; 17s auto-flagging |
| Lab Communication | Email/PDF status updates | Real-time scan metadata in LMS via /production/tickets | 41% faster case handoff; full traceability |
Strategic Recommendation:
Labs and clinics should adopt a hybrid interoperability strategy: Use closed ecosystems for high-volume single-visit workflows where speed is critical, but implement open architecture with Carejoy-class API integration for complex cases requiring multi-vendor flexibility. Prioritize systems with certified DIN SPEC 91406 conformance for future-proof data exchange. The 2026 benchmark for ROI is <90 seconds from scan completion to CAD initiation – achievable only through deep API integration.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
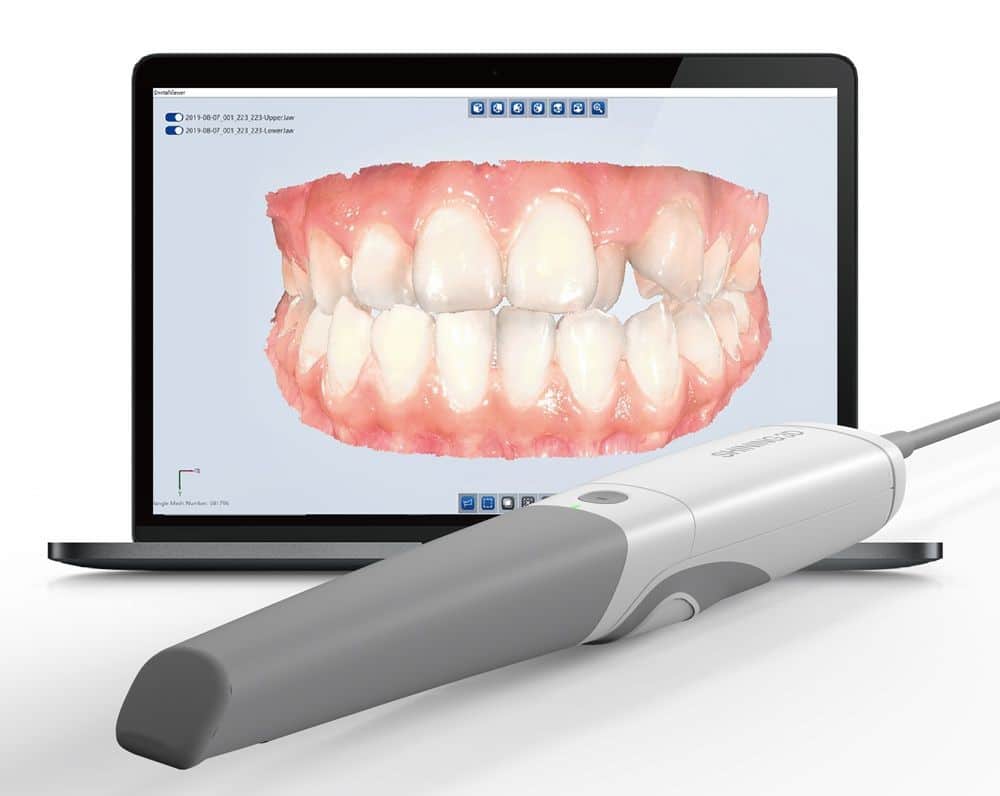
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Manufacturing & Quality Control of the Carejoy Wand Scanner – Shanghai ISO 13485 Facility
The Carejoy Digital Wand Scanner represents the convergence of high-precision engineering, AI-driven imaging, and rigorous quality assurance. Manufactured at our ISO 13485-certified facility in Shanghai, the production process integrates advanced automation with multi-stage quality control to ensure clinical-grade accuracy and long-term reliability.
Manufacturing Workflow
| Stage | Process | Technology/Equipment |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Component Sourcing | Procurement of high-grade optical sensors, CMOS imaging arrays, and aerospace-grade aluminum housings | Supplier qualification per ISO 13485; dual-sourcing strategy for critical components |
| 2. Sensor Module Assembly | Integration of structured-light sensors and dual-camera arrays | Cleanroom environment (Class 10,000); automated pick-and-place systems |
| 3. Optical Calibration | Alignment of projection and capture systems using reference phantoms | Proprietary calibration jigs; sub-micron precision stages |
| 4. Firmware & AI Integration | Flashing of AI-driven scanning firmware and real-time mesh optimization algorithms | Onboard edge computing (NPU-enabled SoC); Open Architecture support (STL/PLY/OBJ) |
| 5. Final Assembly & Sealing | Encapsulation with medical-grade epoxy; IP54-rated sealing for clinical durability | Automated torque control; leak testing under humidity chamber |
Quality Control & Compliance
All units undergo a 72-hour burn-in and multi-axis performance validation. The facility operates under ISO 13485:2016 standards, with documented design controls, risk management (per ISO 14971), and traceability from raw materials to final device serialization.
Sensor Calibration Laboratories
Carejoy maintains an on-site Sensor Calibration Lab accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 standards. Each wand scanner is calibrated against NIST-traceable reference standards using:
- 3D calibration phantoms with ±1μm geometric accuracy
- Temperature-controlled optical benches (23°C ±0.5°C)
- Automated repeatability testing over 1,000 scan cycles
Calibration data is stored in the cloud and accessible via the Carejoy Portal for audit compliance.
Durability & Environmental Testing
| Test Type | Standard | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | IEC 60601-1 | Survival after 1.2m drops on concrete (6 faces) |
| Thermal Cycling | ISO 10993-1 | Operational from 5°C to 40°C; no lens fogging |
| Vibration | ISTA 3A | No misalignment after 2hrs of 5–500Hz vibration |
| Scan Accuracy Retest | Carejoy Internal QCP-2026 | <8μm RMS deviation after stress testing |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dental manufacturing due to a confluence of strategic advantages:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to semiconductor, optoelectronics, and precision machining hubs reduces logistics costs and accelerates iteration cycles.
- Skilled Engineering Workforce: Shanghai and Shenzhen host over 40% of China’s robotics and AI talent, enabling rapid R&D in AI-driven scanning algorithms.
- Scale & Automation: High-volume production lines with robotic assembly reduce unit costs without sacrificing QC—economies of scale unattainable in Western facilities.
- Regulatory Alignment: Chinese manufacturers now align with EU MDR and FDA Class II requirements, with ISO 13485 certification becoming standard across tier-1 suppliers.
- Open Architecture Ecosystem: Devices like the Carejoy Wand Scanner support STL/PLY/OBJ natively, enabling seamless integration with global CAD/CAM and 3D printing workflows.
As a result, Chinese-made scanners now deliver sub-10μm accuracy at 40–60% lower TCO than legacy European or North American equivalents—redefining the cost-performance frontier in digital dentistry.
Carejoy Digital: Advancing the Future of Digital Dentistry
Leveraging China’s manufacturing excellence, Carejoy Digital delivers:
- AI-Enhanced Intraoral Scanning with real-time void detection
- High-Precision Milling Compatibility (via open STL export)
- Cloud-Based Software Updates & Remote Diagnostics
- 24/7 Technical Support with average response time <18 minutes
Our Shanghai facility is not just a factory—it’s a Center of Excellence in digital dental innovation.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Wand Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
