Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for other options besides dental implants
In the rapidly evolving dental market, the demand for alternatives to traditional dental implants is surging. As B2B buyers from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe seek innovative solutions, understanding these alternatives becomes paramount. This guide delves into a variety of options, from removable dentures to advanced dental bridges, empowering stakeholders to make informed sourcing decisions that align with their specific market needs.
The critical importance of exploring other options besides dental implants lies in addressing diverse patient preferences, budget constraints, and varying levels of dental health across different demographics. This comprehensive resource will cover essential aspects, including types of alternatives, materials utilized, manufacturing and quality control processes, leading suppliers, pricing structures, and emerging market trends. Additionally, a dedicated FAQ section will clarify common queries, ensuring that international buyers are well-equipped to navigate this competitive landscape.
By leveraging the insights presented in this guide, buyers will be better positioned to evaluate the benefits and limitations of various dental solutions, fostering partnerships that enhance service delivery. As the dental industry continues to innovate, staying ahead of the curve is vital for success. This guide serves as a strategic tool for B2B buyers, enabling them to identify the best alternatives to dental implants and ultimately enhance patient satisfaction and business performance.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Understanding other options besides dental implants Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dental Bridges | Fixed prosthetic devices that span gaps in teeth. | Restorative dentistry, aesthetics. | Pros: Cost-effective, preserves adjacent teeth. Cons: Requires alteration of neighboring teeth. |
| Partial Dentures | Removable appliances replacing missing teeth. | Geriatric care, dental clinics. | Pros: Non-invasive, easy to clean. Cons: Less stable, may require frequent adjustments. |
| Complete Dentures | Full arch replacements for edentulous patients. | Senior care, dental practices. | Pros: Restores function and aesthetics. Cons: May cause discomfort, requires adaptation. |
| Resin-Bonded Bridges | Less invasive, uses existing teeth as anchors. | Cosmetic dentistry, quick solutions. | Pros: Minimal tooth preparation, aesthetically pleasing. Cons: Less durable, may not suit all cases. |
| Zirconia Crowns | Strong, biocompatible crowns for damaged teeth. | General dentistry, cosmetic solutions. | Pros: Highly durable, natural appearance. Cons: Higher cost, requires precise fitting. |
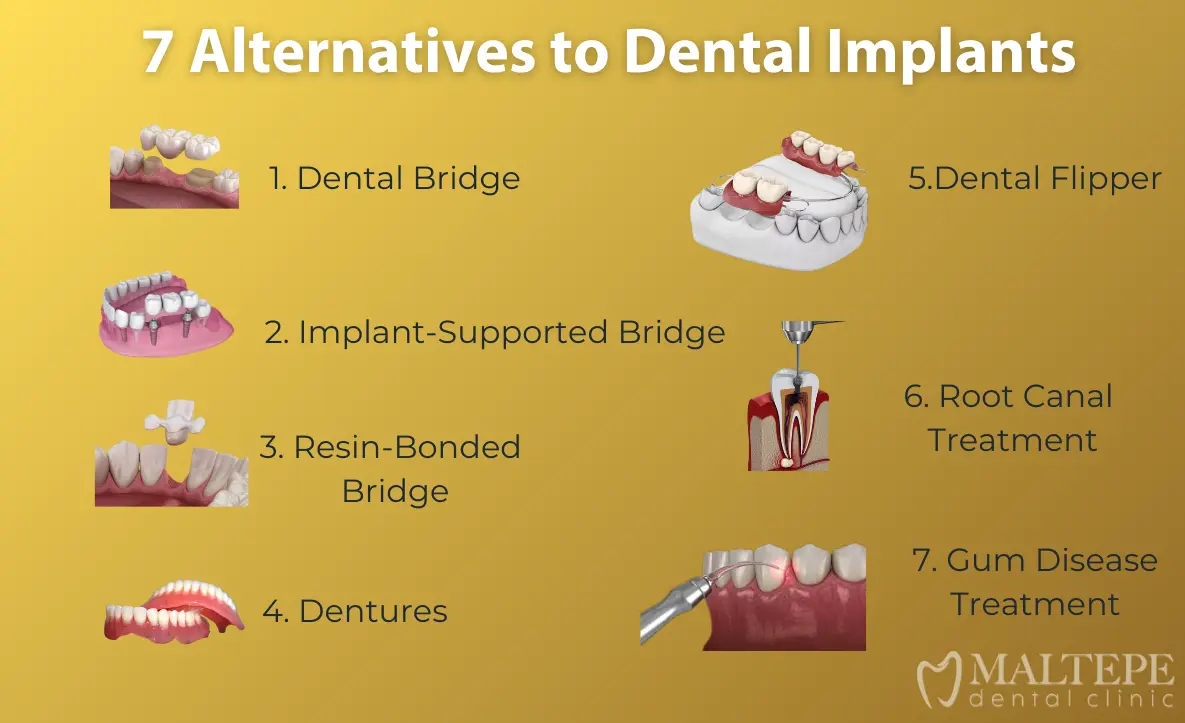
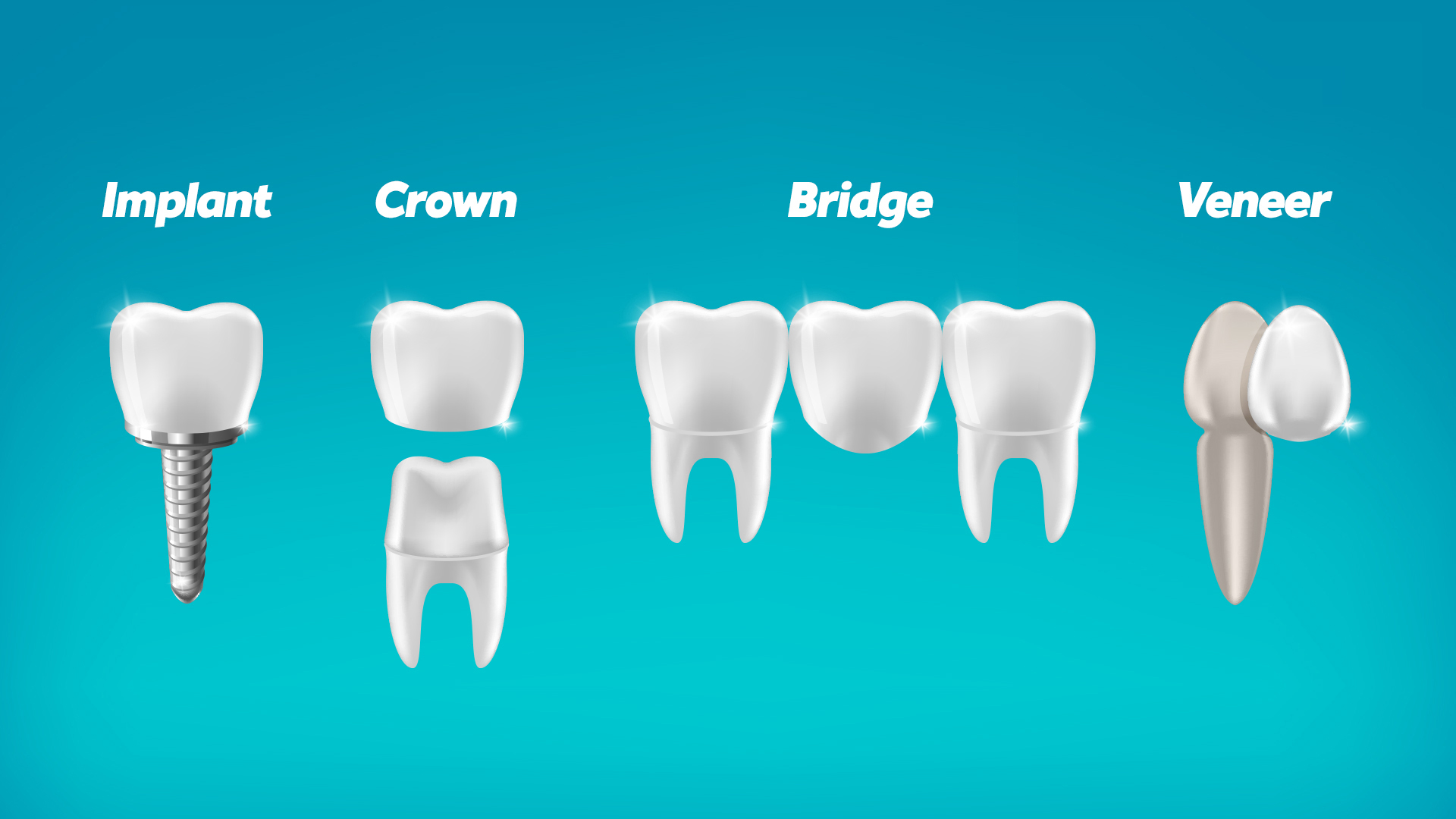
Dental Bridges
Dental bridges are fixed prosthetic devices designed to fill the gaps created by one or more missing teeth. They typically consist of two or more crowns for the teeth on either side of the gap, anchoring a false tooth in between. For B2B buyers, dental bridges offer an effective solution for restorative dentistry, appealing to practices focused on aesthetics. Key purchasing considerations include the materials used (e.g., porcelain, metal) and the bridge’s longevity, which can influence patient satisfaction and repeat business.
Partial Dentures
Partial dentures are removable appliances that replace missing teeth while allowing the patient to retain their natural teeth. They are particularly useful in geriatric care, where patients may prefer a non-invasive solution. B2B buyers should consider the materials (acrylic or metal) and the design’s comfort and fit. While partial dentures are easy to clean and adjust, they may require frequent maintenance, which can impact long-term relationships with patients.
Complete Dentures
Complete dentures are full arch replacements for individuals who have lost all their natural teeth. They are widely used in senior care and dental practices, making them a staple in restorative options. B2B buyers should evaluate the quality of materials and the customization options available, as these factors significantly affect patient comfort and satisfaction. While complete dentures restore both function and aesthetics, they may require a period of adaptation for new users, influencing initial patient experiences.
Resin-Bonded Bridges
Resin-bonded bridges offer a less invasive alternative to traditional bridges by using existing teeth as anchors. This solution is particularly appealing in cosmetic dentistry and for quick fixes. B2B buyers should consider the aesthetic qualities and the minimal tooth preparation required, which can enhance patient acceptance. However, these bridges may not be suitable for all cases due to durability concerns, necessitating careful assessment of patient needs and expectations.
Zirconia Crowns
Zirconia crowns are increasingly popular due to their strength and biocompatibility. They serve as an excellent option for restoring damaged teeth while providing a natural appearance. For B2B buyers, the key considerations include the crown’s durability and the precision of fitting required during installation. Although zirconia crowns tend to be more expensive, their long-term benefits and patient satisfaction rates can justify the investment, making them an attractive option for dental practices focused on quality care.
Related Video: 3 Types of Dental Implants and Surface treatments explained!
Key Industrial Applications of other options besides dental implants
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of other options besides dental implants | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Healthcare | Removable dentures | Cost-effective solution for patients with missing teeth. | Quality of materials, durability, and ease of maintenance. |
| Orthodontics | Retainers | Essential for maintaining teeth position post-braces treatment. | Customization options and patient comfort. |
| Veterinary Medicine | Prosthetic devices | Improves quality of life for pets with missing limbs or teeth. | Biocompatibility and adaptability to various animal species. |
| Aesthetic Dentistry | Veneers | Enhances the appearance of teeth without invasive procedures. | Aesthetic quality, longevity, and compatibility with dental health. |
| Geriatric Care | Mouthguards | Protects elderly patients’ teeth during sleep or while eating. | Comfort, adjustability, and safety for sensitive teeth. |
Healthcare: Removable Dentures
Removable dentures serve as a practical alternative to dental implants, particularly in regions where access to advanced dental care is limited. They are an affordable solution for patients with missing teeth, allowing for improved functionality and aesthetics. For international B2B buyers, sourcing high-quality materials that ensure durability and comfort is essential. Additionally, understanding local manufacturing capabilities can help in reducing costs and lead times.
Orthodontics: Retainers
Retainers are crucial in orthodontics for maintaining the position of teeth after braces have been removed. They provide a non-invasive option for patients, particularly in emerging markets where orthodontic treatments may be less accessible. B2B buyers should focus on customization options to cater to diverse patient needs, as well as ensuring that the materials used are comfortable and durable for long-term wear.
Veterinary Medicine: Prosthetic Devices
The use of prosthetic devices in veterinary medicine is gaining traction, particularly in enhancing the quality of life for pets with missing limbs or teeth. This application is particularly relevant in regions with a growing pet ownership culture. B2B buyers must consider the biocompatibility of materials and their adaptability to various animal species, ensuring that the prosthetics are both functional and safe for the animals.
Aesthetic Dentistry: Veneers
Veneers provide a non-invasive solution to improve the appearance of teeth, making them a popular choice in aesthetic dentistry. They are particularly relevant in regions where cosmetic dentistry is on the rise, offering patients a way to enhance their smiles without the need for implants. Buyers should prioritize aesthetic quality and longevity in their sourcing decisions, as well as compatibility with existing dental health.
Geriatric Care: Mouthguards
Mouthguards play a vital role in geriatric care, protecting elderly patients’ teeth during sleep or while eating. This application addresses the specific dental needs of older populations, who may be more susceptible to dental issues. For B2B buyers, sourcing comfortable and adjustable mouthguards that cater to sensitive teeth is crucial, as it directly impacts patient compliance and satisfaction.
Strategic Material Selection Guide for other options besides dental implants
When considering alternatives to dental implants, the choice of materials plays a crucial role in ensuring product performance, durability, and overall patient satisfaction. Below, we analyze several common materials used in dental applications, focusing on their properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Titanium
Key Properties: Titanium is renowned for its excellent strength-to-weight ratio and biocompatibility. It exhibits high corrosion resistance and can withstand significant temperature fluctuations, making it suitable for various dental applications.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of titanium is its durability and resistance to wear, which ensures longevity in dental applications. However, it can be relatively expensive compared to other materials, and manufacturing complexity can increase costs. Additionally, while titanium is biocompatible, some patients may experience allergic reactions, which is a consideration for product suitability.
Impact on Application: Titanium is particularly compatible with osseointegration, making it ideal for applications requiring strong integration with bone. Its resistance to corrosion also makes it suitable for environments where exposure to bodily fluids is common.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM F136 for titanium used in dental implants. Understanding regional market preferences, such as those in Saudi Arabia, where biocompatibility is a significant concern, is essential.
Zirconia
Key Properties: Zirconia is a ceramic material known for its high strength and aesthetic appeal. It is highly resistant to wear and has excellent thermal properties, making it suitable for various dental applications.
Pros & Cons: The aesthetic advantage of zirconia is significant; it can be color-matched to natural teeth, making it a preferred choice for visible dental restorations. However, its brittleness can lead to fractures under high stress, limiting its use in certain applications. Additionally, zirconia can be more costly due to the complexity of its manufacturing process.
Impact on Application: Zirconia is particularly effective in applications requiring aesthetic considerations, such as crowns and bridges. Its compatibility with dental cements also enhances its usability in restorative procedures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with standards such as ISO 6872 for dental ceramics is crucial. Buyers in regions like Europe may prioritize aesthetic outcomes, while those in South America might focus on cost-effectiveness.
Polyetheretherketone (PEEK)
Key Properties: PEEK is a high-performance thermoplastic known for its excellent mechanical properties and biocompatibility. It offers good resistance to chemicals and can withstand high temperatures.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of PEEK is its lightweight nature combined with high strength, making it suitable for a variety of dental applications. However, it is typically more expensive than traditional materials like metal and may require specialized manufacturing techniques, which can complicate production.
Impact on Application: PEEK is particularly useful in applications where flexibility and strength are required, such as in dental prosthetics. Its chemical resistance also makes it suitable for use in environments with varying pH levels.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the need for compliance with standards like ASTM F2026 for PEEK. In markets such as Africa, where cost considerations are paramount, the higher price point of PEEK may be a barrier.
Glass Ceramics
Key Properties: Glass ceramics are known for their excellent aesthetic properties and translucency, closely mimicking natural tooth enamel. They have good mechanical strength and are resistant to wear.
Pros & Cons: The aesthetic appeal of glass ceramics is one of their strongest advantages, making them ideal for cosmetic applications. However, they can be more brittle than other materials, which may lead to fractures, especially under high stress.
Impact on Application: Glass ceramics are particularly suitable for anterior restorations where aesthetics are crucial. Their compatibility with various bonding agents enhances their usability in restorative dentistry.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ISO 6872 is important for ensuring quality. Buyers from the Middle East may prioritize aesthetic outcomes, while those from Europe may focus on both aesthetics and durability.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for other options besides dental implants | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium | Dental implants and prosthetics | Excellent durability and biocompatibility | Higher cost and potential allergic reactions | High |
| Zirconia | Crowns, bridges, and aesthetic restorations | Superior aesthetics and natural appearance | Brittleness under stress | Med |
| Polyetheretherketone (PEEK) | Flexible dental prosthetics and frameworks | Lightweight and high strength | Higher manufacturing complexity | High |
| Glass Ceramics | Anterior restorations requiring aesthetic appeal | Excellent aesthetic properties | Brittle and prone to fractures | Med |
This guide provides actionable insights for B2B buyers, helping them make informed decisions based on material properties, application suitability, and regional market considerations.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for other options besides dental implants
Understanding Manufacturing Processes for Dental Alternatives
When exploring options beyond dental implants, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols is essential for international B2B buyers. The production of dental alternatives—such as bridges, crowns, dentures, and other prosthetic devices—typically involves several key stages and techniques, each requiring meticulous attention to detail to ensure product quality and compliance with international standards.
Main Stages of Manufacturing
-
Material Preparation
– Selection of Materials: The choice of materials is crucial; common options include ceramics, metals (like titanium and gold), and polymers. Each material has distinct properties affecting durability, aesthetics, and biocompatibility.
– Preprocessing: Materials often undergo treatments such as sterilization, surface finishing, or chemical coating to enhance their performance and safety. -
Forming
– Techniques Used: Common techniques include CAD/CAM (Computer-Aided Design/Computer-Aided Manufacturing), injection molding, and 3D printing. CAD/CAM allows for precise customization, while 3D printing offers rapid prototyping capabilities.
– Shaping and Sizing: This stage ensures that the products meet specific dimensional tolerances and fit requirements for individual patients. -
Assembly
– Joining Components: For products like dentures or bridges, various components may need to be assembled. Techniques can include welding, bonding, or mechanical fastening.
– Integration of Technology: Advanced technologies, such as electronic sensors for smart prosthetics, are increasingly integrated during this stage. -
Finishing
– Surface Treatment: Finishing processes such as polishing, glazing, or coating are applied to enhance aesthetics and reduce wear.
– Final Inspection: This is a critical step where products are visually and dimensionally inspected to ensure they meet specifications before packaging.
Quality Assurance Protocols
Quality assurance is vital in ensuring that the products meet both safety and performance standards. Here are the key components of a robust QC system.
International Standards
- ISO 9001: This general quality management standard is applicable across industries, including dental manufacturing. It emphasizes consistent quality and customer satisfaction.
- Industry-Specific Standards:
- CE Marking: Required for products sold in the European market, indicating compliance with health and safety regulations.
- API Standards: For materials used in dental products, particularly those involving metals and polymers, adherence to specific API standards is crucial.
Quality Control Checkpoints
-
Incoming Quality Control (IQC)
– This initial checkpoint verifies the quality of incoming raw materials. Suppliers should provide certificates of analysis (CoA) to confirm compliance with required specifications. -
In-Process Quality Control (IPQC)
– During production, regular inspections are conducted to monitor critical parameters and ensure that processes remain within defined limits. -
Final Quality Control (FQC)
– At this stage, completed products undergo rigorous testing for functionality, aesthetics, and biocompatibility. Documentation of these tests is essential for compliance and traceability.
Common Testing Methods
B2B buyers should be aware of various testing methods that manufacturers employ to ensure product quality:
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing strength, hardness, and elasticity of materials.
- Biocompatibility Testing: Ensuring materials are safe for use in the human body, often involving in vitro and in vivo studies.
- Sterility Testing: Critical for products that will come into direct contact with oral tissues.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For international buyers, verifying supplier quality control is a pivotal step in the procurement process. Here are actionable strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting regular audits can provide insights into the manufacturer’s quality management system. This includes reviewing documentation, processes, and adherence to standards.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Buyers should ask for detailed quality reports that outline testing methods, results, and compliance with relevant standards.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent third-party inspectors can provide an unbiased assessment of the manufacturer’s quality practices and product reliability.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
International B2B buyers must navigate various regulatory landscapes, which can differ significantly across regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Here are important considerations:
- Regulatory Compliance: Understanding local regulations in your target market is essential. For instance, while CE marking is crucial in Europe, other regions may have their own certification requirements.
- Cultural Considerations: Quality perceptions can vary by region. Buyers must align their expectations with local standards and practices to ensure compatibility and acceptance in the target market.
- Supply Chain Transparency: Establishing strong relationships with suppliers who prioritize transparency in their quality assurance processes can mitigate risks and enhance product reliability.
Conclusion
For B2B buyers exploring alternatives to dental implants, a thorough understanding of manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols is essential. By focusing on material selection, production techniques, and rigorous quality control measures, buyers can ensure they source reliable, compliant products that meet market demands. Additionally, leveraging audits, quality reports, and third-party inspections will help in establishing trust and maintaining high standards in the procurement process.
Related Video: SMART Quality Control for Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for other options besides dental implants Sourcing
When considering alternatives to dental implants, international B2B buyers must conduct a thorough analysis of the costs and pricing structures associated with these options. Understanding the components of cost and the factors that influence pricing can lead to more informed purchasing decisions.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The choice of materials significantly impacts the overall cost. Alternatives such as dentures, bridges, or partials may utilize lower-cost materials compared to titanium used in implants. When sourcing these options, buyers should evaluate the quality and durability of materials, as this will affect long-term satisfaction and potential replacement costs.
-
Labor: Labor costs vary by region and the complexity of the dental solution. Countries with lower labor costs may offer competitive pricing but could also raise concerns about quality. It’s essential for buyers to balance cost with the skill level of the technicians involved in producing dental solutions.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses all operational expenses, including utilities, rent, and administrative costs. Suppliers with efficient operations can offer more competitive pricing. Buyers should inquire about a supplier’s overhead costs to understand how they affect the final price.
-
Tooling: The costs associated with the tools and equipment necessary for manufacturing dental products can be substantial. Custom solutions may require specialized tooling, which can drive up initial costs. Buyers should assess the necessity of customization against the potential benefits.
-
Quality Control (QC): Quality assurance processes are vital, especially in the dental industry where patient safety is paramount. Suppliers that invest in robust QC measures may have higher costs, but they often provide better-quality products. Understanding a supplier’s QC protocols can help buyers gauge potential risks.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Logistics: Shipping and handling costs can vary widely based on the origin of the products and the destination. Factors such as distance, transport mode, and customs duties should be considered. Buyers should explore suppliers that offer favorable logistics arrangements to minimize additional costs.
-
Margin: The supplier’s profit margin will influence pricing. Buyers should seek transparency regarding how margins are calculated and be wary of excessive markups that do not correlate with product value.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ: Purchasing in larger quantities typically leads to lower per-unit costs. Establishing a minimum order quantity (MOQ) can help in negotiating better rates.
-
Specifications/Customization: Highly customized products often come with a premium. Buyers should weigh the benefits of customization against the potential cost increases.
-
Materials and Quality/Certifications: Higher quality materials and recognized certifications (such as ISO or CE) can lead to higher costs but may be necessary for compliance and customer satisfaction.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and reliability of suppliers can significantly affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to perceived value, while newer entrants might offer lower prices to gain market share.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the Incoterms applied in the transaction is crucial. They dictate who is responsible for shipping costs, insurance, and risk at different stages, impacting the total cost of ownership.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Buyers should approach negotiations with a clear understanding of market prices and alternatives. Being well-informed allows for better leverage in discussions.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Always consider total cost of ownership rather than just the initial purchase price. This includes maintenance, replacement, and potential warranty costs.
-
Pricing Nuances: Different regions may have unique pricing strategies due to local market conditions. Buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe should be aware of these differences to avoid overpaying.
-
Disclaimer for Indicative Prices: It’s important to note that prices can fluctuate based on market conditions, exchange rates, and changes in supply chain dynamics. Buyers should always seek updated quotes to ensure accuracy.
In summary, a comprehensive understanding of the costs and pricing structures associated with dental implant alternatives will empower international B2B buyers to make strategic sourcing decisions that align with their business goals.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for other options besides dental implants
Key Technical Properties for Alternatives to Dental Implants
When exploring alternatives to dental implants, understanding essential technical properties is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. Here are several critical specifications that B2B buyers should consider:
-
Material Grade
The material grade of dental alternatives (such as bridges, dentures, or crowns) refers to the quality and type of materials used, which can include metals, ceramics, and polymers. Higher-grade materials often provide better durability and biocompatibility, which is essential for patient safety and comfort. For international buyers, selecting materials that meet local regulatory standards can also be a critical factor. -
Tolerance
Tolerance indicates the permissible limit of variation in the dimensions of the dental products. It is essential for ensuring a precise fit, which can significantly affect the performance and longevity of the solution. For B2B buyers, understanding tolerance levels can aid in assessing product quality and compatibility with existing dental frameworks. -
Biocompatibility
This property refers to the ability of a material to perform with an appropriate host response when applied in medical contexts. For dental alternatives, biocompatibility is vital to minimize the risk of allergic reactions or adverse effects. Buyers should prioritize products that have been rigorously tested for biocompatibility, especially in regions with varying regulatory standards. -
Mechanical Properties
Key mechanical properties include tensile strength, hardness, and flexibility. These characteristics determine how well the dental alternatives can withstand chewing forces and their overall longevity. B2B buyers should look for products that provide detailed mechanical property data to ensure they meet the demands of daily use. -
Aesthetic Quality
The aesthetic quality of dental products, such as color matching and translucency, is essential for patient satisfaction. Products that closely resemble natural teeth can enhance the end-user experience. Buyers should evaluate the aesthetic performance of alternatives to ensure they meet the expectations of their clientele.
Common Trade Terminology
Familiarity with industry jargon is equally important for navigating the purchasing process. Here are several common terms that B2B buyers should know:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
An OEM is a company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer. Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify the quality and reliability of the products they are sourcing. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
MOQ refers to the smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell. Knowing the MOQ is essential for B2B buyers to manage inventory costs and ensure they are not over-committing to stock that may not be needed. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
An RFQ is a document sent to suppliers to solicit price quotes for specific products or services. It is an important tool for buyers to obtain competitive pricing and understand the available options in the market. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
Incoterms are a set of predefined international trade terms that clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers. They dictate aspects such as shipping, insurance, and risk transfer. Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for B2B buyers to avoid misunderstandings and ensure smooth transactions. -
Lead Time
Lead time is the period between the initiation of an order and its completion. Understanding lead times is critical for inventory management and planning, allowing buyers to align their supply chain with their operational needs. -
Certification
Certification refers to the verification that products meet specific standards, often determined by industry regulations or quality assurance bodies. For dental products, certifications can assure buyers of the product’s safety and effectiveness, making it a key factor in the purchasing decision.
By grasping these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers can make more informed choices when considering alternatives to dental implants, ensuring they select the best solutions for their needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the other options besides dental implants Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global market for alternatives to dental implants is experiencing significant growth, driven by a combination of technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and increasing awareness of oral health. Key trends include the rise of innovative materials such as biocompatible ceramics and bioactive glasses, which offer improved aesthetics and functionality. Additionally, digital dentistry is revolutionizing the sector through the integration of 3D printing and CAD/CAM technologies, enabling more precise and efficient production of dental prosthetics and restorations.
International B2B buyers, particularly from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, should note that there is a growing demand for personalized dental solutions. This trend is fueled by a shift towards patient-centered care, where customization enhances patient satisfaction and outcomes. Furthermore, the expansion of e-commerce platforms and digital marketplaces is simplifying sourcing processes, allowing buyers to access a wider range of suppliers and products globally.
Emerging markets are increasingly becoming focal points for investment and collaboration. Countries in the Middle East and Africa are witnessing a surge in dental clinics and health awareness campaigns, creating opportunities for suppliers to engage with local stakeholders. This is particularly relevant in regions where traditional dental solutions may be less accessible, highlighting the importance of establishing strong partnerships with local distributors and healthcare providers.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical consideration in the sourcing of alternatives to dental implants. The environmental impact of dental materials is under scrutiny, prompting buyers to seek products that minimize ecological footprints. Ethical sourcing involves selecting suppliers who prioritize sustainable practices, such as using recycled materials and reducing waste in their production processes.
For B2B buyers, understanding the importance of green certifications is essential. Certifications like ISO 14001 or specific eco-labels can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to environmental responsibility. Additionally, using materials such as plant-based polymers or sustainably sourced metals can enhance a company’s reputation and appeal to environmentally conscious consumers.
Moreover, implementing a transparent supply chain is crucial for maintaining ethical standards. This involves ensuring that all stakeholders, from raw material suppliers to manufacturers, adhere to sustainable practices. Buyers should actively engage with suppliers to assess their sustainability efforts, fostering long-term partnerships that align with ethical values and contribute to overall brand integrity.
Brief Evolution/History
The alternatives to dental implants sector has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially dominated by traditional denture solutions, the market has diversified with the introduction of advanced materials and technologies. The 1990s saw the emergence of more durable and aesthetically pleasing options, such as all-ceramic crowns and bridges.
As awareness of oral health and aesthetics increased, so did innovations in dental restoration techniques. Recent years have highlighted a trend toward minimally invasive solutions that not only enhance patient comfort but also reduce recovery time. This evolution reflects a broader shift in the dental industry towards holistic, patient-focused care, paving the way for new opportunities and challenges for international B2B buyers.
Related Video: Lesson 1 – A Brief Overview of International Trade
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of other options besides dental implants
-
What factors should I consider when vetting suppliers for alternatives to dental implants?
When vetting suppliers, prioritize their industry experience, reputation, and certifications. Request references and case studies to gauge their reliability. Evaluate their manufacturing capabilities, including technology used, production capacity, and compliance with international quality standards. Additionally, consider their communication responsiveness and willingness to provide after-sales support. This holistic assessment will help ensure you partner with a supplier that can meet your specific needs effectively. -
Can I customize products, and what are the typical lead times?
Customization is often available, but it varies by supplier. Discuss your specific requirements early on to determine the extent of customization they can accommodate. Lead times for customized products can range from a few weeks to several months, depending on the complexity and the supplier’s production schedule. Always clarify these timelines upfront and consider potential delays in logistics, especially for international shipments. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQs) and payment terms I should expect?
MOQs can differ significantly among suppliers, typically influenced by the type of product and manufacturing processes. For alternatives to dental implants, MOQs may range from 50 to 200 units. Payment terms can also vary; many suppliers require a deposit upfront, with the balance due upon delivery or within a specified period post-delivery. Ensure you negotiate terms that align with your cash flow and inventory management practices. -
How can I ensure quality assurance and certifications for the products?
Request copies of relevant certifications, such as ISO 13485 for medical devices, to verify that the supplier meets international quality standards. Conduct audits if possible or hire third-party inspection services to assess product quality before shipment. Establish a clear quality assurance process that includes pre-shipment inspections and defect rates. This diligence helps mitigate risks associated with product quality and compliance. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing from international suppliers?
Logistics can be complex, especially when importing medical devices. Confirm the supplier’s shipping methods, estimated delivery times, and incoterms (International Commercial Terms) to understand who bears the responsibility for shipping costs and risks. Factor in customs regulations and potential tariffs in your sourcing strategy. Building a relationship with a reliable logistics provider can also streamline the process and reduce delays. -
How can I address disputes with suppliers effectively?
Establish clear communication channels and define dispute resolution mechanisms in your contract. Document all agreements and communications to maintain a record in case of issues. If a dispute arises, attempt to resolve it amicably through direct negotiation. If necessary, consider mediation or arbitration as stipulated in your contract. Having a legal framework in place can protect your interests and facilitate a smoother resolution process. -
What are the common challenges faced when sourcing alternatives to dental implants?
Challenges can include inconsistent product quality, long lead times, and compliance with local regulations. Language barriers and cultural differences may also complicate negotiations. To mitigate these issues, conduct thorough market research, engage local experts, and establish clear communication protocols. Building strong relationships with suppliers and understanding their operational processes can also help navigate potential challenges effectively. -
How do I stay updated on industry trends and new product developments?
Regularly engage with industry publications, attend trade shows, and participate in professional associations relevant to dental products and medical devices. Networking with other B2B buyers and suppliers can provide valuable insights into emerging trends and innovations. Additionally, consider subscribing to newsletters from key industry players to receive timely updates on new products and technologies that may benefit your sourcing strategy.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for other options besides dental implants
In navigating the landscape of dental solutions beyond implants, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to optimize outcomes. By leveraging alternatives such as dental bridges, dentures, and dental crowns, buyers can enhance their product offerings while catering to diverse patient needs across different regions. This approach not only diversifies inventory but also mitigates risks associated with supply chain disruptions.
Key takeaways include the importance of understanding regional preferences and regulatory standards, as these factors significantly influence purchasing decisions. Engaging with reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality materials and innovative solutions will be crucial in maintaining competitive advantage. Additionally, exploring partnerships with local manufacturers can lead to cost savings and improved service delivery, especially in rapidly developing markets in Africa and South America.
Looking forward, the demand for versatile dental solutions is set to grow, driven by an increasing awareness of oral health. B2B buyers are encouraged to adopt a proactive sourcing strategy that embraces innovation and sustainability. By doing so, they can position themselves as leaders in the dental market and better serve their clientele. Embrace this opportunity to expand your offerings and foster long-term relationships with partners in the dental supply chain.
