Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for dental implants and mri
In the evolving landscape of healthcare, dental implants and MRI technology stand out as critical components that enhance patient outcomes and optimize operational efficiency. For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the intricacies of these products is essential for making informed sourcing decisions. The demand for high-quality dental implants and advanced MRI systems is surging, driven by an increasing emphasis on patient care and technological innovation.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of dental implants and MRI, offering insights into various types, materials, and manufacturing standards. It highlights quality control measures and profiles key suppliers, providing a clear picture of the market dynamics. Additionally, the guide addresses cost considerations and presents answers to frequently asked questions, ensuring that buyers are equipped with the knowledge needed to navigate this complex landscape effectively.
By leveraging this guide, B2B buyers can enhance their procurement strategies, ensuring that they source products that not only meet regulatory standards but also align with their operational needs and budget constraints. In a global market characterized by rapid technological advancements and increasing competition, this resource serves as a valuable tool for maximizing investment and fostering partnerships that drive success.
Understanding dental implants and mri Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Endosteal Implants | Placed in the jawbone; most common type. | General dentistry, oral surgery | Pros: High success rate. Cons: Requires sufficient bone density. |
| Subperiosteal Implants | Positioned under the gum but above the jawbone. | Patients with insufficient jawbone. | Pros: Less invasive. Cons: Limited use and higher costs. |
| Zygomatic Implants | Anchored in the zygomatic bone; used for severe bone loss. | Complex restorations, reconstructive dentistry | Pros: Suitable for atrophic maxilla. Cons: Requires specialized skills. |
| Mini Dental Implants | Smaller diameter, less invasive, and quick to install. | Temporary solutions, denture stabilization | Pros: Easy placement. Cons: Less durable than standard implants. |
| MRI-Compatible Implants | Designed to be safe for MRI scans; non-ferromagnetic. | Patients needing regular MRI checks | Pros: No interference with imaging. Cons: Limited material options. |
Endosteal Implants
Endosteal implants are the most commonly used type of dental implant, inserted directly into the jawbone. They are typically made from titanium, which integrates well with bone, promoting stability. B2B buyers should consider the anatomical suitability of their patients, as sufficient bone density is crucial for success. The high success rate and long-term durability make them appealing for dental practices, but they necessitate thorough pre-surgical assessments to ensure patient eligibility.
Subperiosteal Implants
Subperiosteal implants are placed beneath the gum tissue but above the jawbone, making them a viable option for patients with insufficient bone density who cannot undergo bone grafting. They are custom-made using advanced imaging techniques. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of less invasive procedures against the higher costs and limited application of these implants. This option is particularly relevant for clinics in regions where bone grafting may not be readily available or feasible.
Zygomatic Implants
Zygomatic implants are a specialized type designed for patients with significant bone loss in the upper jaw. These implants are anchored in the zygomatic bone, allowing for immediate stabilization of prosthetics. B2B buyers need to consider the complexity of procedures involving zygomatic implants and the need for skilled practitioners. While they offer a solution for challenging cases, the higher costs and specialized training required can be barriers for some practices.
Mini Dental Implants
Mini dental implants are smaller in diameter and less invasive, making them a quick and effective solution, particularly for stabilizing dentures. They are ideal for patients seeking temporary solutions or those who may not qualify for traditional implants due to bone loss. B2B buyers should assess the durability and longevity of mini implants versus standard options, as they may not be suitable for all patients. Their ease of placement can reduce chair time, making them attractive for high-volume practices.
MRI-Compatible Implants
MRI-compatible implants are specifically designed to be non-ferromagnetic, ensuring safety during MRI scans. This type is particularly relevant for patients who require regular imaging for medical reasons. B2B buyers should explore the available materials and designs that maintain compatibility with MRI technology. While they offer a unique advantage, the limited options and potential for higher costs may influence purchasing decisions, especially in markets with stringent healthcare regulations.
Related Video: What are Transformer Models and how do they work?
Key Industrial Applications of dental implants and mri
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of dental implants and mri | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Integration of dental implants with MRI for pre-surgical planning | Enhances surgical precision and patient outcomes | Ensure compatibility with existing imaging systems and regulatory compliance. |
| Dental Clinics | Use of MRI to assess the jawbone structure before implant placement | Reduces surgical complications and improves patient satisfaction | Look for MRI systems that allow for detailed imaging of soft and hard tissues. |
| Medical Device Manufacturing | Development of MRI-compatible dental implants | Expands product offerings and meets evolving market demands | Consider materials that minimize MRI artifacts and ensure patient safety. |
| Research Institutions | Conducting studies on the efficacy of dental implants using MRI imaging | Supports innovation and enhances credibility in the market | Seek partnerships with institutions that have advanced imaging capabilities. |
| Insurance Providers | Assessment of implant success rates via MRI data collection | Informs risk assessment and policy development | Collaborate with healthcare providers to establish reliable data-sharing protocols. |
Healthcare
In the healthcare sector, the integration of dental implants with MRI technology plays a crucial role in pre-surgical planning. By utilizing MRI scans, healthcare professionals can obtain high-resolution images of the jaw and surrounding structures, allowing for better assessment and planning. This capability significantly enhances surgical precision and improves patient outcomes. International buyers should focus on sourcing MRI systems that are compatible with existing dental practices and comply with local regulatory standards to ensure seamless implementation.
Dental Clinics
Dental clinics increasingly use MRI imaging to evaluate the jawbone structure before the placement of dental implants. This application helps in identifying anatomical challenges and reduces the risk of surgical complications. By ensuring that the implants are placed correctly, clinics can enhance patient satisfaction and long-term success rates. For B2B buyers, it is essential to choose MRI machines that provide detailed imaging of both soft and hard tissues, as well as those that offer ease of integration into the clinic’s workflow.
Medical Device Manufacturing
The medical device manufacturing sector is witnessing a growing demand for MRI-compatible dental implants. These innovative products are designed to minimize artifacts in MRI images, ensuring that diagnostic imaging remains clear and accurate. By developing such implants, manufacturers can expand their product offerings and cater to a market that increasingly values safety and efficacy. Buyers in this sector should prioritize sourcing materials that are not only compatible with MRI technology but also meet stringent safety regulations.
Research Institutions
Research institutions utilize MRI imaging to conduct studies on the efficacy and longevity of dental implants. This application supports innovation in the field and enhances the credibility of research findings. Collaborating with institutions that have advanced MRI capabilities can provide valuable insights into implant performance and patient outcomes. B2B buyers looking to partner with research institutions should seek those with a strong track record in dental research and access to cutting-edge imaging technology.
Insurance Providers
Insurance providers are increasingly leveraging MRI data to assess the success rates of dental implants. By analyzing imaging data, they can inform risk assessment processes and develop more accurate policy offerings. This approach not only enhances the credibility of insurance products but also supports better management of claims related to dental procedures. For B2B buyers in this sector, establishing reliable data-sharing protocols with healthcare providers is essential to ensure comprehensive data collection and analysis.
Related Video: 3 Types of Dental Implants and Surface treatments explained!
Strategic Material Selection Guide for dental implants and mri
When selecting materials for dental implants and MRI applications, international B2B buyers must consider various factors including mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and regulatory compliance. Here, we analyze four common materials used in these fields: Titanium, Zirconia, Stainless Steel, and Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK). Each material has distinct characteristics that can significantly impact performance and suitability for specific applications.
Titanium
Key Properties:
Titanium is renowned for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio, corrosion resistance, and biocompatibility. It can withstand high temperatures and pressures, making it suitable for both dental implants and MRI applications.
Pros & Cons:
The durability of titanium is a significant advantage, as it can last for many years in the human body without degradation. However, the manufacturing process can be complex and costly, which may deter some buyers. Additionally, titanium can be susceptible to galvanic corrosion when in contact with other metals.
Impact on Application:
Titanium is highly compatible with biological tissues, making it an ideal choice for dental implants. In MRI applications, titanium does not interfere with magnetic fields, ensuring clear imaging results.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from regions like Africa and the Middle East should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM F136 for titanium used in medical devices. Understanding local regulations regarding biocompatibility is also crucial.
Zirconia
Key Properties:
Zirconia is a ceramic material characterized by its high strength, toughness, and aesthetic appeal. It has excellent wear resistance and can withstand high temperatures, making it suitable for dental implants.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of zirconia is its aesthetic quality, as it can be made to match natural tooth color. However, it is more brittle compared to metals, which may limit its applications in load-bearing situations. Additionally, zirconia can be more expensive than titanium.
Impact on Application:
Zirconia is particularly effective in dental applications where aesthetics are paramount. However, it may not be the best choice for areas requiring high mechanical strength.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers from Europe should be aware of the European Union’s Medical Device Regulation (MDR) compliance requirements. Understanding the local market’s preferences for aesthetics in dental applications is also important.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties:
Stainless steel is known for its good corrosion resistance, strength, and affordability. It has a moderate temperature rating and is widely used in various medical applications.
Pros & Cons:
The cost-effectiveness of stainless steel makes it a popular choice for dental implants, especially in markets with budget constraints. However, it lacks the biocompatibility of titanium and zirconia, which can lead to complications in some patients.
Impact on Application:
While stainless steel can be used in dental implants, its magnetic properties can interfere with MRI imaging, making it less suitable for certain applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should ensure compliance with ASTM A313 standards and consider the local market’s acceptance of stainless steel implants, particularly in regions with varying healthcare budgets.
Polyether Ether Ketone (PEEK)
Key Properties:
PEEK is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and biocompatibility. It can withstand high temperatures and is lightweight.
Pros & Cons:
PEEK offers a unique advantage in flexibility and comfort, making it suitable for dental applications. However, it is less rigid than metals, which may limit its use in load-bearing scenarios. PEEK is also relatively expensive compared to other materials.
Impact on Application:
PEEK is increasingly used in dental implants due to its ability to mimic the elasticity of natural bone. In MRI applications, it does not interfere with imaging, making it a viable option.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should be aware of the specific regulatory requirements for PEEK in their regions, particularly in Europe where stringent regulations apply. Understanding the local market’s perception of new materials like PEEK is also essential.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for dental implants and mri | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium | Dental implants, MRI components | Excellent biocompatibility | Complex manufacturing process | High |
| Zirconia | Aesthetic dental implants | Natural tooth appearance | Brittle under stress | High |
| Stainless Steel | Budget-friendly dental implants | Cost-effective | Poor biocompatibility, MRI interference | Low |
| PEEK | Flexible dental implants, MRI components | Lightweight and comfortable | Less rigid than metals | Med |
This guide serves as a resource for B2B buyers to make informed decisions regarding material selection for dental implants and MRI applications, ensuring compliance with local standards and market preferences.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for dental implants and mri
Manufacturing dental implants and MRI equipment involves a series of meticulously controlled processes aimed at achieving high precision and quality. For B2B buyers, particularly in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these processes and the associated quality assurance measures is crucial for informed purchasing decisions.
Manufacturing Processes for Dental Implants
-
Material Preparation
– Selection of Materials: Titanium and its alloys are the primary materials used for dental implants due to their biocompatibility and strength. The choice of material impacts the implant’s longevity and integration with bone.
– Surface Treatment: Surface modifications (like sandblasting, acid etching, or anodization) enhance osseointegration by increasing the surface area and altering the topography. This step is critical in improving the success rate of the implants. -
Forming
– Machining: Precision machining techniques, including CNC (Computer Numerical Control) milling, are employed to shape the implants. This process requires high tolerance to ensure that the implants fit perfectly into the designated anatomical spaces.
– Casting and Forging: For certain designs, casting or forging may be utilized to create the initial shape before further refinement through machining. Each method has its advantages concerning material properties and cost. -
Assembly
– Component Integration: After forming, different components of the implant (like abutments and screws) are assembled. This step may include additional processes such as welding or adhesive bonding, depending on the design specifications.
– Sterilization: Before packaging, implants undergo sterilization, typically using ethylene oxide or gamma radiation, to eliminate any microbial contamination. -
Finishing
– Surface Finishing: Final surface treatments are applied to enhance aesthetics and functionality. Processes such as polishing, coating, or further texturing may be used.
– Quality Inspection: Each finished implant is subject to rigorous quality checks to ensure compliance with specifications.
Manufacturing Processes for MRI Equipment
-
Component Fabrication
– Magnet Production: The heart of an MRI machine is its magnet system, often made from superconducting materials. The manufacturing process for magnets involves intricate steps like wire winding and cooling.
– Gradient Coils and RF Coils: These components are fabricated using advanced techniques such as injection molding and CNC machining to ensure they meet precise specifications. -
System Assembly
– Integration of Components: The assembly of MRI machines requires integrating various components, including the magnet, gradient coils, RF coils, and the computer system, all of which must work in concert.
– Testing During Assembly: As components are assembled, they are tested to ensure they function correctly and safely. This includes electrical and mechanical tests to prevent issues later in the production cycle. -
Calibration and Testing
– Quality Calibration: Once assembled, MRI machines undergo extensive calibration to ensure that imaging results are accurate and reliable.
– Final Testing: Before leaving the factory, machines undergo rigorous testing, including phantom imaging tests, to verify performance under clinical conditions.
Quality Assurance Measures
Quality assurance is critical in ensuring the safety and efficacy of dental implants and MRI machines. Key international standards and checkpoints are pivotal for B2B buyers to understand.
-
International Standards
– ISO 9001: This standard outlines the criteria for a quality management system. Compliance indicates that a manufacturer consistently provides products that meet customer and regulatory requirements.
– ISO 13485: Specifically for medical devices, this standard focuses on the quality management system requirements for organizations involved in the design, production, and distribution of medical devices. -
Industry-Specific Certifications
– CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European Economic Area, CE marking indicates that a product meets EU safety, health, and environmental protection standards.
– API Certification: For MRI equipment, API (American Petroleum Institute) certifications may be relevant, especially for components that interact with fluids. -
Quality Control Checkpoints
– Incoming Quality Control (IQC): This initial checkpoint involves inspecting raw materials and components upon arrival at the manufacturing facility.
– In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Regular checks during the manufacturing process ensure adherence to specifications and standards.
– Final Quality Control (FQC): This stage verifies that the finished products meet all necessary specifications before shipment.
Common Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed throughout the manufacturing process to ensure quality:
- Mechanical Testing: Tensile, fatigue, and impact tests assess the physical properties of materials used in implants and MRI components.
- Non-Destructive Testing (NDT): Techniques such as ultrasonic and X-ray testing are used to identify internal flaws without damaging the product.
- Biocompatibility Testing: For dental implants, biocompatibility tests ensure that materials do not provoke an adverse reaction when implanted in the body.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, especially in emerging markets, verifying the quality control practices of suppliers is essential:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits can provide insight into a supplier’s manufacturing processes and quality control measures. Look for adherence to international standards and certifications.
- Quality Reports: Request detailed quality assurance reports that outline testing methods, results, and any non-conformities addressed during the manufacturing process.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of a supplier’s quality control practices and compliance with industry standards.
Navigating Quality Control Nuances
B2B buyers must be aware of the nuances in quality control across different regions:
- Regional Regulations: Understand the specific regulatory requirements in your region (e.g., Egypt’s Ministry of Health regulations for dental products) to ensure compliance when importing.
- Cultural Considerations: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding quality and certification. Buyers should familiarize themselves with local market preferences and standards.
By comprehensively understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for dental implants and MRI equipment, B2B buyers can make informed decisions, ensuring they source high-quality products that meet the specific needs of their markets.
Related Video: SMART Quality Control for Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for dental implants and mri Sourcing
Understanding the Cost Structure of Dental Implants and MRI Sourcing
When sourcing dental implants and MRI systems, understanding the comprehensive cost structure is crucial for international B2B buyers. The primary cost components include materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and profit margin.
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts costs. Dental implants typically use titanium or zirconia, while MRI systems rely on advanced electronics and magnets. High-quality materials often come at a premium, but they contribute to durability and performance.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region. For instance, manufacturing in regions with lower labor costs can reduce overall expenditure, but may also affect quality and lead times. Ensure that suppliers adhere to international labor standards.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes all indirect costs related to production, such as utilities, rent, and administrative expenses. Efficient manufacturing processes can help minimize these costs.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling can be significant, especially for custom implants or MRI systems. Buyers should consider whether the supplier has the necessary tooling capabilities to meet specific requirements.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous QC processes are essential in the medical field. Although they may add to the cost, they ensure compliance with international standards and certifications, reducing the risk of recalls and enhancing product reliability.
-
Logistics: Transportation costs can vary widely based on the shipping method, distance, and any customs duties. Buyers should consider the logistics footprint in their total cost analysis.
-
Margin: Suppliers will include a profit margin in their pricing, which can vary based on the level of competition and market demand.
Price Influencers in Dental Implants and MRI Systems
Several factors can influence pricing, and understanding these can aid in negotiation and cost management:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk purchasing can lead to significant discounts. Establishing a long-term relationship with suppliers may also yield better pricing terms.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized products typically command higher prices. Clearly defining specifications upfront can help avoid unexpected costs later in the process.
-
Materials and Quality Certifications: Higher quality and certified products often come at a premium. However, investing in quality can lead to lower total costs in the long run due to reduced failure rates and warranty claims.
-
Supplier Factors: The supplier’s reputation, experience, and geographical location can all influence pricing. Established suppliers may charge more but often provide greater reliability and support.
-
Incoterms: Understanding Incoterms is essential for pricing clarity. They define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international shipping, impacting costs related to insurance, freight, and customs clearance.
Buyer Tips for Cost-Efficient Sourcing
For international buyers, especially from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, consider the following strategies:
-
Negotiation: Engage in open discussions with suppliers about pricing structures. Highlight potential for long-term partnerships to leverage better pricing.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Focus on the TCO rather than just the initial purchase price. Consider maintenance, potential downtime, and product lifespan to assess overall value.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware of regional pricing differences. For example, European suppliers may have higher standards and certifications, which could justify higher prices compared to other regions.
-
Market Research: Stay informed about market trends and competitor pricing. This knowledge can empower negotiations and help in making informed sourcing decisions.
Disclaimer
The pricing and cost analysis presented is indicative and may vary based on specific circumstances, including regional market conditions, supplier negotiations, and changes in raw material costs. Always conduct thorough due diligence and consult with multiple suppliers to ensure the best terms for your sourcing needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for dental implants and mri
Understanding the essential technical properties and trade terminology in the fields of dental implants and MRI is crucial for international B2B buyers. This knowledge not only enhances decision-making but also facilitates smoother transactions and better supplier relationships. Below is a breakdown of critical specifications and common trade terms relevant to these industries.
Key Technical Properties for Dental Implants
-
Material Grade
Dental implants are typically made from titanium or titanium alloys due to their biocompatibility and strength. The material grade affects the implant’s durability and integration with bone. Buyers should ensure that the implants meet ISO standards, such as ISO 5832-2 for titanium alloys, to guarantee quality and safety. -
Surface Treatment
The surface of dental implants can significantly influence osseointegration—the process by which the implant fuses with the jawbone. Treatments such as sandblasting, acid-etching, or coating with hydroxyapatite enhance surface roughness and increase the implant’s surface area. Buyers should inquire about the specific treatments applied to ensure optimal performance. -
Tolerance
Tolerance refers to the allowable deviation from a specified dimension. In dental implants, precise tolerances ensure that components fit together correctly, which is critical for stability and functionality. Understanding tolerance levels can help buyers assess the quality of the implants and their compatibility with existing dental systems. -
Load-Bearing Capacity
This property indicates the maximum load an implant can withstand without failure. It is crucial for determining the suitability of an implant for specific patient needs. Buyers should request data on load-bearing capacities to ensure they select implants that can support the expected forces in dental applications. -
Corrosion Resistance
Given the exposure of dental implants to saliva and bodily fluids, corrosion resistance is vital. Titanium alloys generally provide excellent resistance, but it’s essential to confirm this property through certifications. Buyers should prioritize implants with proven corrosion resistance to ensure longevity and patient safety.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Common Trade Terms in Dental Implants and MRI
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM refers to a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. In dental implants, understanding whether a supplier is an OEM can help buyers gauge product authenticity and quality. This is particularly important when sourcing implants that require specific regulatory certifications. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ defines the smallest quantity of products that a supplier is willing to sell. This term is crucial for B2B buyers, especially those entering new markets or testing products. Understanding MOQ can influence purchasing decisions and inventory management, particularly in regions with limited demand. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document that buyers send to suppliers to request pricing and terms for specific products. It’s an essential step in the procurement process, allowing buyers to compare offers and negotiate better terms. Crafting a clear RFQ can lead to more competitive pricing and favorable conditions. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of international rules that define the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in international transactions. They clarify who is responsible for shipping, insurance, and tariffs. Familiarity with Incoterms is vital for B2B buyers to mitigate risks and ensure compliance during import/export activities. -
Lead Time
Lead time refers to the time taken from placing an order to receiving the product. Understanding lead times is essential for inventory planning and can affect patient care in dental practices. Buyers should communicate clearly with suppliers to establish realistic lead times and avoid disruptions.
By grasping these essential technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers in the dental implant and MRI markets can make informed decisions, ensuring they select the right products and establish beneficial supplier relationships.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the dental implants and mri Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global dental implants and MRI markets are witnessing significant transformation driven by technological advancements, increasing demand for precision healthcare, and an aging population. For international B2B buyers, especially in regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding these dynamics is crucial.
Key Drivers:
1. Technological Advancements: Innovations such as 3D printing, digital workflows, and AI-enhanced imaging are revolutionizing both sectors. B2B buyers should look for suppliers who leverage these technologies to offer enhanced product quality and efficiency.
2. Rising Demand for Aesthetic Procedures: The increasing focus on aesthetics in dentistry is fueling demand for high-quality dental implants. This trend is particularly pronounced in urban areas across Europe and the Middle East, where cosmetic dental procedures are becoming a norm.
3. Healthcare Accessibility: As healthcare systems evolve, particularly in Africa and South America, there is a growing push towards improved access to advanced medical technologies, including MRI machines. Suppliers that can provide cost-effective, reliable solutions will be in high demand.
Emerging Sourcing Trends:
– Regional Sourcing: Buyers are increasingly sourcing from local or regional manufacturers to reduce lead times and enhance supply chain resilience. This is especially relevant for buyers in Africa and South America, where logistics can be a challenge.
– Digital Procurement Platforms: The rise of e-commerce and digital marketplaces is facilitating easier access to suppliers, enabling buyers to compare products and prices more effectively.
Understanding these market dynamics will enable B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions that align with current trends and future market directions.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a cornerstone of purchasing decisions in the dental implants and MRI sectors. The environmental impact of manufacturing processes, materials used, and waste generated is under scrutiny, making it essential for buyers to consider sustainability in their sourcing strategies.
Importance of Ethical Supply Chains:
1. Regulatory Compliance: With increasing regulations focused on environmental protection, companies must ensure their suppliers comply with international standards to avoid potential legal repercussions.
2. Consumer Demand: There is a growing expectation from patients and healthcare providers for ethical practices. B2B buyers that prioritize suppliers with strong sustainability credentials can enhance their brand reputation and appeal to eco-conscious clients.
Green Certifications and Materials:
– Look for suppliers who offer ISO 14001 certification, which indicates effective environmental management systems.
– Opt for dental implants made from biocompatible materials that are recyclable or biodegradable, reducing the overall environmental footprint.
– In the MRI sector, consider vendors that utilize energy-efficient technologies and sustainable manufacturing practices.
By focusing on sustainability and ethical sourcing, B2B buyers can contribute positively to the environment while also meeting the demands of an increasingly conscientious market.
Brief Evolution/History
The dental implants and MRI sectors have evolved significantly over the past few decades. Dental implants have transitioned from rudimentary materials to highly sophisticated, titanium-based solutions that integrate seamlessly with human bone. This shift has been propelled by advancements in materials science and surgical techniques, enhancing patient outcomes.
Similarly, MRI technology has progressed from basic imaging capabilities to high-resolution, functional imaging that plays a crucial role in diagnostics. The introduction of open MRI machines and portable units has made these technologies more accessible, particularly in developing regions. Understanding this evolution is vital for B2B buyers, as it highlights the importance of investing in innovative, future-proof solutions that meet the needs of modern healthcare environments.
Related Video: Global Trends Chapter 2 | Part 1 | Video Posted!
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of dental implants and mri
-
What criteria should I use to vet suppliers of dental implants and MRI equipment?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their certifications (ISO, CE, etc.), experience in international trade, and reputation in the industry. Request references from other buyers, particularly those within your region, to assess reliability. Analyze their production capabilities, compliance with local regulations, and after-sales support. Additionally, consider their experience in handling customs and logistics for international shipments, as this can significantly impact delivery times and overall satisfaction. -
Can dental implants and MRI equipment be customized to meet specific needs?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for dental implants and MRI systems. Discuss your requirements during initial consultations and inquire about the range of available modifications, such as size, material, and technical specifications. Ensure that the supplier has the capability to deliver customized products within your desired timelines. It’s essential to document all customization agreements to prevent misunderstandings later in the process. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for dental implants and MRI equipment?
MOQs for dental implants can vary widely depending on the supplier and product type, ranging from a few units to hundreds. For MRI equipment, the MOQ is often higher due to the complexity and cost of the machinery. Lead times typically range from 4 to 12 weeks, influenced by customization requests and shipping logistics. Always clarify these details upfront to align your procurement strategies with supplier capabilities. -
What payment terms are commonly accepted by suppliers in this industry?
Payment terms can vary, but common practices include letters of credit, advance payments, or net payment terms (e.g., net 30, net 60). Ensure that you understand the payment structure and associated fees, particularly for international transactions. Consider negotiating terms that align with your cash flow and financial strategy. Additionally, assess the supplier’s payment reliability and any potential currency exchange risks. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certification compliance for dental implants and MRI equipment?
Request copies of relevant quality assurance certifications from suppliers, such as ISO 13485 for medical devices. Conduct due diligence by verifying the authenticity of these certifications through the issuing bodies. It may also be beneficial to visit the manufacturing facility or engage third-party inspection services to assess quality control processes. Establish clear quality expectations in your contract to mitigate risks associated with non-compliance. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing dental implants and MRI equipment?
Logistics play a crucial role in the procurement process. Assess the supplier’s shipping capabilities, including their experience with international freight forwarders and customs clearance. Understand the associated costs, including duties and taxes, and factor these into your budget. Additionally, ensure that the supplier can provide tracking information and support during the shipping process to address any potential delays promptly.
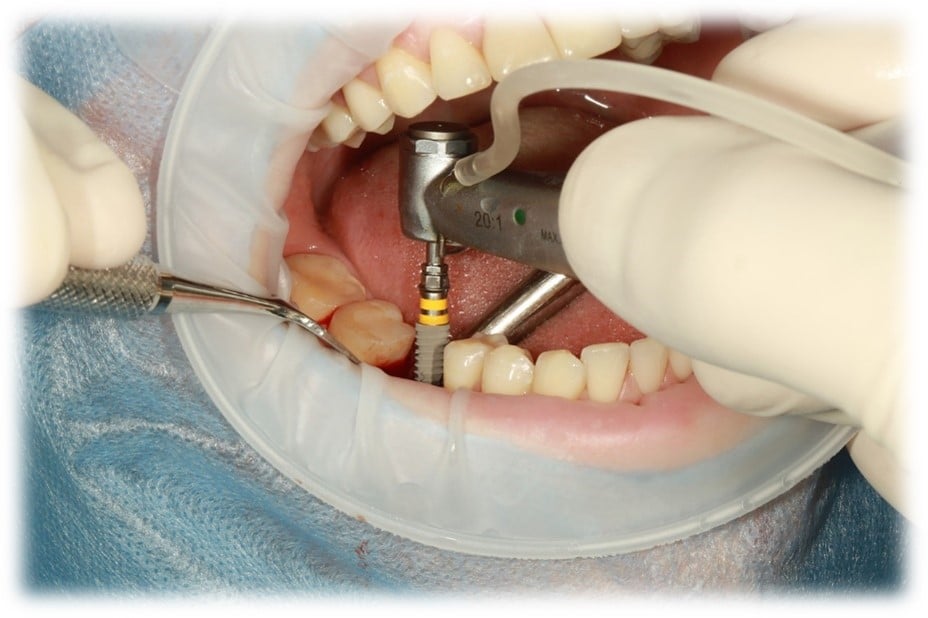
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
How should I handle disputes with suppliers regarding product quality or delivery issues?
Establish a clear communication protocol with your suppliers to address disputes effectively. Document all agreements and communications related to product specifications, delivery timelines, and quality expectations. If a dispute arises, approach the supplier with documented evidence and attempt to resolve the issue amicably. If necessary, include mediation or arbitration clauses in your contracts to provide a framework for resolving conflicts without resorting to litigation. -
What are the key regulatory considerations for importing dental implants and MRI equipment?
Regulatory requirements vary by region, but generally include obtaining necessary import permits, ensuring compliance with local medical device regulations, and adhering to safety standards. Familiarize yourself with the specific regulations in your target market, such as those from the European Medicines Agency (EMA) in Europe or the National Agency for Food and Drug Administration and Control (NAFDAC) in Nigeria. Engaging a local regulatory expert can facilitate compliance and streamline the import process, minimizing potential delays or fines.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for dental implants and mri
The landscape of dental implants and MRI technologies is evolving rapidly, offering significant opportunities for international B2B buyers. Strategic sourcing has emerged as a critical approach to navigating this dynamic market, allowing businesses to secure high-quality products while optimizing costs. Key takeaways include the importance of forging strong relationships with reliable suppliers, leveraging technology for efficient procurement processes, and being informed about regional regulations that impact sourcing decisions.
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, embracing a collaborative sourcing strategy can enhance access to innovative products and services tailored to local needs. Companies should prioritize due diligence when evaluating suppliers, ensuring they meet international quality standards and can provide robust after-sales support.
Looking ahead, the demand for advanced dental implants and MRI technologies is set to rise, driven by increasing healthcare investments and a growing emphasis on patient-centric care. Now is the time to act: engage with suppliers, explore partnerships, and invest in technologies that will position your business for success in this competitive marketplace. By adopting a proactive sourcing strategy, international buyers can not only meet current demands but also anticipate future trends in the dental and medical imaging sectors.
