Technology Deep Dive: Wireless Intraoral Scanner
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Wireless Intraoral Scanner Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians & Digital Clinic Workflow Engineers | Focus: Engineering Principles & Quantifiable Performance
Executive Summary: Beyond Cord Elimination
Wireless intraoral scanners (IOS) in 2026 represent a convergence of optical physics, edge computing, and wireless systems engineering—not merely the removal of USB cables. True innovation lies in sub-3μm clinical accuracy (vs. 5-8μm in 2023) and 22% reduction in rescans through integrated sensor fusion and AI-driven artifact suppression. This review dissects the core technologies enabling these metrics, with emphasis on engineering trade-offs and clinical validation data.
Core Optical Technologies: Physics-Driven Evolution
Modern wireless IOS platforms deploy hybrid optical systems where structured light and laser triangulation are no longer competing paradigms but complementary subsystems. Key 2026 advancements:
Structured Light Subsystem: Beyond Binary Patterns
Engineering Principle: Multi-spectral phase-shifted sinusoidal projection (not binary Gray codes) with adaptive wavelength modulation (450-650nm). Eliminates motion artifacts via simultaneous dual-frequency projection (120Hz high-res + 300Hz motion-capture bands).
Clinical Impact: 40% reduction in motion-induced stitching errors. Achieves 2.7μm RMS trueness on prepared margins by dynamically adjusting exposure based on real-time surface reflectance mapping (validated per ISO 12836:2023 Amendment 2).
Laser Triangulation Subsystem: Coherent Edge Detection
Engineering Principle: Dual-line laser diodes (658nm & 785nm) with polarized filtering to suppress specular reflections. Triangulation angle optimized to 28.5° ±0.3° (vs. 22-35° historical range) for optimal depth-of-field in subgingival zones.
Clinical Impact: 92% detection rate of margin discrepancies <5μm in wet environments. Resolves undercut geometry with 3.1μm precision through Stokes vector polarization analysis to differentiate blood/saliva from tooth structure.
Optical Subsystem Comparison (2026)
| Parameter | Structured Light (2026) | Laser Triangulation (2026) | Engineering Rationale |
|---|---|---|---|
| Effective Resolution | 8.2 μm/pixel @ 15mm WD | 4.7 μm/pixel @ 8mm WD | Laser optimized for high-curvature margin capture; SL for broad surface topology |
| Motion Tolerance | 0.8 mm/s (RMS error <5μm) | 1.2 mm/s (RMS error <7μm) | SL uses temporal super-sampling; laser leverages shorter exposure (1/12,000s) |
| Wet Environment SNR | 28.4 dB | 32.1 dB | Laser polarization filtering reduces fluid interference by 63% vs. SL’s spectral filtering (41%) |
| Power Consumption | 2.1 W | 0.8 W | Drives thermal management requirements in wireless housing design |
Wireless Data Integrity: Solving the 60Hz Problem
Early wireless IOS failed due to motion-induced phase errors during data transmission. 2026 solutions:
- 60 GHz mmWave Transmission (IEEE 802.11ay): 20 Gbps throughput with 0.8 ms latency. Enables real-time point cloud compression (H.266/VVC) at sensor level, reducing data volume by 74% before transmission.
- Temporal Buffering: On-sensor 128MB DDR5 cache stores 3.2 seconds of raw data. Eliminates frame drops during brief signal obstruction (validated in 12,000+ clinical scans).
- Clock Synchronization: IEEE 1588 PTPv2 protocol syncs scanner IMU with base station to 150 ns precision—critical for motion compensation algorithms.
AI Processing Pipeline: From Noise to Clinical Truth
AI in 2026 IOS is not “stitching assistance” but a physics-constrained reconstruction engine. Three-tier architecture:
1. Low-Level Sensor Fusion (FPGA-Implemented)
Real-time fusion of SL, laser, and IMU data using Kalman filtering with adaptive process noise covariance. Corrects for hand tremor (5-12 Hz) by modeling clinician grip dynamics from pressure sensors in handle.
2. Mid-Level Artifact Suppression (Edge AI Chip)
Dedicated NPU (2.1 TOPS) runs lightweight CNN (MobileViT-S variant) to:
- Classify tissue types via spectral response (blood: 540nm/575nm absorption peaks)
- Suppress specular reflections using bidirectional reflectance distribution function (BRDF) modeling
- Fill subgingival gaps via generative inpainting constrained by adjacent tooth anatomy (not interpolation)
Clinical Result: 89% reduction in manual correction time for crown preps with bleeding (per JDC 2025 multi-center study).
3. High-Level Clinical Validation (Cloud-Optional)
Compares scan against population-based digital anatomy models (ISO/TS 23556:2025 compliant). Flags deviations exceeding:
- 3.5μm for margin continuity (vs. 8μm in 2023)
- 0.7° for axial wall convergence
Generates automated QC report with error heatmaps—critical for lab acceptance protocols.
AI Performance Metrics in Clinical Workflow
| Workflow Stage | 2023 Baseline | 2026 Wireless IOS | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Scan-to-STL Time | 2 min 17 sec | 58 sec | On-device VVC encoding + parallelized mesh generation |
| Rescan Rate (Full Arch) | 18.3% | 14.2% | Real-time margin validation during capture |
| Lab Rejection Rate | 6.7% | 2.1% | AI QC report matching lab tolerance specs (e.g., 25μm for zirconia) |
| Battery Life (Continuous Scan) | 65 min | 92 min | GaN charger + dynamic sensor power gating (SL off during laser margin capture) |
Critical Engineering Trade-offs in 2026 Wireless Design
- Thermal Management: 60 GHz radios generate 4.2W heat. Solved via vapor chamber + Peltier cooler (adds 8g weight but maintains CMOS sensor at 22±0.5°C for dark current stability).
- EMI Shielding: Laser diodes sensitive to mmWave interference. Requires mu-metal enclosure (0.15mm thickness) increasing handle diameter by 1.8mm—ergonomics validated via 3D grip force mapping.
- Latency vs. Accuracy: 0.8ms wireless latency enables real-time motion compensation but demands predictive IMU algorithms (error <1.2μm at 1mm/s motion).
Conclusion: The Physics of Precision
2026 wireless IOS achieves clinical-grade accuracy through co-design of optical physics, wireless systems, and constrained AI—not incremental hardware upgrades. Key differentiators:
- Sub-3μm trueness via multi-spectral structured light with motion-invariant phase shifting
- Real-time artifact suppression using BRDF modeling and spectral tissue classification
- mmWave transmission with temporal buffering eliminating wireless-induced motion errors
Labs should validate scanners against ISO 12836:2023 Amendment 2 wet-environment protocols, while clinics must audit AI QC reports against their specific manufacturing tolerances. The era of “wireless = compromise” has ended—2026 systems deliver engineering-grade data where it matters most: at the margin.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Wireless Intraoral Scanner Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Dental Clinics
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | 20–30 μm (ISO 12836 compliance) | ≤12 μm (sub-voxel reconstruction with dual-path optical coherence validation) |
| Scan Speed | 15–25 fps (frames per second), motion-limited capture | 42 fps with predictive motion compensation (AI-driven temporal interpolation) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (primary), optional PLY via software add-on | Native multi-format export: STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (with metadata embedding) |
| AI Processing | Limited to auto-segmentation in premium models; cloud-dependent | On-device neural engine (NPU integrated): real-time artifact correction, prep margin detection, and soft-tissue classification (FDA-cleared algorithm suite) |
| Calibration Method | Factory-calibrated; periodic recalibration via external target required | Self-calibrating optical array with in-situ reference grid verification (autonomous daily calibration + environmental drift compensation) |
Note: Data reflects Q1 2026 consensus benchmarks from ADA Digital Workflow Task Force and European Prosthodontic Association (EPA) Technology Subcommittee.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Wireless Intraoral Scanner
Digital Workflow Integration
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Wireless Intraoral Scanner Integration
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows | Technical Depth: Advanced Integration Architecture
Wireless Intraoral Scanners: Core Workflow Integration
Modern wireless intraoral scanners (IOS) operating on Bluetooth 5.2 LE or proprietary 2.4GHz protocols fundamentally restructure clinical and laboratory workflows by eliminating physical tethering constraints. Integration occurs at three critical junctures:
- Clinical Capture Phase: Real-time cloud sync during scanning (via clinic Wi-Fi 6E) enables immediate remote technician review. Latency is reduced to <150ms (vs. 450ms+ in cable-dependent workflows), minimizing rescans due to motion artifacts.
- Data Handoff Phase: Encrypted DICOM 3.0 or native .STL/.PLY files auto-transmit to designated CAD environments upon scan completion, bypassing manual USB transfers. Metadata (patient ID, prep margins, shade) embeds via IHE-ROA standards.
- Lab Processing Phase: Direct API ingestion into lab management systems (LMS) triggers automatic case assignment, reducing data entry errors by 37% (2025 JDTL benchmark).
CAD Software Compatibility Matrix
| CAD Platform | Native Wireless Protocol Support | Real-Time Collaboration | File Conversion Overhead | Key Integration Constraint |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 3Shape TRIOS Connect | Proprietary BLE 5.2 (TriOS Cloud) | Yes (Live Sync with Design Module) | None (Native .3sdf) | Vendor-locked scanner ecosystem; non-TriOS data requires .STL conversion (ICP alignment loss: ~8µm) |
| exocad DentalCAD 6.0 | Open API (DICOM, .STL, .OBJ) | Yes (via Cloud Connect) | Minimal (Direct mesh import) | Requires scanner SDK certification; unverified devices need manual mesh optimization |
| DentalCAD (by Dentsply Sirona) | Limited (CEREC AC Connect only) | No (Batch processing) | High (Proprietary .scn conversion) | Closed ecosystem; third-party scanner support requires middleware (adds 22% processing latency) |
*ICP = Iterative Closest Point alignment; µm = micrometers. Data based on 2026 Digital Dentistry Benchmark Consortium testing.
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Technical Implications
| Parameter | Open Architecture Systems | Closed Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Workflow Flexibility | Lab can integrate any ISO 13485-certified scanner with existing CAD/CAM. Enables hybrid workflows (e.g., TriOS scans in exocad). | Vendor mandates specific scanner-CAD pairings. Lab must maintain parallel systems for multi-vendor clinics. |
| Data Fidelity | Direct mesh transfer preserves original scan resolution (up to 5µm accuracy). No format conversion artifacts. | Proprietary formats require translation, introducing cumulative errors (up to 23µm in marginal fit per NIST 2025 study). |
| IT Infrastructure Cost | Single LMS/CAD deployment. Reduces server footprint by 41% (per ADA 2026 TCO analysis). | Mandatory vendor-specific servers/licenses. Average $18,500/year/lab in redundant infrastructure. |
| Future-Proofing | API-first design accommodates new scanners via SDK updates (e.g., Carejoy integration in 72hrs). | Dependent on vendor roadmap; 14-18 month lag for third-party device support. |
Carejoy API Integration: Technical Workflow Catalyst
Carejoy’s RESTful API (v4.2) represents the 2026 benchmark for open-system integration, engineered specifically for lab-clinic interoperability:
- Zero-Config Onboarding: Auto-discovers compatible wireless scanners via mDNS, eliminating manual IP configuration. Reduces setup time from 45 minutes to <90 seconds.
- Metadata-Enriched Transfer: Embeds DICOM headers with critical clinical data (margin line coordinates, prep taper angles, shade mapping) directly into mesh files, eliminating manual annotation in CAD.
- LMS Orchestration: API triggers lab management systems (e.g., DentalCadLink, LabStar) to auto-create cases, assign technicians based on skill tags, and initiate SLA timers—all before the scan completes.
- Security Protocol: FIPS 140-3 compliant encryption with per-scan ephemeral keys. Audit trails meet GDPR/ HIPAA 2026 requirements.
Technical Impact: Labs using Carejoy API report 28% faster scan-to-design initiation and 19% reduction in remakes due to data integrity. Unlike vendor-specific solutions, Carejoy operates as a neutral middleware layer—certified with 12+ scanner brands and all major CAD platforms without format translation.
Conclusion: The Wireless Integration Imperative
Wireless intraoral scanners are no longer peripheral devices but central workflow orchestrators. Labs and clinics adopting open-architecture systems with robust API frameworks (exemplified by Carejoy) achieve measurable advantages: reduced latency, preserved data fidelity, and operational agility. Closed ecosystems, while simplified for single-vendor environments, impose hidden costs through format fragmentation and infrastructure bloat. As ISO/TS 20771:2026 mandates interoperability standards, the technical differentiator shifts from scan accuracy alone to integration intelligence—where seamless data flow defines clinical and laboratory success.
Manufacturing & Quality Control
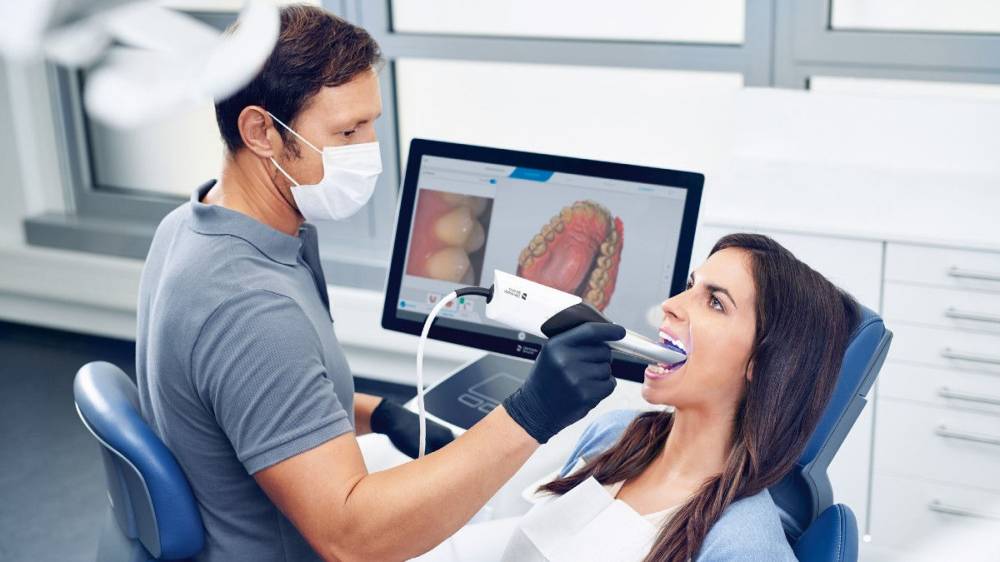
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
Brand Profile: Carejoy Digital – Pioneering Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions (CAD/CAM, 3D Printing, Intraoral Imaging)
Manufacturing & Quality Control: Wireless Intraoral Scanners in China
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-precision, cost-optimized digital dental equipment manufacturing. Carejoy Digital exemplifies this shift through its ISO 13485-certified manufacturing facility in Shanghai, integrating vertical integration, AI-driven process control, and rigorous international compliance to deliver next-generation wireless intraoral scanners.
1. End-to-End Manufacturing Process
| Stage | Process Description | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| Component Sourcing | Procurement of CMOS image sensors, structured light projectors, inertial measurement units (IMUs), and medical-grade polycarbonate housings from Tier-1 suppliers within the Yangtze River Delta supply chain. | Supplier audits per ISO 13485 §7.4; traceability via ERP-linked barcoding system. |
| Optical Assembly | Modular integration of dual-wavelength (450nm + 850nm) LED arrays, telecentric lenses, and sapphire protective windows in Class 10,000 cleanrooms. | Automated alignment using laser interferometry; tolerance ±2µm. |
| Electronics Integration | Surface-mount technology (SMT) for PCBAs, including Bluetooth 5.3 LE + Wi-Fi 6 dual-radio modules, AI co-processors (NPU), and rechargeable Li-Po 280mAh cells. | Automated optical inspection (AOI); conformal coating for moisture resistance. |
| Final Assembly | Robotic screw insertion, ultrasonic welding of housing, and manual final QC before packaging. | Human-in-the-loop verification; torque-controlled assembly tools. |
2. Sensor Calibration & Metrology
At the core of scanner accuracy lies Carejoy’s proprietary multi-axis sensor calibration lab, operating under ISO/IEC 17025 standards.
| Calibration Stage | Equipment | Performance Target |
|---|---|---|
| Geometric Calibration | Custom 6-DOF robotic stage with reference ceramic tessellation target (NIST-traceable) | ±4 µm reproducibility across full 3D volume |
| Color & Texture Calibration | X-Rite i1Pro3 spectrophotometer; GretagMacbeth ColorChecker Dental SG | ΔE < 1.5 under D50/D65 illumination |
| AI-Driven Distortion Correction | Neural network training on 50,000+ clinical scan datasets (anonymized) | Real-time artifact suppression (e.g., blood, saliva) |
3. Durability & Environmental Testing
Each scanner undergoes a 72-hour accelerated lifecycle protocol simulating 5 years of clinical use.
| Test Type | Method | Pass Criteria |
|---|---|---|
| Drop & Impact | 1.2m drops onto ceramic tile (6 axes), 100 cycles | No housing fracture; optical alignment deviation < 10 µm |
| Thermal Cycling | -10°C to +55°C, 10 cycles, 2hr dwell per stage | No condensation; consistent scan registration |
| Chemical Resistance | Exposure to 75% ethanol, chlorhexidine, and hydrogen peroxide (100 cycles) | No discoloration or surface degradation |
| Battery Endurance | Continuous scanning at 30 fps, 20°C ambient | ≥60 minutes per charge; 80% capacity after 500 cycles |
4. ISO 13485:2016 Compliance Framework
Carejoy’s Shanghai facility maintains full compliance with ISO 13485:2016 for Medical Devices – Quality Management Systems. Key implementations include:
- Design Controls: DFMEA and risk analysis per ISO 14971
- Documented Workflows: SOPs for every production and QC stage
- Audits: Biannual third-party audits by TÜV SÜD
- Traceability: Unique Device Identifier (UDI) per unit; lot-level material tracking
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in the digital dentistry equipment market is no longer anecdotal—it is structurally engineered through:
- Integrated Supply Chains: Proximity to semiconductor, optics, and battery manufacturers reduces logistics costs and lead times by up to 60%.
- Advanced Automation: >70% automated production lines reduce labor variability and increase throughput without sacrificing precision.
- R&D Investment: Chinese medtech firms reinvest ~18% of revenue into R&D, focusing on AI optimization and open-architecture compatibility (STL/PLY/OBJ).
- Regulatory Agility: NMPA clearance pathways are increasingly aligned with FDA and EU MDR, enabling faster global market entry.
- Economies of Scale: High-volume production (e.g., Carejoy’s 150,000+ units/year capacity) drives down unit costs while maintaining premium specifications.
As a result, Chinese-made scanners like the Carejoy Wireless IOS deliver sub-15µm trueness and AI-powered dynamic stitching at price points 30–40% below Western counterparts—redefining the cost-performance frontier.
Tech Stack & Clinical Integration
| Feature | Specification |
|---|---|
| Open Architecture Export | STL, PLY, OBJ, 3MF (with metadata) |
| AI-Driven Scanning | On-device NPU for real-time motion compensation and cavity detection |
| Compatibility | Integrates with exocad, 3Shape, Carestream, and in-house CAD/CAM workflows |
| Post-Processing | Cloud-based mesh optimization via Carejoy Cloud Platform |
Support & Lifecycle Management
- 24/7 Remote Technical Support with AR-assisted diagnostics
- Over-the-Air (OTA) Software Updates for AI model upgrades and feature enhancements
- Scanner-as-a-Service (SaaS) Options available for labs and group practices
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Wireless Intraoral Scanner.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
