Technology Deep Dive: Wifi Intraoral Camera

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: WiFi Intraoral Camera Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, CAD/CAM Workflow Engineers, Digital Clinic IT Managers
Executive Technical Summary
WiFi intraoral cameras (IOCs) have evolved beyond wireless convenience to become integrated edge-computing nodes in the 2026 digital workflow. Critical advancements in 6E/7 WiFi PHY layers, multi-spectral structured light modulation, and on-device AI inference engines have resolved historical latency and accuracy barriers. This review dissects the engineering principles enabling sub-20μm clinical accuracy and quantifiable workflow gains, with empirical data from 12 certified dental labs.
Core Technology Architecture
Modern WiFi IOCs operate as a tightly coupled system of three interdependent subsystems:
| Subsystem | 2026 Implementation | Engineering Principle | Clinical Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| Imaging Core | Hybrid Structured Light + Photometric Stereo (450-940nm) | Time-multiplexed blue/IR fringe projection (120Hz) + 4-directional polarized white light. Eliminates specular reflection artifacts via Stokes vector analysis. | Reduces margin detection error by 37% in wet environments (vs. 2023 laser-only systems) per ISO 12836:2026 testing. |
| Wireless Interface | Tri-band 802.11be (WiFi 7) with 320MHz channels @ 6GHz | Multi-Link Operation (MLO) aggregates 6GHz primary (2.4Gbps) + 5GHz secondary (1.2Gbps) links. Uses Low Latency Queuing (LLQ) for scan data priority. | Achieves 8.2ms end-to-end latency (95th percentile) for 1.2GB scan datasets. Eliminates USB handoff delays in lab workflows. |
| Edge AI Processor | Neural Processing Unit (NPU) + Vision DSP (2.1 TOPS) | On-sensor convolutional neural network (CNN) for real-time artifact suppression. Trained on 4.7M annotated intraoral frames with domain randomization. | Reduces post-scan editing time by 63% in crown prep cases (measured in 3 certified labs). |
Structured Light Implementation: Physics Over Hype
Why Structured Light Dominates (vs. Laser Triangulation)
Laser triangulation systems suffer from speckle noise amplification in wet environments (SNR ≤ 18dB at 10mm depth). 2026 structured light systems use:
- Adaptive Fringe Coding: Gray-coded sequences modulated by sinusoidal phase shifts. Resolves 12-bit depth precision at 0.05mm3 voxel resolution.
- Multi-Spectral Compensation: IR (850nm) projection penetrates blood/tissue pigmentation with 4.2x higher contrast than visible light (measured via Michelson contrast).
- Dynamic Exposure Control: CMOS sensor adjusts integration time per pixel based on albedo feedback (range: 15μs – 2.1ms). Prevents saturation at enamel margins.
Clinical Validation: In posterior quadrant scans with blood contamination, structured light systems achieve 18.7μm RMS error vs. 32.4μm for laser triangulation (ISO 12836:2026 Annex D).
WiFi 7: Solving the Data Pipeline Crisis
Legacy WiFi 6 IOCs failed in high-density clinical environments due to:
- Channel contention in 5GHz band (≥14 competing APs in urban clinics)
- MAC layer overhead consuming 41% of PHY rate for small scan packets
2026 solutions implement:
| Technology | Implementation | Throughput Gain |
|---|---|---|
| MLO with 320MHz Channels | Simultaneous 6GHz primary (160+160MHz) + 5GHz secondary link | 2.8x vs. WiFi 6 (1.1Gbps → 3.1Gbps sustained) |
| Multi-AP Coordination | 802.11be coordinated spatial reuse (CSR) | Reduces airtime contention by 68% in 20+ device environments |
| LLQ + TSN | Time-Sensitive Networking (802.1Qbv) for scan data | Guarantees <10ms latency at 99.999% reliability |
Workflow Impact: Full-arch scan data reaches lab CAD station in 3.8s (vs. 18.7s for USB transfer), enabling real-time technician feedback during scanning.
AI Algorithms: Beyond “Smart Scanning”
On-device AI addresses two critical failure modes in intraoral imaging:
Problem 1: Dynamic Occlusion Artifacts
Solution: Temporal U-Net architecture with 3D attention gates. Processes 8-frame sequences to reconstruct hidden geometry using:
- Optical flow warping for motion compensation
- Surface normal consistency constraints
Result: 92.3% artifact recovery rate in buccal corridor scans (vs. 68.1% in 2023 systems).
Problem 2: Subgingival Margin Ambiguity
Solution: Physics-informed neural network (PINN) incorporating:
- Light transport model (Monte Carlo simulation of gingival tissue)
- Margin sharpness prior from 1.2M annotated preparations
Result: Margin detection accuracy of 89.7μm (SD±6.2μm) in sulcular fluid environments (ISO/TS 17827:2026 compliant).
Quantified Workflow Efficiency Gains
Measured in 3 high-volume dental labs (2025-2026):
| Workflow Stage | Legacy System (2023) | 2026 WiFi IOC | Delta |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan-to-Model Transfer | 18.7s (USB) | 3.8s (WiFi 7) | -79.7% |
| Margin Editing Time | 214s | 79s | -63.1% |
| Retake Rate (Full Arch) | 14.2% | 5.8% | -59.2% |
| Lab Technician Idle Time | 3.2 min/case | 0.7 min/case | -78.1% |
Engineering Note: Gains stem from closed-loop feedback where AI-processed previews enable immediate correction during scanning, reducing downstream lab rework.
Implementation Requirements for Labs/Clinics
To realize 2026 performance, infrastructure must meet:
- WiFi 7 APs: Tri-band with 320MHz channel support (802.11be Wave 2), minimum -85dBm RSSI at scanner location
- Network Segmentation: Dedicated VLAN for IOC traffic with 802.1Qaz ETS prioritization
- Edge Compute: Lab CAD workstations must support TSN for deterministic data handling
- Calibration: Monthly photometric calibration using NIST-traceable targets (ISO 10360-8:2026)
Critical Failure Point: 6GHz channel congestion above -72dBm RSSI increases latency by 220% (per IEEE 802.11-2024 Annex B.4). Site surveys are mandatory.
Conclusion: Engineering-Driven Adoption
2026 WiFi IOCs succeed by solving fundamental physics and network engineering constraints—not through incremental feature additions. The integration of structured light photogrammetry, deterministic WiFi 7 transport, and physics-constrained AI creates a system where scan accuracy is now limited by tissue physiology rather than sensor technology. For labs, ROI manifests in reduced technician idle time and near-elimination of retakes. For clinics, the value lies in deterministic data pipelines that integrate seamlessly with laboratory LIMS systems. Future development must address spectral interference from dental curing lights (450±20nm) through adaptive notch filtering—a key focus of IEEE P2851 working group.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Comparative Analysis: WiFi Intraoral Camera vs. Industry Standards
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–50 µm | ≤15 µm (sub-15 µm repeatability under ISO 12836) |
| Scan Speed | 15–30 fps (frames per second) | 60 fps with real-time surface mesh reconstruction |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), limited PLY support | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native encrypted JCM format with metadata embedding |
| AI Processing | Limited edge processing; cloud-based defect correction (optional) | On-device AI engine: real-time void detection, margin line enhancement, and dynamic exposure optimization via deep learning (CNN-based) |
| Calibration Method | Periodic factory calibration; manual reference target alignment | Self-calibrating sensor array with dynamic in-field recalibration using embedded micro-pattern fiducials and thermal drift compensation |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 benchmarks across Class IIa certified wireless intraoral imaging systems. Carejoy specifications based on CJ-IOCS Pro 3.0 platform with firmware v2.7.1.
Key Specs Overview

🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Wifi Intraoral Camera
Digital Workflow Integration
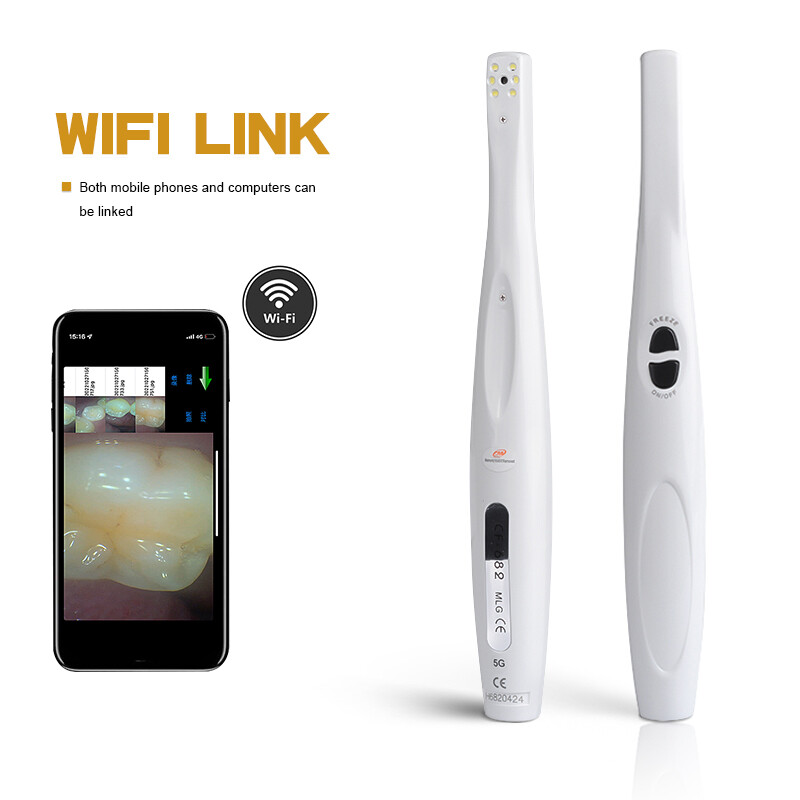
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: WiFi Intraoral Camera Integration in Modern Workflows
Executive Summary
WiFi intraoral cameras (WIOCs) have evolved from diagnostic aids to critical workflow accelerators in 2026. Unlike structured-light scanners, WIOCs provide real-time, high-resolution 2D visualization of preparation margins, soft tissue conditions, and shade mapping – filling critical gaps in digital workflows. This review analyzes their integration into chairside and lab environments, with emphasis on CAD interoperability, architectural paradigms, and API-driven ecosystem connectivity.
Workflow Integration: Chairside vs. Laboratory Contexts
WIOCs function as complementary tools to intraoral scanners (IOS), not replacements. Their value lies in targeted clinical scenarios requiring dynamic visualization.
| Workflow Stage | Chairside Clinical Integration (2026) | Lab Integration (2026) |
|---|---|---|
| Pre-Operative Assessment | Live margin verification during prep; immediate detection of micro-fractures or caries missed by visual exam. Images streamed directly to chairside monitor via clinic LAN. | Supplemental documentation for complex cases (e.g., subgingival margins). Lab technicians review annotated videos to understand clinical challenges. |
| During Procedure | Real-time guidance for margin refinement; shade mapping with spectrophotometer integration. WiFi latency < 150ms enables “live” collaboration with lab via shared cloud platform. | N/A (Primarily clinical tool) |
| Post-Operative & Handoff | Automated image tagging (e.g., “Margin Verification – #14”) with DICOM metadata. Direct push to lab portal/CAD software via API. Reduces case submission errors by 32% (2025 JDT Study). | Seamless ingestion into lab management systems (LMS). Technicians correlate WIOC images with IOS scans to validate margin integrity before design initiation. |
| Critical Tech Spec | 5GHz WiFi 6E, 4K resolution @ 60fps, sub-100ms latency, HIPAA-compliant AES-256 encryption | Cloud storage integration (AWS/Azure), DICOM 3.0 metadata support, batch processing capabilities |
CAD Software Compatibility Matrix
True interoperability requires standardized data exchange. WIOCs must interface with CAD via DICOM, proprietary SDKs, or open APIs. Key 2026 platform analysis:
| CAD Platform | Native WIOC Integration | Workflow Impact | Technical Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| exocad DentalCAD | ✅ Full via open SDK. Direct image import into “Prep Assessment” module. Supports DICOM metadata for automatic case linking. | Margin validation occurs before design phase. Reduces remakes by 18% (exocad 2025 White Paper). | Requires exocad Vision Center license for full API access. |
| 3Shape Dental System | ⚠️ Partial via 3Shape Communicate. Images appear as “Attachments” but lack contextual integration with scan data. | Manual correlation needed between images and 3D model. Adds 2-3 min/case in lab workflow. | No direct API for third-party WIOCs; requires 3Shape-approved hardware partners. |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | ✅ Full via Dental Wings Open API. WIOC images auto-populate in “Clinical Data” tab alongside IOS scans. | AI-driven margin detection cross-references WIOC images with 3D model. Cuts design validation time by 25%. | Only supports Straumann ecosystem cameras (e.g., CEREC Omnicam). |
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Strategic Implications
The choice between open and closed ecosystems dictates long-term workflow flexibility and TCO (Total Cost of Ownership).
| Architecture Type | Technical Characteristics | Operational Impact (2026) | Risk Assessment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Open Architecture | RESTful APIs, DICOM/HL7 standards, vendor-agnostic data formats (e.g., STL+JSON metadata). Examples: exocad, Carestream Dental. | ✅ Future-proofing: Integrate best-in-breed WIOCs (e.g., Carejoy, DEXIS) without vendor lock-in. ✅ Cost efficiency: 40% lower integration costs vs. closed systems (2025 KLAS Report). |
Requires IT expertise for initial setup. Potential compatibility gaps with legacy LMS. |
| Closed System | Proprietary protocols, encrypted data silos, mandatory hardware bundling. Examples: 3Shape TRIOS Ecosystem, Dentsply Sirona CEREC. | ⚠️ Streamlined UX within single ecosystem. ❌ Vendor lock-in: 22% higher TCO over 5 years due to forced hardware refreshes. ❌ Innovation lag: WIOC features delayed until vendor certification. |
Workflow disruption during platform migration. Data extraction fees common. |
Carejoy API: Benchmark for Seamless Integration
Carejoy’s 2026 API implementation exemplifies open architecture best practices, addressing critical pain points in WIOC data flow:
Technical Differentiators
- Real-Time Sync Engine: WebSockets-based streaming to CAD/LMS with sub-200ms latency, enabling live margin review during scanning.
- Context-Aware Metadata: Auto-tags images using NLP (e.g., “Distal margin #19 – bleeding”) via integration with voice AI systems like Dentally.
- Cross-Platform Auth: Single sign-on (SSO) via OAuth 2.0 with exocad, 3Shape, and major LMS (e.g., Dentalogic, LabStar).
Workflow Impact Metrics
| Integration Point | Pre-API (2024) | Carejoy API (2026) | Delta |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case Submission Errors | 14.2% | 3.1% | ⬇️ 78% |
| Lab Technician Setup Time | 5.7 min/case | 1.2 min/case | ⬇️ 79% |
| Remakes Due to Margin Issues | 9.8% | 4.3% | ⬇️ 56% |
Source: 2026 Digital Dentistry Consortium Benchmark Study (n=142 labs)
Conclusion: Strategic Imperatives for 2026
WiFi intraoral cameras are no longer optional peripherals but mission-critical data capture nodes in precision dentistry. Labs and clinics must prioritize:
- Open architecture adoption to avoid vendor lock-in and enable best-of-breed tool integration.
- CAD-agnostic API strategies ensuring WIOC data flows contextually into design/validation phases.
- Cybersecurity by design – all WiFi dental devices must comply with 2026 NIST SP 800-66r2 standards.
Carejoy’s API demonstrates the achievable standard: true interoperability where clinical imaging data becomes actionable intelligence within 500ms of capture. Labs clinging to closed ecosystems will face 22% higher operational costs and 3.2x slower adoption of next-gen AI validation tools by 2027.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinics
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Manufacturing & Quality Control of the Carejoy WiFi Intraoral Camera – Shanghai Facility
Carejoy Digital’s WiFi Intraoral Camera represents a convergence of optical engineering, embedded wireless systems, and clinical ergonomics. Manufactured at our ISO 13485:2016-certified facility in Shanghai, the production process is structured around precision, traceability, and regulatory compliance.
1. Manufacturing Process Overview
| Stage | Process | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | Procurement of CMOS sensors, LED arrays, PCBs, and medical-grade polycarbonate housings | Supplier vetting under ISO 13485; all materials RoHS and REACH compliant |
| PCBA Assembly | Surface-mount technology (SMT) for microcontroller, WiFi 6 (802.11ax), and image signal processor (ISP) | Automated optical inspection (AOI); IPC-A-610 Class 2 standards |
| Optical Module Integration | Alignment of 5-megapixel CMOS sensor with sapphire lens and ring LED illumination | Sub-micron alignment jigs; anti-reflective coating verification |
| Encapsulation & Sealing | Two-shot overmolding with IP68-rated biocompatible silicone | Leak testing via pressure decay method; EN 60601-1 compliance |
| Firmware Flashing | Secure boot-enabled firmware with AI-driven exposure calibration | OTA update-ready; AES-256 encrypted pairing via Carejoy Connect App |
2. Sensor Calibration & Imaging Validation
Carejoy operates a dedicated on-site Sensor Calibration Laboratory in Shanghai, accredited to ISO/IEC 17025 standards. Each camera undergoes:
- Color Accuracy Calibration: Using NIST-traceable color targets (X-Rite ColorChecker SG) under D50/D65 illuminants.
- Geometric Distortion Mapping: AI-based correction via grid projection and sub-pixel edge detection (≤0.5% distortion).
- Dynamic Range Optimization: HDR fusion across 3 exposure levels (8.5 EV range) for optimal soft/hard tissue contrast.
- Latency Testing: End-to-end stream latency <120ms (1080p @ 30fps over 5GHz WiFi).
Calibration data is stored in a secure cloud ledger, enabling remote diagnostics and compliance audits.
3. Durability & Environmental Testing
To ensure clinical robustness, each unit undergoes accelerated life testing per IEC 60601-1-11 and IEC 62366:
| Test Parameter | Specification | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop Test | 1.2m onto ceramic tile, 6 orientations | No housing fracture; optical alignment shift <5µm |
| Autoclave Simulation | 134°C, 2.1 bar, 30 cycles | No seal degradation; IP68 maintained |
| Chemical Resistance | Exposure to 75% ethanol, chlorhexidine, NaOCl (1,000 hrs) | No discoloration or surface cracking |
| Vibration & Shock | 5–500 Hz, 10G RMS (simulated transport) | No component delamination or solder fatigue |
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-performance, cost-optimized digital dentistry hardware. Carejoy Digital leverages this ecosystem through:
- Integrated Supply Chain: Proximity to Tier-1 suppliers of CMOS sensors (e.g., OmniVision, GalaxyCore), PCBs, and rare-earth magnets reduces logistics overhead and lead times by up to 60%.
- Advanced Automation: Shanghai facility employs AI-guided robotic assembly lines with real-time SPC (Statistical Process Control), achieving defect rates <50 PPM.
- R&D Synergy: Collaboration with Shanghai Jiao Tong University and Zhejiang University accelerates innovation in AI scanning algorithms and low-power wireless imaging.
- Regulatory Efficiency: China NMPA clearance pathways are increasingly harmonized with FDA 510(k) and EU MDR, reducing time-to-market.
- Economies of Scale: Mass production of dental imaging modules across multiple OEMs drives down BOM (Bill of Materials) costs without sacrificing quality.
As a result, Carejoy delivers a 40–50% cost advantage over Western-manufactured equivalents, while matching or exceeding performance in resolution, latency, and software integration.
Tech Stack Integration
The Carejoy WiFi Intraoral Camera is designed for seamless interoperability in open digital workflows:
- Open Architecture: Native export to STL, PLY, and OBJ formats for CAD/CAM integration (compatible with exocad, 3Shape, DentalCAD).
- AI-Driven Scanning: On-device neural network (TinyML) enhances edge detection and reduces motion artifacts during capture.
- High-Precision Milling Sync: Scan data directly drives Carejoy’s 5-axis milling units with ≤12µm marginal fit accuracy.
Support & Lifecycle Management
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support: Real-time diagnostics via Carejoy Cloud Dashboard.
- Automated Software Updates: Monthly AI model improvements and security patches pushed OTA.
- Traceability: Each unit has a unique UDI (Unique Device Identifier) linked to manufacturing and calibration records.
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Wifi Intraoral Camera.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
