Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for all on x dental implants
In the rapidly evolving landscape of restorative dentistry, All-on-X dental implants have emerged as a transformative solution for patients facing complete tooth loss or extensive dental challenges. These implants offer a permanent, stable foundation for a full arch of prosthetic teeth, significantly improving oral function, aesthetic appearance, and overall quality of life. For B2B buyers, especially in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including key markets like Turkey and Thailand—understanding the nuances of All-on-X dental implants is critical to making informed procurement decisions.
This guide serves as a comprehensive resource, detailing the various types of All-on-X implants, materials used in their construction, manufacturing standards, and quality control measures. Additionally, it delves into the landscape of suppliers and pricing structures, providing insights into market trends that can influence sourcing strategies. The inclusion of frequently asked questions will further empower buyers to navigate the complexities of this innovative dental solution.
By equipping international B2B buyers with actionable insights, this guide aims to streamline the decision-making process, ensuring that dental practices can offer cutting-edge solutions to their patients. Ultimately, understanding the All-on-X implant market is not just about procurement; it’s about enhancing patient care and building trust in restorative dentistry solutions.
Understanding all on x dental implants Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| All-on-4 Implants | Utilizes four implants placed at strategic angles, often avoiding bone grafting. | Ideal for practices focusing on efficiency. | Pros: Fewer implants reduce costs; Cons: Not suitable for all bone types. |
| All-on-6 Implants | Involves six implants for enhanced stability, often recommended for patients with bone loss. | Suitable for advanced practices with complex cases. | Pros: Greater stability; Cons: Higher costs and surgical time. |
| Immediate Load Implants | Allows for immediate placement of a prosthetic after implant insertion. | Attracts clients seeking quick solutions. | Pros: Instant results; Cons: Higher risk of complications. |
| Hybrid Dentures | Combines features of fixed and removable prosthetics, offering flexibility in care. | Versatile solution for varied patient needs. | Pros: Easier maintenance; Cons: Less stability than fixed options. |
| Mini Dental Implants | Smaller diameter implants used in less dense bone or for temporary solutions. | Cost-effective for budget-conscious practices. | Pros: Less invasive; Cons: Limited long-term durability. |
All-on-4 Implants
All-on-4 implants are designed for patients with limited bone density. By utilizing four strategically angled implants, this method maximizes available bone support, often eliminating the need for bone grafting. For B2B buyers, especially dental practices in regions with varying patient demographics, this option provides a reliable solution for patients who may have previously been considered unsuitable for standard implants. It is essential to evaluate the practice’s ability to offer this treatment efficiently, as it can significantly enhance patient satisfaction and retention.
All-on-6 Implants
All-on-6 implants provide an alternative for patients requiring additional support due to bone loss or other anatomical considerations. With six implants, this system offers enhanced stability and is particularly beneficial for practices dealing with complex cases. B2B buyers should consider the implications of increased surgical time and costs associated with this option, as well as the potential for improved patient outcomes, which can lead to higher patient referrals and practice growth.
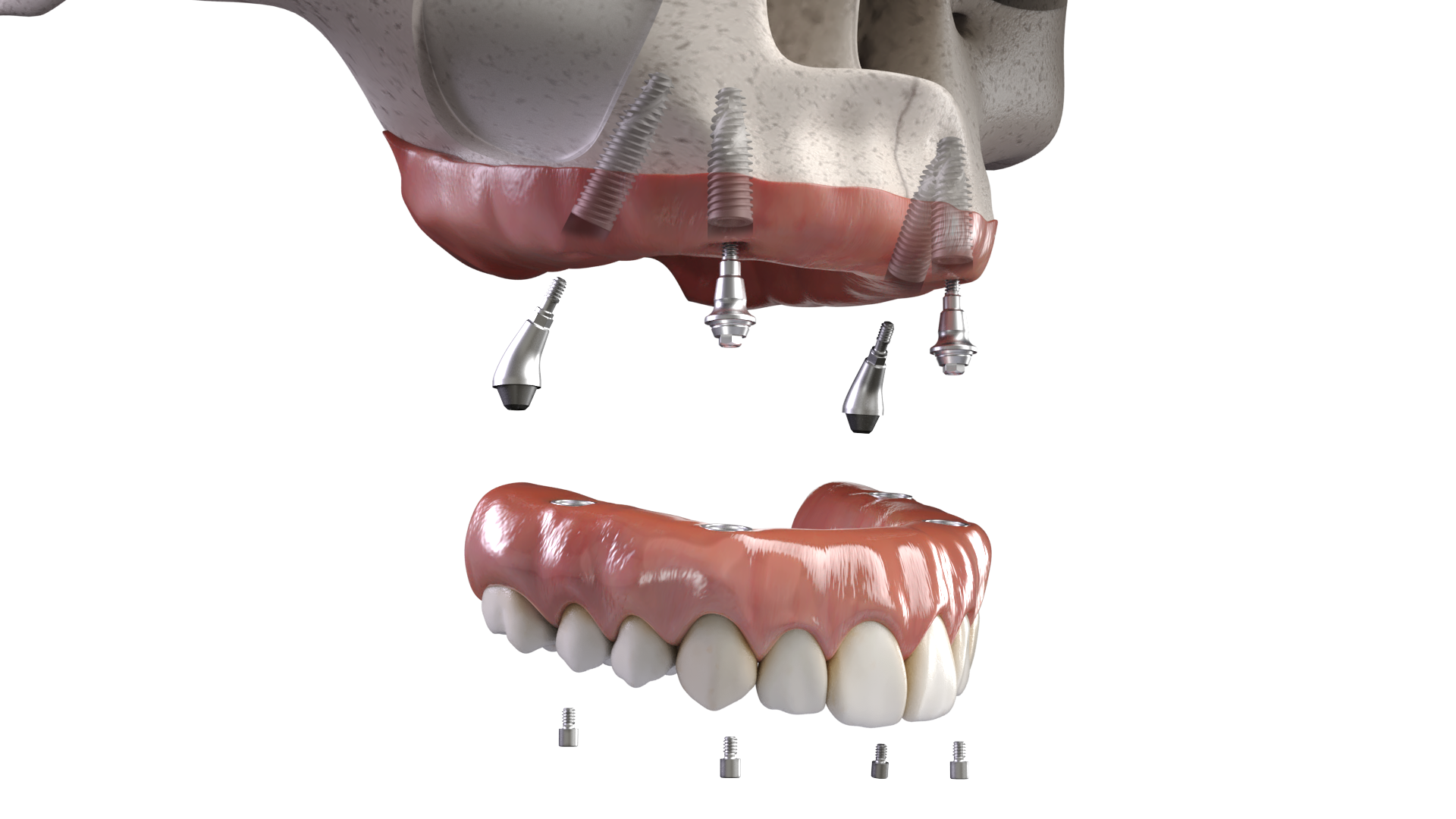
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Immediate Load Implants
Immediate load implants allow for the placement of a prosthetic tooth immediately after the implant surgery, catering to patients who desire quick results. This option is particularly appealing for dental practices looking to attract clients seeking rapid solutions. However, B2B buyers must weigh the benefits against the increased risk of complications and the need for diligent post-operative care. Ensuring that the dental team is well-trained in this technique is crucial for maintaining high standards of patient care.
Hybrid Dentures
Hybrid dentures combine the benefits of fixed and removable prosthetics, providing flexibility for both patients and dental practices. This type of implant system can be particularly advantageous for practices that cater to a diverse patient base with varying needs. B2B buyers should consider the maintenance requirements and patient education necessary for hybrid dentures, as these factors can affect long-term satisfaction and repeat business.
Mini Dental Implants
Mini dental implants offer a less invasive solution for patients with limited bone density or those seeking temporary options. These smaller implants can be a cost-effective alternative for budget-conscious practices. However, B2B buyers should be aware of the limitations in durability and long-term success associated with mini implants. Proper patient selection and follow-up care are vital to ensuring satisfactory outcomes and minimizing complications.
Related Video: All on 4 Dental Implants Explained
Key Industrial Applications of all on x dental implants
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of all on x dental implants | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dental Clinics | Full-arch restoration for patients with multiple missing teeth | Enhanced patient satisfaction and retention, increased revenue through comprehensive care | Quality of implants, training for staff, regulatory compliance |
| Hospitals | Treatment for edentulous patients in surgical departments | Streamlined patient care, reduced hospitalization time, improved surgical outcomes | Supplier reliability, implant technology, post-operative support |
| Dental Laboratories | Manufacturing of custom prosthetic arches for all-on-X implants | Increased efficiency in prosthetic production, ability to cater to diverse patient needs | Material quality, technological compatibility, production timelines |
| Health Insurance Providers | Coverage for all-on-X procedures in dental plans | Attracting more clients by offering comprehensive dental solutions, reduced long-term costs | Understanding of local regulations, partnerships with dental providers |
| Dental Education Institutions | Training programs on all-on-X implant procedures | Enhances educational offerings, attracts more students, promotes advanced dentistry | Curriculum development, partnerships with implant manufacturers, access to cadaver labs |
Dental Clinics
In dental clinics, all-on-X dental implants are frequently used for full-arch restorations, especially for patients who have lost multiple teeth. This treatment not only improves patients’ quality of life but also enhances clinic revenue through comprehensive care offerings. For international buyers, sourcing high-quality implants and ensuring staff are adequately trained in the procedure are critical considerations. Additionally, understanding local regulations regarding implant procedures is essential to ensure compliance.
Hospitals
Hospitals utilize all-on-X implants in surgical departments to treat edentulous patients, providing a permanent solution that can significantly reduce hospitalization time. This approach improves surgical outcomes and leads to higher patient satisfaction. For B2B buyers in this sector, it is vital to consider the reliability of suppliers and the technological advancements in implant systems. Moreover, post-operative support is crucial to ensure patient safety and satisfaction.
Dental Laboratories
Dental laboratories play a pivotal role in the production of custom prosthetic arches for all-on-X implants. This application allows labs to increase production efficiency and cater to a wider range of patient needs. For businesses in this field, sourcing high-quality materials and ensuring compatibility with various implant technologies are essential. Additionally, maintaining quick production timelines can set a laboratory apart in a competitive market.
Health Insurance Providers
Health insurance providers can benefit from offering coverage for all-on-X procedures as part of their dental plans. This not only attracts more clients but also helps reduce long-term costs associated with ongoing dental issues. For international B2B buyers, understanding local regulations and forming partnerships with dental providers can facilitate smoother integration of these procedures into health plans, ultimately enhancing service offerings.
Dental Education Institutions
Dental education institutions are increasingly incorporating all-on-X implant training into their curricula. This application enhances their educational offerings, attracts more students, and promotes advanced dentistry practices. For institutions, it is important to develop robust training programs in collaboration with implant manufacturers, ensuring access to the latest technologies and techniques. Access to cadaver labs for hands-on training is also a significant consideration for effective learning.
Related Video: Step by Step All-On-4 Dental Implants Surgery with Endosteal Implants Placement
Strategic Material Selection Guide for all on x dental implants
When selecting materials for all-on-X dental implants, it is crucial to consider several factors that impact performance, durability, and patient satisfaction. The materials used must withstand the rigors of oral environments while ensuring biocompatibility and aesthetic appeal. Here, we analyze four common materials used in all-on-X dental implants, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and considerations for international B2B buyers.
Titanium
Key Properties: Titanium is renowned for its exceptional strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. It can withstand the pressures of chewing and is stable in the moist environment of the mouth.
Pros & Cons: Titanium implants are highly durable and have a long track record of success in dental applications. However, they can be relatively expensive compared to other materials, and the manufacturing process can be complex due to the need for precision in implant design.
Impact on Application: Titanium’s corrosion resistance makes it suitable for long-term use in the mouth, where it is exposed to various pH levels and temperatures. Its compatibility with bone allows for osseointegration, providing a solid foundation for prosthetic teeth.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM F136 for titanium alloys. Regions like Europe have stringent regulations regarding medical devices, necessitating thorough documentation and certifications.
Zirconia
Key Properties: Zirconia is a ceramic material that offers excellent aesthetic qualities due to its tooth-like color. It is also known for its strength and resistance to wear.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of zirconia is its aesthetic appeal, making it ideal for visible areas. However, it is less flexible than titanium and may be more prone to fracture under extreme stress, which could limit its use in certain applications.
Impact on Application: Zirconia is particularly well-suited for patients who prioritize aesthetics, as it can mimic the appearance of natural teeth. However, its brittleness may restrict its use in cases requiring high mechanical strength.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the differences in regulatory approval processes for ceramic materials in various regions. Compliance with standards such as ISO 6872 for dental ceramics is essential, especially in markets like Europe.
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone)
Key Properties: PEEK is a high-performance polymer known for its excellent mechanical properties and biocompatibility. It is lightweight and resistant to chemical degradation.
Pros & Cons: PEEK offers a cost-effective alternative to metal implants and is easier to manufacture. However, its lower strength compared to titanium may limit its application in load-bearing situations.
Impact on Application: PEEK’s flexibility and shock-absorbing properties can provide comfort for patients, making it suitable for certain types of dental restorations. However, it may not be ideal for all-on-X applications where high strength is required.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should consider the varying acceptance of polymer-based implants in different markets. Compliance with standards like ASTM F2026 for PEEK is necessary, especially in regions with strict medical device regulations.
Cobalt-Chromium Alloys
Key Properties: Cobalt-chromium alloys are known for their high strength and resistance to wear and corrosion. They are often used in dental applications for their durability.
Pros & Cons: These alloys provide excellent mechanical properties and are less expensive than titanium. However, they can be heavier and may not offer the same level of biocompatibility as titanium or zirconia.
Impact on Application: Cobalt-chromium alloys are suitable for frameworks in dental prosthetics, providing a robust foundation. However, their aesthetic limitations may make them less desirable for visible areas.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ASTM F75 for cobalt-chromium alloys is essential. Buyers should also consider the varying perceptions of metal allergies in different regions, particularly in Europe and North America.
| Material | Typical Use Case for all on x dental implants | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium | Primary material for implant posts | Excellent strength and biocompatibility | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Zirconia | Aesthetic restorations | Superior aesthetics | Prone to fracture under stress | Med |
| PEEK | Alternative for certain implant designs | Lightweight and cost-effective | Lower strength compared to metals | Low |
| Cobalt-Chromium Alloys | Frameworks for dental prosthetics | High strength and durability | Less aesthetic appeal and heavier | Med |
This strategic material selection guide aims to assist international B2B buyers in making informed decisions regarding all-on-X dental implants, emphasizing the importance of material properties and regional compliance requirements.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for all on x dental implants
All-on-X dental implants represent a significant advancement in restorative dentistry, offering patients a permanent solution for multiple missing teeth. For international B2B buyers, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance practices associated with these implants is critical for ensuring product reliability and compliance with international standards. This section delves into the typical manufacturing processes, quality control measures, and how buyers can verify the quality of suppliers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Manufacturing Processes for All-on-X Dental Implants
The manufacturing of All-on-X dental implants involves several key stages, each designed to ensure the highest quality and reliability of the final product.
1. Material Preparation
The initial stage involves sourcing high-quality materials, primarily titanium and zirconia, known for their biocompatibility and strength. Manufacturers often utilize:
- Titanium Alloys: These are commonly used due to their excellent mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
- Zirconia: An alternative material that offers aesthetic benefits, especially for visible parts of the dental prosthesis.
Before use, materials undergo rigorous testing to confirm their purity and mechanical properties. The preparation phase may also include surface treatments to enhance osseointegration, which is the process of bone fusing to the implant.
2. Forming
The forming stage is crucial as it shapes the implants into their final configuration. Techniques include:
- CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines precisely cut and shape the implants from titanium bars or blocks, ensuring high dimensional accuracy.
- Additive Manufacturing: Also known as 3D printing, this innovative method allows for the creation of complex geometries that can enhance the implant’s integration with bone.
Both techniques require stringent controls to maintain tolerances specified in design documents.
3. Assembly
Once individual components are formed, they are assembled. This stage may involve:
- Screw Placement: For multi-part implants, screws are inserted to secure components together.
- Final Inspections: Each assembly undergoes visual and dimensional checks to ensure proper fit and function.
This stage may also include the integration of components like abutments that connect the implant to the prosthetic teeth.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage includes surface treatments and final inspections. Key activities include:
- Surface Treatment: Techniques such as sandblasting or acid etching are used to enhance surface roughness, promoting better integration with bone.
- Polishing: To ensure aesthetic quality, especially for visible parts of the prosthetic teeth.
Final quality checks are performed to confirm that the implants meet all specifications before packaging and shipping.
Quality Assurance in Manufacturing
Quality assurance (QA) is a critical component in the production of All-on-X dental implants. Manufacturers must adhere to various international standards to ensure product safety, effectiveness, and reliability.
International Standards
- ISO 9001: This standard outlines criteria for a quality management system (QMS). Compliance ensures that manufacturers consistently produce quality products.
- ISO 13485: Specifically for medical devices, this standard requires manufacturers to demonstrate their ability to provide medical devices that consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: For companies operating in Europe, CE marking indicates compliance with EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
Industry-Specific Standards
- American National Standards Institute (ANSI) and American Dental Association (ADA) Guidelines: These provide specific requirements for dental materials and devices, ensuring they are safe and effective for patient use.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) involves systematic monitoring of various stages in the manufacturing process to ensure compliance with standards. Key checkpoints include:
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This involves inspecting raw materials upon receipt to ensure they meet specifications before production begins.
-
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): During manufacturing, various inspections are conducted to monitor ongoing production processes. This includes checks on dimensional accuracy and visual inspections for defects.
-
Final Quality Control (FQC): Before the implants are packaged, a comprehensive evaluation of the finished products is conducted. This includes functional testing, dimensional checks, and visual inspections to ensure all implants meet established standards.
Common Testing Methods
Testing methods play a significant role in validating the quality of All-on-X dental implants. Some common methods include:
- Mechanical Testing: Evaluating tensile strength, fatigue resistance, and torsional strength to ensure the implants can withstand the forces they will encounter in the oral environment.
- Biocompatibility Testing: Assessing the biological response of the materials to ensure they do not cause adverse reactions when implanted.
- Sterilization Validation: Ensuring that the sterilization process (typically through autoclaving or ethylene oxide) effectively eliminates all microbial life.
Verifying Supplier Quality Assurance
For B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, verifying supplier quality assurance is crucial. Here are actionable strategies:
-
Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of potential suppliers to evaluate their manufacturing processes and quality control measures. This can include facility tours and discussions with quality assurance teams.
-
Review Quality Reports: Request and review any quality assurance reports, including results from IQC, IPQC, and FQC stages. These documents should detail compliance with international standards.
-
Third-Party Inspections: Engage third-party organizations to perform independent inspections and testing of implants to verify compliance with relevant standards.
Conclusion
The manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for All-on-X dental implants are critical for ensuring the delivery of safe, effective, and high-quality products. B2B buyers must remain vigilant in verifying supplier capabilities and compliance with international standards to ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions. By understanding these processes and standards, buyers can significantly enhance their sourcing strategies, resulting in better patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for all on x dental implants Sourcing
When considering the procurement of All-on-X dental implants, understanding the comprehensive cost structure and pricing dynamics is essential for international B2B buyers. This analysis delves into the various cost components, price influencers, and actionable tips for negotiating and sourcing effectively.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary materials used in All-on-X dental implants include titanium for the implants themselves and high-quality dental-grade acrylic or zirconia for the prosthetic teeth. The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost due to variations in quality and durability.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for both the manufacturing of the implants and the surgical placement. This includes the expertise of dental professionals and technicians, which can vary based on regional labor costs.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the costs associated with running a manufacturing facility, including utilities, equipment maintenance, and employee benefits. In regions with higher operational costs, these overheads can inflate the final price.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in specialized tooling and equipment for producing All-on-X implants is substantial. Advanced machinery is required to ensure precision in the manufacturing process, and these costs are often amortized over the production volume.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are essential to ensure the safety and effectiveness of dental implants. Costs associated with testing and regulatory compliance can add to the overall expense.
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs are influenced by the distance from the manufacturing site to the buyer, as well as the method of transport chosen. International shipping may involve customs duties, which can further affect the total cost.
-
Margin: Manufacturers typically add a margin to cover business risks, profit, and market fluctuations. This margin can vary widely depending on the supplier and market demand.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs due to economies of scale. Buyers should assess their needs carefully to negotiate favorable pricing.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom implants tailored to specific patient needs can significantly increase costs. Buyers should balance the need for customization against budget constraints.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: The choice of materials and the presence of certifications (e.g., ISO, FDA) can affect pricing. Higher-quality materials and certifications often justify a premium.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation, reliability, and location of suppliers can impact pricing. Buyers should consider suppliers with established track records to ensure quality and service.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the International Commercial Terms (Incoterms) is crucial for managing logistics and costs. Terms such as FOB (Free on Board) or CIF (Cost, Insurance, and Freight) can affect the final price and responsibilities of both parties.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage suppliers in discussions about pricing, especially for bulk orders. Highlighting long-term partnership potential can yield better terms.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Evaluate the total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider factors such as longevity, maintenance, and potential complications.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of currency fluctuations and import tariffs that can affect overall costs. Establishing contracts in stable currencies can mitigate some risks.
-
Research Local Regulations: Different regions may have varying regulations concerning dental implants. Understanding these can help in sourcing compliant products without incurring additional costs.
-
Supplier Visits: If feasible, visiting manufacturing sites can provide insights into the production processes and quality control measures, allowing for more informed purchasing decisions.
Disclaimer
Prices for All-on-X dental implants can vary widely based on factors outlined above. It is advisable to obtain multiple quotes and conduct thorough market research to ensure competitive pricing tailored to specific needs and regions.
Spotlight on Potential all on x dental implants Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘all on x dental implants’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for all on x dental implants
Key Technical Properties of All-on-X Dental Implants
Understanding the essential technical properties of all-on-X dental implants is crucial for B2B buyers in the dental industry. These specifications not only inform product selection but also impact the longevity and performance of the implants. Here are some critical properties to consider:
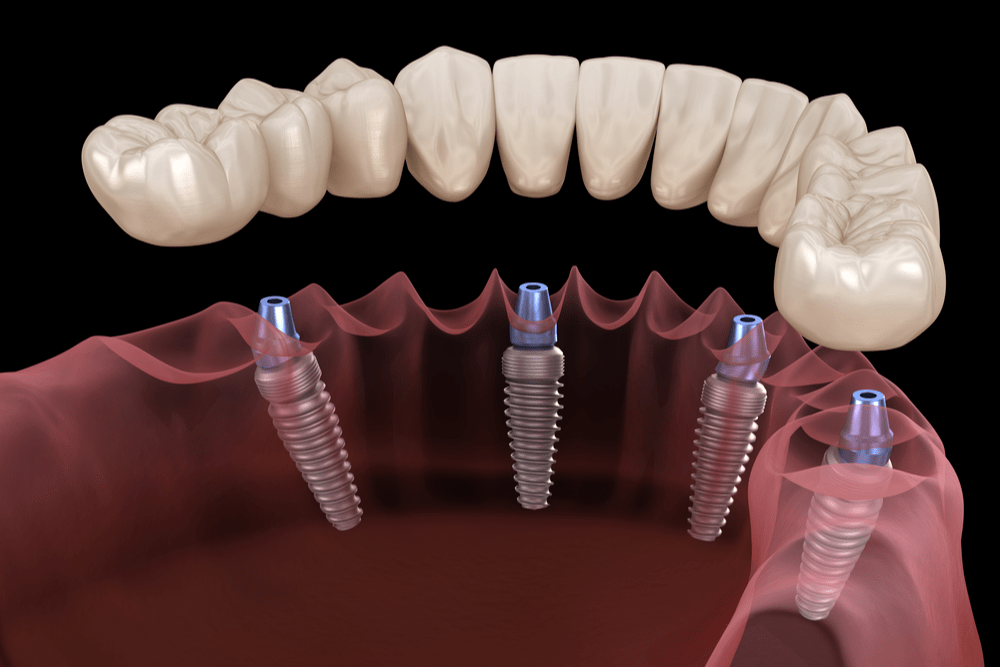
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Material Grade: All-on-X dental implants are primarily made from titanium or titanium alloys, known for their biocompatibility and strength. Grade 5 titanium (Ti-6Al-4V) is commonly used due to its excellent mechanical properties and resistance to corrosion. This is vital for ensuring the longevity of the implants in the oral environment.
-
Implant Diameter and Length: These dimensions can vary, with typical diameters ranging from 3.3 mm to 5 mm and lengths from 8 mm to 16 mm. The choice of diameter and length affects the implant’s stability and the distribution of occlusal forces. Understanding these specifications helps in selecting the right implant for specific patient needs.
-
Tolerance Levels: Tolerance refers to the permissible limit or limits of variation in a physical dimension. For dental implants, tight tolerances are critical to ensure proper fit and function. Tolerances typically range from ±0.1 mm to ±0.5 mm. Poor tolerance can lead to implant failure or complications, making it essential for manufacturers to adhere to precise specifications.
-
Surface Treatment: The surface of all-on-X implants is often treated to enhance osseointegration, the process by which the implant integrates with the bone. Common treatments include sandblasting and acid etching, which increase the surface area and promote better bone contact. Buyers should prioritize implants with proven surface treatments that enhance stability and reduce healing time.
-
Load Capacity: This property indicates how much functional force the implant can withstand without failure. Load capacity is critical for ensuring that the implant can handle the stresses of chewing and biting. Manufacturers typically provide load capacity ratings, and understanding these can assist buyers in selecting suitable implants for their patients.
Common Trade Terms in the All-on-X Dental Implant Market
Navigating the trade terminology used in the dental implant industry is essential for effective communication and decision-making. Here are some commonly used terms that B2B buyers should be familiar with:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer): This term refers to companies that produce parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In the context of dental implants, buyers may engage with OEMs to source implants that meet their specific standards and requirements.
-
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): This is the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Understanding MOQ is crucial for buyers to plan their inventory and avoid overstocking or stockouts, which can impact service delivery.
-
RFQ (Request for Quotation): An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to request pricing and other terms for specific products. B2B buyers should utilize RFQs to obtain competitive pricing and ensure they are making informed purchasing decisions.
-
Incoterms: These are international commercial terms that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international trade. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for understanding shipping costs, risks, and responsibilities, particularly for buyers importing dental implants from abroad.
-
Biocompatibility: This term refers to the ability of a material to perform with an appropriate host response when applied in a medical context. For dental implants, high biocompatibility is essential to minimize the risk of rejection and complications post-surgery.
-
Osseointegration: This is the process by which the implant anchors itself to the jawbone, allowing for stability and function similar to natural teeth. Understanding osseointegration is crucial for evaluating the effectiveness and success rates of different implant systems.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, international B2B buyers can make more informed decisions when sourcing all-on-X dental implants, ultimately leading to better outcomes for their patients and practices.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the all on x dental implants Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for all-on-X dental implants is experiencing significant growth, driven by increasing awareness of oral health and advancements in dental technology. The rise in dental tourism, particularly in regions like Turkey and Thailand, offers international B2B buyers opportunities to source high-quality dental implants at competitive prices. Moreover, the growing prevalence of edentulism and the aging population in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are contributing to a higher demand for comprehensive tooth replacement solutions.
Emerging trends in the all-on-X sector include the adoption of digital dentistry technologies, such as 3D imaging and computer-aided design (CAD) systems. These technologies streamline the planning and placement of implants, enhancing precision and reducing surgical time. Additionally, the integration of tele-dentistry allows dental professionals to consult with patients remotely, facilitating access to care and expanding market reach for B2B suppliers.
For international buyers, understanding local regulations and standards is essential, particularly in regions with varying levels of healthcare infrastructure. Buyers should also be aware of the trend towards minimally invasive procedures, which are gaining traction due to their lower complication rates and faster recovery times. This shift is pushing manufacturers to innovate and provide products that align with these evolving preferences.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is increasingly becoming a focal point in the all-on-X dental implant sector, with buyers prioritizing environmentally responsible products. The environmental impact of dental materials, particularly in terms of waste and resource consumption, is prompting manufacturers to explore sustainable alternatives. Key considerations include the use of biocompatible materials and recyclable packaging, which can significantly reduce the ecological footprint.
Ethical sourcing has also gained prominence, as B2B buyers seek suppliers who adhere to fair labor practices and maintain transparency in their supply chains. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 45001 (Occupational Health and Safety) are becoming important criteria for selecting suppliers. Additionally, the use of “green” materials, such as titanium sourced from responsibly managed mines, can enhance a company’s reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Incorporating sustainability into procurement strategies not only meets regulatory requirements but also aligns with the growing consumer demand for ethical business practices. B2B buyers should actively seek partnerships with manufacturers committed to sustainability, as this can differentiate their offerings in a competitive market.
Brief Evolution/History
The all-on-X dental implant technique has evolved significantly since its inception in the early 2000s. Originally developed as a solution for patients with severe tooth loss, the method quickly gained recognition for its efficiency and effectiveness. Unlike traditional implant approaches that require multiple surgeries and prolonged healing times, the all-on-X method allows for the placement of a full arch of teeth using only four to six implants.
This evolution has been marked by advancements in implant materials and surgical techniques, leading to improved outcomes and patient satisfaction. As dental professionals continue to refine the procedure, the all-on-X technique has become a standard offering in many dental practices, further solidifying its position in the global market. For B2B buyers, understanding this history provides context for the ongoing innovations and trends shaping the future of dental implant solutions.
Related Video: Trump’s New US-Vietnam Trade Deal: Impact on China & Global Supply Chains Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of all on x dental implants
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for all-on-X dental implants?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their certifications, reputation, and experience in the dental implant industry. Verify that they comply with international quality standards such as ISO or CE marking. Request references from other buyers, and assess their production capabilities, including technology used and manufacturing processes. Consider visiting the supplier’s facility if possible, as this can provide insights into their operations and quality control measures. -
Can I customize all-on-X dental implants for my market?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for all-on-X dental implants, including variations in materials, sizes, and designs tailored to meet specific market needs. Discuss your requirements upfront and inquire about the supplier’s capacity to accommodate these changes. Additionally, ensure that any customizations align with regulatory standards in your target market to avoid compliance issues. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for all-on-X dental implants?
MOQs for all-on-X dental implants can vary by supplier, typically ranging from 50 to 200 units per order. Lead times usually depend on the complexity of the order and supplier capabilities, averaging from 4 to 12 weeks. It’s crucial to confirm these details in advance to ensure they align with your inventory and delivery schedules. Establishing a good relationship with your supplier can often lead to more flexible terms. -
What payment terms are common when sourcing all-on-X dental implants?
Payment terms can vary significantly between suppliers, but common practices include a 30% deposit upon order confirmation and the remaining balance before shipment. Some suppliers may offer extended terms for bulk orders or repeat customers. Ensure clarity on payment methods accepted, such as bank transfers or letters of credit, and discuss any potential financing options that may be available to facilitate larger purchases. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certification for all-on-X dental implants?
To ensure quality assurance, request documentation of certifications such as ISO 13485 for medical devices. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s quality control processes, including testing protocols and compliance with Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP). Regular audits and inspections can further confirm adherence to quality standards. Establishing a quality agreement with your supplier can also outline expectations and responsibilities. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when importing all-on-X dental implants?
Logistics is critical when importing dental implants. Understand the shipping methods available, customs regulations, and any import duties applicable in your country. Consider partnering with a logistics provider experienced in medical device transportation to navigate these complexities efficiently. Additionally, ensure that your supplier can provide the necessary documentation for customs clearance, including certificates of origin and compliance. -
How should I handle disputes with suppliers of all-on-X dental implants?
Dispute resolution should be outlined in your contract with the supplier. Common methods include negotiation, mediation, or arbitration, depending on the severity of the issue. Document all communications and maintain records of transactions to support your case if a dispute arises. Establishing a clear escalation process in advance can facilitate timely resolutions and maintain business relationships. -
What are the key regulatory considerations when sourcing all-on-X dental implants internationally?
Regulatory considerations include understanding the certification requirements for dental implants in your target market, which may involve compliance with local health authorities and obtaining necessary approvals. Familiarize yourself with the specific regulations in countries such as Turkey, South Africa, and Brazil, as they may differ significantly. Collaborating with a legal expert in medical device regulations can help ensure compliance and avoid costly delays in bringing products to market.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for all on x dental implants
As the demand for All-on-X dental implants continues to grow across global markets, strategic sourcing becomes essential for international B2B buyers. Understanding the unique advantages of this innovative dental solution, such as fewer implants required and reduced need for bone grafting, can significantly enhance your procurement strategy. By focusing on reputable suppliers who offer high-quality implants and comprehensive support services, buyers can ensure the delivery of superior patient outcomes while optimizing cost efficiency.
Key considerations for sourcing include evaluating suppliers based on their experience, the technology they employ, and their ability to provide ongoing training and support. Establishing strong partnerships with manufacturers and dental professionals can lead to improved patient satisfaction and loyalty, a critical factor in the competitive dental market.
Looking ahead, the landscape for All-on-X implants is promising, with advancements in technology and techniques poised to enhance treatment outcomes. International buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should seize the opportunity to invest in these innovative solutions, ensuring they stay at the forefront of restorative dentistry. Engage with trusted suppliers today to secure your position in this evolving market and transform patient lives with effective, lasting dental solutions.
