Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for pictures of dental implants that failed
In the evolving landscape of dental healthcare, the demand for high-quality dental implants is rising globally. However, the unfortunate reality is that not all dental implants succeed, leading to a significant market for pictures of failed dental implants. These images serve as crucial educational tools for B2B buyers, enabling them to understand the potential pitfalls associated with various implant types and procedures. By analyzing these failures, dental professionals can improve their practices and enhance patient outcomes.
This guide provides an in-depth exploration of the critical aspects surrounding failed dental implants. It covers various types of implants, the materials used, manufacturing quality control processes, and a detailed overview of suppliers in the market. Additionally, it addresses the costs involved, market trends, and frequently asked questions, ensuring a comprehensive resource for informed decision-making.
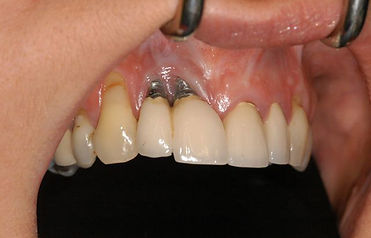
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
For international buyers from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe—including countries like Saudi Arabia and the UAE—this guide is designed to empower your sourcing decisions. By leveraging insights from real-world cases of implant failures, you can better assess product quality and supplier reliability. Ultimately, understanding these factors can lead to more effective procurement strategies, reduced risks, and improved patient satisfaction in your dental practices.
Understanding pictures of dental implants that failed Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Peri-implantitis Images | Signs of inflammation, infection, and bone loss around implant | Diagnostic tools for dental professionals | Pros: Highlights critical issues; Cons: May indicate irreversible damage. |
| Failed Bone Integration | Lack of osseointegration, visible gaps between implant and bone | Assessment for surgical revisions | Pros: Essential for planning corrective surgery; Cons: Can lead to increased costs. |
| Mechanical Failures | Visible fractures or loosening of components | Quality control for implant manufacturers | Pros: Identifies material weaknesses; Cons: May require full replacement. |
| Gum Recession Photos | Receding gums exposing implant fixtures | Patient education and treatment planning | Pros: Useful for preventative measures; Cons: Indicates potential long-term complications. |
| Aesthetic Failures | Poor alignment, color mismatch, or unnatural appearance | Marketing for cosmetic dentistry solutions | Pros: Guides aesthetic improvements; Cons: May necessitate costly revisions. |
Peri-implantitis Images
Peri-implantitis images showcase inflammation and infection surrounding dental implants, often highlighted by swelling and redness in the gums. These images are crucial for dental professionals to identify potential failures early. For B2B buyers, understanding these visuals can aid in selecting dental products that minimize infection risks, thereby enhancing patient outcomes and satisfaction.
Failed Bone Integration
Images depicting failed bone integration reveal gaps between the implant and surrounding bone, indicating a lack of osseointegration. This type of failure necessitates a thorough evaluation and often corrective surgical interventions. B2B buyers must consider the implications of these failures when sourcing implants, ensuring that they select products with proven integration success rates to reduce future complications and costs.
Mechanical Failures
Mechanical failure images illustrate fractures or loosening of implant components, which can significantly affect functionality. For manufacturers, these visuals serve as critical feedback for quality control, helping to refine product designs. B2B buyers should prioritize sourcing implants from reputable manufacturers known for durability, as mechanical failures can lead to additional expenses and patient dissatisfaction.
Gum Recession Photos
Gum recession images highlight the exposure of implant fixtures due to receding gums, often signaling underlying health issues or improper placement. These visuals are valuable for patient education and treatment planning, allowing dental professionals to address potential complications proactively. B2B buyers should consider products that promote gum health and stability to prevent recession, enhancing the longevity of implants.
Aesthetic Failures
Aesthetic failure images focus on misalignment, color discrepancies, and unnatural appearances of dental implants. These visuals are essential for cosmetic dentistry, guiding practitioners in making necessary adjustments for improved outcomes. For B2B buyers, understanding aesthetic failures can inform purchasing decisions, emphasizing the importance of selecting high-quality, aesthetically pleasing dental solutions to meet patient expectations.
Related Video: Removal Of Infected/Failed Dental Implant – All-on-4 – Brighton Implant Clinic
Key Industrial Applications of pictures of dental implants that failed
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of pictures of dental implants that failed | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dental Implant Manufacturing | Quality control assessments for implant design and materials | Ensures high standards, reduces failure rates, improves reputation | Source images from verified cases, ensure clear documentation of failures |
| Dental Education and Training | Training materials for dental professionals | Enhances understanding of potential complications, improves skills | Obtain high-resolution images, consider diverse case scenarios |
| Dental Insurance Providers | Risk assessment and claims processing related to implant failures | Facilitates accurate underwriting, reduces fraudulent claims | Collaborate with dental professionals for accurate case documentation |
| Dental Marketing and Advertising | Promotional content highlighting expertise in handling failed implants | Builds trust with potential patients, showcases successful outcomes | Use authentic images, ensure compliance with advertising standards |
| Research and Development | Studies on implant failure rates and prevention methods | Drives innovation, improves product development | Partner with academic institutions for access to comprehensive data |
Industry Applications Overview
Dental Implant Manufacturing
In the dental implant manufacturing sector, pictures of failed dental implants are invaluable for quality control assessments. By analyzing real-life failures, manufacturers can identify design flaws or material weaknesses, leading to enhanced product reliability. For international buyers, sourcing these images from credible dental clinics or labs ensures that they are basing their procurement decisions on comprehensive data that reflects true market conditions.
Dental Education and Training
For dental education, images of failed implants serve as critical training tools. They provide dental students and professionals with visual case studies that illustrate the complexities of implant placement and potential complications. International buyers, particularly those from developing regions, should seek high-resolution images that depict diverse scenarios to enrich their training programs and improve the overall quality of dental care.
Dental Insurance Providers
In the dental insurance industry, pictures of failed implants are essential for risk assessment and claims processing. These images help insurers understand the circumstances surrounding implant failures, facilitating more accurate underwriting and reducing the incidence of fraudulent claims. Buyers in this sector should focus on collaborating with dental professionals to obtain authentic case documentation that supports their risk management strategies.
Dental Marketing and Advertising
In marketing, showcasing pictures of failed dental implants can effectively highlight a clinic’s expertise in managing complications. This strategy builds trust with potential patients by demonstrating a commitment to transparency and patient care. International marketers should ensure that the images used are authentic and comply with local advertising regulations to maintain credibility and avoid legal issues.
Research and Development
In research and development, images of failed dental implants are crucial for conducting studies on failure rates and prevention strategies. These images provide empirical evidence that can drive innovation and improve product offerings. International buyers, especially those in emerging markets, should consider partnering with academic institutions to access a broader range of data and insights that can inform their product development efforts.
Related Video: 3 Types of Dental Implants and Surface treatments explained!
Strategic Material Selection Guide for pictures of dental implants that failed
When selecting materials for dental implants, particularly in the context of failed implants, it is crucial for international B2B buyers to understand the properties, advantages, disadvantages, and specific regional considerations associated with each material. Here, we analyze four common materials used in dental implants: titanium, zirconia, stainless steel, and PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone).
Titanium
Key Properties: Titanium is known for its excellent biocompatibility and corrosion resistance, making it a preferred choice for dental implants. It can withstand the pressures exerted during chewing and is resistant to the acidic environment of the mouth.
Pros & Cons: The primary advantage of titanium is its durability and strength, which allows for long-term use. However, it can be more expensive than other materials and may require complex manufacturing processes, especially when creating custom implants.
Impact on Application: Titanium is highly compatible with human bone, promoting osseointegration, which is essential for implant stability. However, it may not be suitable for patients with metal allergies.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure compliance with international standards such as ASTM F136 for titanium alloys. In regions like the Middle East and Europe, where regulatory scrutiny is high, adherence to these standards is critical.
Zirconia
Key Properties: Zirconia is a ceramic material known for its aesthetic appeal and strength. It exhibits good resistance to wear and is less prone to corrosion compared to metals.
Pros & Cons: Zirconia offers excellent aesthetic results, making it ideal for visible dental work. However, it is generally more brittle than titanium, which can lead to fractures under excessive stress.
Impact on Application: This material is particularly suitable for anterior implants where aesthetics are paramount. However, its brittleness may limit its use in posterior applications where greater forces are applied.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should be aware of the varying standards for ceramic materials in different regions, such as ISO 6872 for dental ceramics. Compliance with these standards is essential, particularly in Europe where regulations are stringent.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its strength and resistance to corrosion. It is often used in temporary implants or in situations where cost is a significant factor.
Pros & Cons: The main advantage of stainless steel is its low cost and ease of manufacturing. However, it is less biocompatible than titanium and zirconia, which can lead to higher rates of implant failure.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for temporary applications or for patients who may not be candidates for more permanent solutions. Its use is limited in long-term implants due to potential corrosion and allergic reactions.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that the stainless steel used complies with standards such as ASTM F138. In regions like Africa and South America, where cost may be a significant factor, the affordability of stainless steel can be appealing, but durability must be considered.
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone)
Key Properties: PEEK is a high-performance polymer known for its excellent mechanical properties and biocompatibility. It is resistant to high temperatures and has a low density.
Pros & Cons: PEEK offers a lightweight alternative to metals and can be molded into complex shapes, which is advantageous for custom implants. However, it is generally not as strong as titanium and may not be suitable for all implant applications.
Impact on Application: PEEK is particularly useful in cases where flexibility is required, such as in certain prosthetic applications. Its thermal resistance makes it suitable for environments with varying temperatures.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ISO 10993 for biocompatibility is crucial for PEEK materials. Buyers in the Middle East and Europe should also consider the material’s long-term performance in dental applications.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for pictures of dental implants that failed | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium | Permanent dental implants | Excellent biocompatibility | Higher cost | High |
| Zirconia | Aesthetic anterior implants | Superior aesthetics | Brittle under stress | Med |
| Stainless Steel | Temporary implants | Cost-effective | Less biocompatible | Low |
| PEEK | Custom prosthetics | Lightweight and flexible | Lower strength than metals | Med |
This guide provides a comprehensive overview of material options for dental implants, helping international B2B buyers make informed decisions based on performance, cost, and regional compliance standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for pictures of dental implants that failed
Manufacturing dental implants requires a rigorous and precise approach to ensure quality and performance. For B2B buyers, particularly those from regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures in place is crucial. This not only helps in making informed purchasing decisions but also aids in mitigating risks associated with implant failures.
Manufacturing Processes for Dental Implants
The manufacturing of dental implants typically involves several key stages, each essential for achieving high-quality products. Below are the main stages:
1. Material Preparation
The choice of materials is critical in dental implant manufacturing. Common materials include titanium, titanium alloys, and ceramics, known for their biocompatibility and strength.
- Material Selection: Titanium is favored for its corrosion resistance and ability to integrate with bone (osseointegration).
- Surface Treatment: Techniques like sandblasting, acid etching, or anodization are employed to enhance the surface characteristics, improving osseointegration and reducing the risk of implant failure.
2. Forming
This stage involves shaping the implant components, which typically includes the implant body, abutments, and crowns.
- CNC Machining: Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machines are extensively used to achieve precision in shaping implants.
- Molding and Casting: For certain designs, especially those with complex geometries, molding techniques may be utilized.
3. Assembly
Once individual components are formed, they are assembled into the final product.
- Manual and Automated Processes: Depending on the complexity, assembly may involve both manual and automated processes to ensure accuracy and consistency.
- Quality Checks: Each assembly stage should include checks to identify defects early in the process.
4. Finishing
The finishing stage focuses on enhancing the surface quality and preparing the implants for sterilization.
- Polishing and Coating: Implants may undergo polishing for a smooth finish or coating with bioactive materials to promote integration with the bone.
- Sterilization: Final products are sterilized using methods such as autoclaving or gamma radiation to eliminate any microbial contamination.
Quality Assurance Measures
Quality assurance is paramount in the dental implant industry, as failures can lead to serious health implications for patients. Here are the key aspects of quality assurance:
International Standards
Compliance with international standards ensures that dental implants are safe and effective.
- ISO 9001: This standard focuses on quality management systems, ensuring consistent product quality and continuous improvement.
- ISO 13485: Specific to medical devices, this standard addresses the requirements for a comprehensive quality management system for the design and manufacture of dental implants.
- CE Marking: In Europe, dental implants must meet the requirements of the Medical Devices Directive (MDD) to obtain CE marking, indicating compliance with safety and efficacy standards.
Industry-Specific Standards
In addition to general ISO standards, there are specific standards relevant to dental implants.
- API Standards: For materials and components, adherence to American Petroleum Institute (API) standards can also be relevant, especially for materials used in dental applications.
- ASTM Standards: The American Society for Testing and Materials (ASTM) provides guidelines for testing the physical properties of dental materials.
Quality Control Checkpoints
To ensure the highest quality, several checkpoints are integrated into the manufacturing process:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Raw materials are inspected upon arrival to ensure they meet specified standards.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring is conducted during the manufacturing process, including checks on dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Before products leave the facility, they undergo a comprehensive final inspection, which may include functional testing and performance evaluations.
Testing Methods
Various testing methods are employed to validate the quality and performance of dental implants:
- Mechanical Testing: This includes tensile, compression, and fatigue testing to assess strength and durability.
- Biocompatibility Testing: Implants are tested for biological response to ensure they do not provoke adverse reactions in patients.
- Sterility Testing: Ensures that the sterilization process has effectively eliminated any microbial presence.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
B2B buyers must be proactive in verifying the quality control measures of their suppliers. Here are some strategies:
- Supplier Audits: Conduct regular audits of suppliers to assess compliance with quality standards and practices.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation of their quality control processes, including results from internal and external audits.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging third-party inspection agencies can provide an unbiased assessment of the supplier’s quality management practices.
Nuances for International Buyers
For buyers in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, it is essential to be aware of specific nuances related to quality control:
- Regulatory Compliance: Different regions have varying regulatory requirements. Understanding local regulations is crucial for compliance and market entry.
- Cultural Considerations: Engage with suppliers who understand regional market needs and can provide culturally sensitive products and services.
- Logistics and Supply Chain: Ensure that logistics partners are reliable and capable of maintaining product integrity during transportation, especially for sterile medical devices.
In conclusion, understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for dental implants is vital for B2B buyers. By focusing on suppliers that adhere to international standards and demonstrating robust quality control practices, buyers can significantly reduce the risk of implant failures and enhance patient outcomes.
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for pictures of dental implants that failed Sourcing
Understanding Cost Components for Sourcing Pictures of Failed Dental Implants
When sourcing pictures of failed dental implants, B2B buyers must understand the various cost components that contribute to the overall pricing. This includes materials, labor, manufacturing overhead, tooling, quality control (QC), logistics, and margin. Each of these factors can significantly influence the final price of the product.
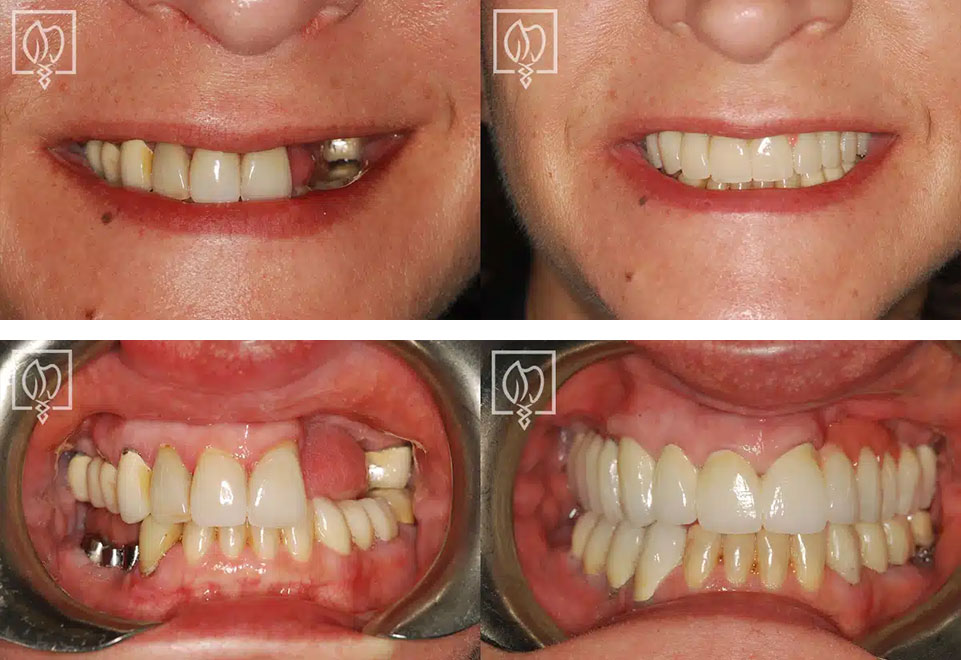
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Materials: The choice of materials used in the imaging process—such as high-resolution cameras or specialized imaging software—can vary widely in cost. Premium equipment may yield better quality images but at a higher initial investment.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for capturing high-quality images and processing them for use. The cost of labor can fluctuate based on regional wage standards, particularly between different continents such as Africa, Europe, and the Middle East.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This encompasses the indirect costs associated with production, such as utilities and administrative expenses. Companies with efficient operational practices may offer more competitive pricing.
-
Tooling: Specific tools or software needed for image processing may add to the initial costs. This includes licenses for software that enhances image quality or manages the images effectively.
-
Quality Control (QC): Implementing stringent QC measures ensures that the images meet industry standards. However, these processes can increase costs. Buyers should inquire about the QC processes used by suppliers to ensure value.
-
Logistics: Costs associated with shipping and handling can vary based on the distance between the supplier and the buyer, as well as the chosen Incoterms. Understanding these logistics costs is crucial for budgeting.
-
Margin: Suppliers will typically include a margin to cover risks and profit. This can vary widely based on market conditions and competition.
Price Influencers
Several factors can influence pricing in the sourcing of images for failed dental implants:
-
Volume/MOQ: Bulk orders generally lead to lower per-unit costs. Buyers should consider their needs carefully to negotiate better terms based on volume.
-
Specifications/Customization: Custom requirements for image formats or quality can increase costs. Clearly defining specifications can help avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Materials: The type of technology used for imaging can affect the price. Higher-quality imaging technologies may command a premium.
-
Quality/Certifications: Suppliers with recognized certifications may charge more due to the assurance of quality. Buyers should weigh the value of these certifications against their budget.
-
Supplier Factors: The reputation and experience of the supplier can affect pricing. Established suppliers may offer higher-quality images but at a premium.
-
Incoterms: Understanding the delivery terms and responsibilities can prevent misunderstandings and additional costs during shipping.
Buyer Tips
For international B2B buyers, particularly from regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, several strategies can enhance cost-efficiency:
-
Negotiation: Always negotiate prices, especially for larger orders. Suppliers may be willing to adjust their pricing based on order size or long-term commitments.
-
Total Cost of Ownership (TCO): Consider not just the purchase price but also the potential costs associated with quality issues, returns, or additional processing. TCO analysis can lead to better long-term decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances: Be aware that prices may vary significantly based on region. Cultural differences in business practices can also affect negotiations. Understanding local market conditions can provide leverage.
-
Research Suppliers: Investigate potential suppliers thoroughly. Look for reviews, case studies, or testimonials to ensure they meet your quality expectations.
Disclaimer
Prices mentioned are indicative and may vary based on market conditions, supplier negotiations, and specific buyer requirements. Always obtain quotes tailored to your unique needs.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for pictures of dental implants that failed
Critical Technical Properties of Failed Dental Implants
Understanding the technical properties of dental implants is crucial for B2B buyers, particularly when evaluating cases of failure. Here are key specifications that should be considered:
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The quality and type of materials used, such as titanium or zirconia, which are common for dental implants.
– Importance: High-grade materials ensure durability and biocompatibility, reducing the risk of rejection or infection. Buyers should prioritize suppliers who provide implants with verified material certifications. -
Tolerance Levels
– Definition: The acceptable limits of variation in implant dimensions, which must be adhered to for proper fitting.
– Importance: Tight tolerances are essential to avoid complications such as misalignment or loosening. Implants with poor tolerances can lead to increased failure rates, making it critical for buyers to verify manufacturing standards. -
Coating Specifications
– Definition: The surface treatments applied to implants, such as hydroxyapatite or titanium plasma spray, to enhance osseointegration.
– Importance: Coatings can significantly affect the implant’s integration with bone. B2B buyers should consider suppliers who utilize advanced coating technologies to improve success rates. -
Load-Bearing Capacity
– Definition: The maximum load an implant can withstand during chewing and other functions.
– Importance: Understanding the load-bearing specifications helps in selecting appropriate implants for various applications, especially in cases requiring full arch restorations. Buyers should assess load ratings to ensure they meet clinical requirements. -
Failure Rate Statistics
– Definition: Data related to the incidence of implant failures within specific time frames, often expressed as a percentage.
– Importance: Access to historical failure rates allows buyers to make informed decisions about the reliability of products. Suppliers should provide transparent data to facilitate comparisons. -
Regulatory Compliance
– Definition: Adherence to international standards and regulations, such as ISO 13485 for medical devices.
– Importance: Compliance ensures that the implants meet safety and quality standards. Buyers in different regions, such as Europe and the Middle East, should verify that suppliers comply with local regulations.
Common Trade Terms in Dental Implant Procurement
Familiarity with industry terminology is vital for effective communication and negotiation. Here are some essential terms:
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships can help buyers identify reliable sources for dental implants and components, ensuring product quality and support. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their operational needs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document used to solicit price bids from suppliers for specific products or services.
– Importance: An RFQ allows buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, facilitating better purchasing decisions.
-
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined international trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce (ICC).
– Importance: Incoterms clarify the responsibilities of buyers and sellers in shipping and delivery. Understanding these terms helps buyers mitigate risks related to transport and customs. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time taken from placing an order until the goods are delivered.
– Importance: Knowing the lead time is crucial for planning and ensuring timely availability of products, especially in urgent situations involving failed implants. -
Warranty Period
– Definition: The timeframe during which a supplier guarantees the product against defects.
– Importance: A clear warranty policy provides buyers with assurance regarding product quality and support in case of failures. Buyers should seek comprehensive warranty terms to protect their investments.
By understanding these properties and terms, international B2B buyers can navigate the complexities of purchasing dental implants more effectively, ensuring they select reliable products and suppliers that meet their clinical and operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the pictures of dental implants that failed Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global dental implant market is witnessing significant growth, driven by an increasing aging population and rising awareness about oral health. B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are particularly focused on sourcing high-quality dental implant products, including those related to failed implants. Key trends include the integration of advanced technologies such as 3D printing and computer-aided design (CAD) in the manufacturing of dental implants. These technologies not only enhance precision but also reduce production costs, making it an attractive option for international buyers.
Emerging sourcing trends indicate a shift towards digital platforms that facilitate easier access to suppliers and a more streamlined procurement process. Buyers are increasingly relying on online marketplaces and supply chain management software to identify reputable manufacturers. Additionally, there is a growing emphasis on collaboration between dental professionals and manufacturers to ensure that products meet specific clinical needs. This collaborative approach fosters innovation and enhances the quality of dental implants, reducing the likelihood of failures.
Market dynamics are also influenced by regulatory changes and increasing competition among manufacturers. For instance, regions like the EU have stringent regulations concerning dental products, compelling suppliers to adhere to high safety and quality standards. As a result, B2B buyers must remain vigilant and conduct thorough due diligence when selecting suppliers to ensure compliance with local regulations.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a critical factor in the sourcing of dental implants, particularly in light of growing environmental concerns. The production and disposal of dental implants can contribute to environmental degradation, making it essential for B2B buyers to consider the ecological footprint of their procurement decisions. Ethical sourcing practices, such as selecting manufacturers that prioritize sustainable materials and processes, are gaining traction.
Buyers should seek suppliers that utilize eco-friendly materials and have certifications like ISO 14001, which indicates a commitment to environmental management. Additionally, the use of recyclable or biodegradable materials in the packaging of dental implants can further mitigate environmental impact.
Incorporating sustainability into the procurement process not only aligns with corporate social responsibility (CSR) goals but also enhances brand reputation in a market increasingly attentive to ethical practices. By prioritizing sustainable sourcing, B2B buyers can contribute to a healthier planet while ensuring the quality and reliability of the dental implants they procure.
Brief Evolution/History
The evolution of dental implants dates back to ancient civilizations, but significant advancements began in the mid-20th century with the introduction of titanium implants. Over the decades, the technology has evolved, leading to improved materials, designs, and surgical techniques. The focus has shifted from merely placing implants to ensuring their longevity and minimizing the risk of failures.
In recent years, the rise of digital dentistry has transformed the landscape, enabling precise planning and execution of implant procedures. As a result, the conversation around failed dental implants has shifted towards prevention and innovative solutions to address failures when they occur. This historical context is vital for B2B buyers, as it highlights the importance of sourcing from manufacturers who are at the forefront of technological advancements and quality assurance.
Related Video: Tariffs will cause ‘massive shock’ to U.S. cost of living and will reshape global trade: Expert
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of pictures of dental implants that failed
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for pictures of failed dental implants?
When vetting suppliers, assess their experience and expertise in dental photography. Look for portfolios showcasing a variety of cases, especially those involving failed implants. Verify their adherence to international standards and certifications. Request references from previous clients to gauge reliability and quality. Additionally, consider their communication style and responsiveness, as these factors can significantly impact your collaboration. -
Can I request customized images of failed dental implants?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for images. You can specify the type of failures you want to showcase, such as peri-implantitis or mechanical failures. Ensure that the supplier understands your requirements and is capable of delivering high-resolution images that meet your marketing or educational needs. Discuss any specific angles, lighting, or contextual elements that should be included to enhance the visual impact. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for sourcing these images?
MOQs can vary widely based on the supplier and the complexity of the images required. Some may allow single image purchases, while others could have a MOQ of 10-20 images. Lead times also depend on the supplier’s workload and the nature of the images requested. Generally, expect a timeframe of 1-4 weeks from order placement to delivery. Always confirm these details upfront to avoid delays in your project timelines. -
What payment methods are typically accepted for purchasing images?
Payment methods depend on the supplier’s policies but usually include options like bank transfers, credit cards, and online payment platforms (e.g., PayPal). For international transactions, consider suppliers that accept payments in multiple currencies or offer favorable exchange rates. It’s also prudent to inquire about any deposit requirements before processing the order, especially for larger purchases. -
How do I ensure the quality of the images I receive?
To ensure image quality, request samples before finalizing your order. Discuss the resolution and format of the images—high-resolution JPEG or TIFF files are often preferred for print and digital use. Verify that the supplier has a quality assurance process in place, which may include reviews and edits before final delivery. Additionally, consider asking about any certifications or standards they adhere to in their photography practices. -
What logistics considerations should I be aware of when sourcing these images internationally?
When sourcing images internationally, consider factors such as shipping costs, import duties, and delivery timelines. Ensure that your supplier provides digital files to eliminate physical shipping concerns. If physical materials are involved, confirm the logistics arrangements, including tracking and insurance options. Understanding customs regulations in your country is also crucial to prevent unexpected delays or costs. -
How can I resolve disputes with suppliers regarding the images?
To resolve disputes effectively, maintain clear and documented communication throughout the purchasing process. Establish a contract that outlines deliverables, timelines, and dispute resolution procedures. If an issue arises, promptly communicate your concerns and seek a mutually agreeable solution. Many suppliers are willing to negotiate or offer refunds for unsatisfactory products, but having a clear agreement can facilitate this process. -
What certifications or quality standards should I look for in suppliers?
Look for suppliers who comply with international quality standards, such as ISO certifications. Additionally, inquire whether they have specific certifications related to dental imaging or medical photography. These certifications indicate a commitment to quality and professionalism. Suppliers should also be willing to provide documentation verifying their compliance with relevant health and safety regulations, particularly if the images are to be used in clinical settings.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for pictures of dental implants that failed
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of images related to failed dental implants serves as a critical resource for international B2B buyers. Understanding the nuances of implant failure, including common causes such as improper placement and material deficiencies, can empower buyers to make informed decisions when sourcing products or services. High-quality images not only illustrate the severity of potential issues but also highlight the importance of choosing experienced professionals to mitigate risks associated with dental implant procedures.
As buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe explore options, they should prioritize suppliers who provide comprehensive case studies, before-and-after galleries, and educational resources on the intricacies of dental implants. Engaging with reputable providers can lead to better outcomes and improved patient satisfaction.
Moving forward, international buyers are encouraged to leverage this guide as a tool for enhancing their procurement strategies. By aligning with industry leaders who prioritize quality and expertise, businesses can ensure their clients receive the best possible care and outcomes in dental implant procedures. Embrace this opportunity to elevate your sourcing strategy and improve your offerings in the dental market.
