Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for zirconia dental implants
In an era marked by rapid advancements in dental technology, zirconia dental implants have emerged as a cornerstone in the quest for durable, aesthetically pleasing, and biocompatible restoration solutions. B2B buyers in regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are increasingly recognizing the critical importance of sourcing high-quality zirconia implants to meet the growing demand for long-lasting dental solutions. These advanced ceramics not only offer exceptional strength and wear resistance but also mimic the natural appearance of teeth, making them an ideal choice for both patients and practitioners.
This comprehensive guide delves into the multifaceted world of zirconia dental implants, providing in-depth insights into various types of zirconia, including monolithic, layered, and hybrid options, each tailored for specific clinical applications. It explores manufacturing processes and stringent quality control measures essential for ensuring product reliability. Buyers will gain valuable knowledge about leading suppliers, cost considerations, and emerging market trends that influence procurement strategies.
By addressing common inquiries and uncertainties, this guide empowers international B2B buyers to make informed sourcing decisions. Understanding the global landscape of zirconia dental implants not only reduces risks associated with procurement but also unlocks new competitive advantages, enabling businesses to thrive in this dynamic market. Engaging with this resource will equip buyers to navigate the complexities of sourcing zirconia implants effectively, ensuring they meet both quality and regulatory standards.
Understanding zirconia dental implants Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| Monolithic Zirconia | Single block structure, high strength, and durability | Dental crowns, bridges, molars | Pros: Excellent wear resistance; Cons: Limited aesthetic options |
| Layered Zirconia | Zirconia core with porcelain layer for aesthetics | Anterior crowns, cosmetic restorations | Pros: Superior aesthetics; Cons: More complex manufacturing |
| Hybrid Zirconia | Combination of zirconia with other advanced materials | High-demand restorations, implants | Pros: Enhanced performance; Cons: Cost variability |
| Fully Stabilized Zirconia | Maintains stable phase across temperature ranges | Biomedical implants, precision components | Pros: Exceptional durability; Cons: Higher material costs |
| Partially Stabilized Zirconia | Mixture of phases for optimized toughness | Industrial applications, dental implants | Pros: Good strength; Cons: Phase transformation risks |
Monolithic Zirconia
Monolithic zirconia is crafted from a single block of zirconia, providing exceptional strength and durability, making it ideal for posterior crowns where high chewing forces are prevalent. Its solid structure minimizes the risk of fracture, ensuring longevity in demanding applications. B2B buyers should consider the balance between strength and aesthetic needs, as this type may not offer the same visual appeal as layered options.
Layered Zirconia
Layered zirconia combines a zirconia core with an outer layer of porcelain, delivering both strength and aesthetic appeal. This design is particularly suited for anterior crowns, where appearance is crucial. B2B buyers should weigh the benefits of superior aesthetics against the complexities of manufacturing, which may affect cost and lead times. Customization options are also a significant consideration for meeting patient-specific needs.
Hybrid Zirconia
Hybrid zirconia incorporates other advanced materials, such as silicon nitride, enhancing its mechanical properties and thermal resistance. This type is increasingly used in high-demand environments, including dental restorations and biomedical applications. Buyers should assess the performance benefits against cost variations, as hybrid materials can be priced differently based on their composition and manufacturing processes.
Fully Stabilized Zirconia
Fully stabilized zirconia is engineered to maintain a stable phase across a wide temperature range, ensuring durability and chemical inertness. This type is often utilized in biomedical implants and precision engineering applications. B2B purchasers must consider the higher raw material costs and the necessity of rigorous quality control to ensure product reliability and compliance with industry standards.
Partially Stabilized Zirconia
Partially stabilized zirconia features a blend of phases optimized for toughness and strength, making it versatile for various applications, including dental implants and industrial components. While it offers good mechanical properties, buyers should be cautious of potential phase transformation over time, which can compromise stability. Evaluating supplier consistency and material specifications is crucial for minimizing risks associated with this type.
Related Video: All about ZIRCONIA CROWNS – (Types/Phase transformation/Transformation Toughening/Prep Guidelines)
Key Industrial Applications of zirconia dental implants
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of zirconia dental implants | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dental Clinics | Use of monolithic zirconia for crowns and bridges | High durability and aesthetic appeal, leading to increased patient satisfaction and retention | Quality control, certifications, and supplier reliability |
| Prosthodontics | Layered zirconia for anterior restorations | Combines strength and aesthetics, enhancing service offerings and patient outcomes | Material compatibility, customization options, and lead times |
| Dental Laboratories | Hybrid zirconia for custom restorations | Enhanced performance and versatility, allowing for innovative solutions in complex cases | Sourcing advanced materials, processing capabilities, and technical support |
| Medical Device Manufacturers | Biocompatible zirconia implants | Long-lasting, safe solutions that reduce patient complications and improve outcomes | Regulatory compliance, testing standards, and traceability |
| Research Institutions | Zirconia for experimental dental applications | Opportunities for innovation and development of next-generation dental solutions | Access to high-quality materials, collaboration with suppliers, and funding for research |
Dental Clinics
Zirconia dental implants are increasingly used in dental clinics for monolithic crowns and bridges. These implants offer exceptional durability, making them ideal for high-wear areas in the mouth, such as molars. The aesthetic quality of zirconia closely resembles natural teeth, which enhances patient satisfaction and retention rates. For B2B buyers in the dental sector, sourcing high-quality zirconia that meets stringent industry standards is crucial. Ensuring that suppliers provide certifications and maintain rigorous quality control measures can mitigate risks associated with material failure.
Prosthodontics
In prosthodontics, layered zirconia is favored for anterior restorations where aesthetics are paramount. This application combines the strength of zirconia with the natural appearance of porcelain, allowing for custom solutions that meet patient expectations. B2B buyers must prioritize sourcing zirconia that offers excellent material compatibility and customization options to cater to diverse patient needs. Additionally, understanding lead times and supplier capabilities can help streamline the procurement process and enhance service delivery in prosthodontics.
Dental Laboratories
Dental laboratories benefit from using hybrid zirconia in custom restorations. This advanced material blends zirconia with other ceramics, providing enhanced mechanical properties and thermal resistance. Such versatility is essential for addressing complex dental cases that require innovative solutions. For international buyers, sourcing advanced materials with proven performance is vital. Establishing relationships with suppliers who offer technical support and have robust processing capabilities can facilitate the development of high-quality dental products.
Medical Device Manufacturers
In the medical device sector, biocompatible zirconia implants are crucial for ensuring patient safety and longevity. These implants minimize complications, making them a preferred choice for dental professionals. B2B buyers must focus on regulatory compliance and testing standards when sourcing zirconia materials for implants. Ensuring traceability throughout the supply chain can also enhance the credibility of the final product, making it more appealing to healthcare providers and patients alike.
Research Institutions
Research institutions utilize zirconia for experimental dental applications, exploring new ways to enhance dental solutions. This innovative use of zirconia opens opportunities for developing next-generation products that can significantly improve patient outcomes. B2B buyers in research must access high-quality materials and establish collaborations with suppliers who understand the unique needs of experimental work. Funding for research and development initiatives is also critical for advancing these applications and bringing new solutions to market.
Related Video: The Benefits of Zirconia Implants: Explained
Strategic Material Selection Guide for zirconia dental implants
Analysis of Common Materials for Zirconia Dental Implants
When selecting materials for zirconia dental implants, B2B buyers must consider various types of zirconia, each with unique properties and applications. Here, we analyze four common materials used in zirconia dental implants, focusing on their performance characteristics, advantages, disadvantages, and specific considerations for international buyers.
1. Monolithic Zirconia
Key Properties:
Monolithic zirconia is manufactured from a single block of zirconia, which provides exceptional strength and durability. It exhibits high wear resistance and can withstand significant chewing forces, making it ideal for posterior crowns.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of monolithic zirconia is its superior strength and fracture toughness, which makes it highly resistant to chipping or cracking. However, its aesthetic appeal is limited compared to layered options, as it lacks the translucency of porcelain. Additionally, while it is cost-effective due to the absence of layering, the initial investment can still be higher than traditional materials.
Impact on Application:
Monolithic zirconia is particularly effective in high-stress environments, such as molars, where durability is paramount. Its robust nature ensures longevity, but buyers must consider its aesthetic limitations for visible restorations.
Considerations for International Buyers:
B2B buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure compliance with local dental standards and regulations. Familiarity with ASTM and ISO standards will facilitate smoother procurement processes.
2. Layered Zirconia
Key Properties:
Layered zirconia combines a zirconia core with a porcelain outer layer, providing both strength and aesthetic appeal. This material is designed to mimic the natural appearance of teeth, making it suitable for anterior crowns.
Pros & Cons:
The main advantage of layered zirconia is its aesthetic quality, as the porcelain layer offers translucency and color matching capabilities. However, the layering process can introduce manufacturing complexity and increase costs, making it less suitable for budget-conscious buyers.
Impact on Application:
Layered zirconia is ideal for visible dental restorations, where aesthetics are crucial. However, the bond between the layers can be a potential failure point under extreme stress, necessitating careful selection of the manufacturing process.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should verify that suppliers adhere to quality control measures to ensure the integrity of the layered structure. Understanding local preferences for aesthetics can also guide purchasing decisions.
3. Hybrid Zirconia
Key Properties:
Hybrid zirconia is a composite material that blends zirconia with other advanced ceramics, enhancing its mechanical and thermal properties. This versatility allows for improved performance in demanding applications.
Pros & Cons:
The key advantage of hybrid zirconia is its adaptability, providing a balance between strength and aesthetic qualities. However, the complexity of manufacturing hybrid materials can lead to increased costs and variability in product quality.
Impact on Application:
Hybrid zirconia is suitable for a range of dental applications, particularly where both durability and aesthetics are needed. Its enhanced thermal resistance makes it ideal for high-demand environments.
Considerations for International Buyers:
Buyers should prioritize suppliers with proven expertise in hybrid materials to ensure consistent quality. Additionally, understanding the local market’s acceptance of hybrid solutions can influence purchasing strategies.
4. Fully Stabilized Zirconia
Key Properties:
Fully stabilized zirconia maintains its tetragonal or cubic phase across varying temperatures, offering exceptional durability and chemical stability. This property makes it suitable for both dental and industrial applications.
Pros & Cons:
The primary advantage of fully stabilized zirconia is its high performance in demanding environments, ensuring long-term reliability. However, its higher raw material costs and complex processing requirements can deter some buyers.
Impact on Application:
This material is particularly effective in biomedical implants and precision engineering, where durability is critical. Its biocompatibility further enhances its appeal for dental applications.
Considerations for International Buyers:
International buyers must ensure compliance with stringent regulations for biomedical materials. Familiarity with certification processes and quality assurance protocols is essential for successful procurement.
Summary Table
| Material | Typical Use Case for zirconia dental implants | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Monolithic Zirconia | Posterior crowns | Exceptional strength and durability | Limited aesthetic appeal | Medium |
| Layered Zirconia | Anterior crowns | Aesthetic quality | Manufacturing complexity | High |
| Hybrid Zirconia | Versatile dental applications | Adaptability and enhanced performance | Increased costs and variability | Medium |
| Fully Stabilized Zirconia | Biomedical implants | High durability and chemical stability | Higher raw material costs | High |
This strategic material selection guide equips international B2B buyers with the insights necessary to make informed decisions regarding zirconia dental implants, ensuring they align with both performance requirements and market standards.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for zirconia dental implants
In the production of zirconia dental implants, a meticulous approach to manufacturing and quality assurance is essential to ensure optimal performance and longevity of the final product. This section delves into the typical manufacturing processes and quality control measures that B2B buyers should consider when sourcing zirconia dental implants, particularly in the context of international markets such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
Manufacturing Processes for Zirconia Dental Implants
The manufacturing process for zirconia dental implants consists of several critical stages, each requiring precision and adherence to industry standards.
1. Material Preparation
The first step involves the preparation of zirconia powder (ZrO₂), which is typically obtained through various processing methods such as the melt-quenching method or sol-gel process. The quality of the powder is paramount, as it affects the mechanical properties of the final product. Key considerations during this phase include:
- Purity: Ensuring the zirconia powder is free from contaminants that could compromise the structural integrity of the implants.
- Particle Size Distribution: The morphology of the powder influences sintering behavior and final density.
2. Forming
Once the zirconia powder is prepared, it undergoes a forming process. There are several techniques employed, including:
- Pressing: The powder is compacted into molds under high pressure, which helps shape the initial form of the dental implant.
- Injection Molding: This method allows for more complex geometries and is ideal for mass production. The powdered zirconia is mixed with a binder and injected into molds.
- 3D Printing: Emerging as a cutting-edge technique, 3D printing allows for custom shapes and intricate designs, enhancing the adaptability of implants to individual patient needs.
3. Sintering
Sintering is a critical phase where the shaped zirconia undergoes heat treatment at high temperatures (typically between 1300°C and 1600°C). This process enhances the density and mechanical strength of the implant. Key points include:
- Controlled Atmosphere: The sintering process must be conducted in a controlled environment to prevent oxidation or contamination.
- Sintering Time and Temperature: Precise control over these parameters is crucial to achieving the desired microstructure.
4. Assembly
In cases where dental implants consist of multiple components (such as abutments), assembly occurs after sintering. This may involve:
- Fitting and Bonding: Components are fitted together, and bonding agents may be used to ensure structural integrity.
- Surface Treatment: Additional surface treatments, such as sandblasting or acid etching, can enhance osseointegration by improving surface roughness.
5. Finishing
The final stage involves finishing processes to ensure the implants meet specific aesthetic and functional criteria. Techniques include:
- Polishing: To achieve a smooth surface that mimics natural teeth.
- Coating: Application of biocompatible coatings, such as CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition) coatings, to enhance wear resistance and biocompatibility.
Quality Assurance Protocols
Quality assurance (QA) is integral to the manufacturing of zirconia dental implants, ensuring compliance with both international standards and industry-specific regulations.
Relevant International Standards
B2B buyers should be aware of the following standards that govern the quality of dental implants:
- ISO 9001: A standard focused on quality management systems, ensuring consistent product quality and customer satisfaction.
- ISO 13485: Specifically for medical devices, this standard outlines requirements for a quality management system that demonstrates the ability to provide medical devices and related services that consistently meet customer and regulatory requirements.
- CE Marking: For products sold in Europe, CE marking indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control (QC) checkpoints are implemented throughout the manufacturing process to ensure that each implant meets the required specifications. Key QC checkpoints include:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Inspection of raw materials and components upon arrival to verify compliance with specifications.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing stages to detect defects early.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive inspection of the finished product, including dimensional checks and mechanical property assessments.
Common Testing Methods
Several testing methods are employed to assess the quality of zirconia dental implants:
- Mechanical Testing: Tensile strength, hardness, and fracture toughness tests to evaluate performance under stress.
- Biocompatibility Testing: Ensures that materials do not induce an adverse reaction in biological systems.
- Surface Roughness Measurement: Critical for assessing osseointegration potential.
Verification of Supplier Quality Control
For international B2B buyers, verifying the quality control processes of suppliers is crucial. Strategies include:
- Supplier Audits: Conducting on-site audits to assess the manufacturing capabilities and quality management systems of suppliers.
- Requesting Quality Reports: Regularly obtaining quality control reports and documentation of testing results from suppliers.
- Third-Party Inspections: Engaging independent organizations to perform quality checks and certifications, ensuring impartial assessment.
Quality Control and Certification Nuances for International Buyers
B2B buyers from Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe must navigate various challenges related to quality assurance:
- Regulatory Variability: Different regions have distinct regulations and standards that may affect the acceptance of dental implants. Understanding local requirements is essential.
- Communication Barriers: Language and cultural differences can complicate the verification of quality standards and processes. Clear communication and documentation are key to overcoming these challenges.
- Logistical Considerations: Shipping and handling of zirconia implants require adherence to strict protocols to avoid damage or contamination during transit. Buyers should verify that suppliers have robust logistical processes in place.
By understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance protocols for zirconia dental implants, B2B buyers can make informed sourcing decisions that align with their specific market needs and regulatory requirements. This knowledge not only aids in selecting reliable suppliers but also enhances the overall quality of dental products offered to end-users.
Related Video: SMART Quality Control for Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for zirconia dental implants Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics associated with sourcing zirconia dental implants is crucial for international B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse markets like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. This analysis provides a comprehensive view of the key components that influence costs and pricing strategies, enabling buyers to make informed sourcing decisions.
Cost Components
-
Materials: The primary cost driver in zirconia dental implants is the raw material itself. High-quality zirconia (ZrO₂) is essential for ensuring durability and biocompatibility. Prices can vary significantly based on the purity, type (e.g., cubic, tetragonal), and sourcing location. For instance, fully stabilized zirconia typically commands a higher price due to its superior properties.
-
Labor: Skilled labor is required for the manufacturing of zirconia implants, particularly in the sintering and finishing processes. Labor costs can fluctuate depending on the region and the expertise level of the workforce. Countries with advanced manufacturing capabilities may offer higher wages but can also provide greater quality assurance.
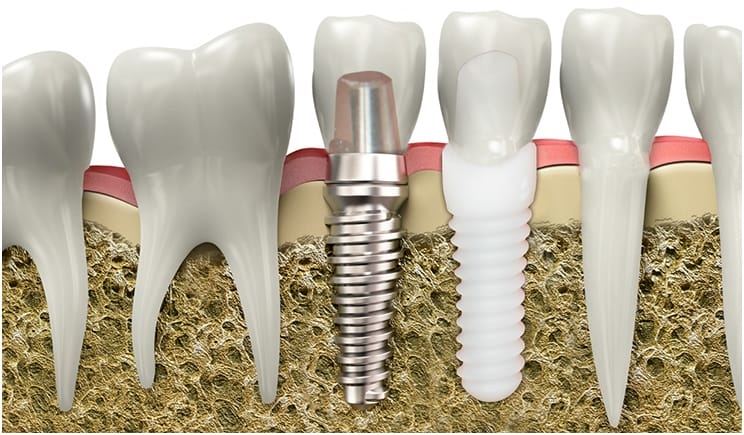
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes expenses related to facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative costs. Efficient manufacturing processes can help reduce these overheads, but they are essential for maintaining quality standards.
-
Tooling: The initial investment in tooling for producing zirconia implants can be significant. Custom molds and CNC machining tools are often necessary, and these costs should be factored into the overall pricing model.
-
Quality Control (QC): Ensuring compliance with international standards requires rigorous quality control measures. This may involve testing for mechanical properties, biocompatibility, and surface finish, which can add to the overall cost.
-
Logistics: Transportation and warehousing expenses are critical, especially for international buyers. Factors such as shipping mode, distance, and customs duties can significantly impact logistics costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers typically add a margin to cover their costs and ensure profitability. This margin can vary based on market demand, competition, and the perceived value of the product.
Price Influencers
-
Volume and Minimum Order Quantity (MOQ): Larger orders usually attract better pricing due to economies of scale. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to optimize costs.
-
Specifications and Customization: Customized implants that meet specific clinical requirements may incur additional costs. Buyers should clarify their needs upfront to avoid unexpected expenses.
-
Material Quality and Certifications: Implants that meet international quality certifications (ISO, CE marking) may be priced higher but offer assurance of safety and efficacy.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and production capacity can affect pricing. Established suppliers may charge more due to their perceived quality and service.
-
Incoterms: The choice of Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can influence the total cost of ownership, as they dictate the responsibilities of buyers and sellers regarding shipping and insurance.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engage in negotiations to secure better terms, particularly on volume pricing and payment terms. Building long-term relationships with suppliers can also lead to favorable pricing.
-
Cost Efficiency: Consider the total cost of ownership rather than just the purchase price. This includes evaluating logistics, maintenance, and potential replacements over the product lifecycle.
-
Pricing Nuances: International buyers should be aware of currency fluctuations and regional market conditions that may affect pricing. Understanding local economic factors can provide leverage in negotiations.
-
Quality Assurance: Always prioritize quality over cost. Sourcing lower-quality implants may save money initially but can lead to higher costs due to failures or complications.
Disclaimer
Prices for zirconia dental implants can vary widely based on the factors mentioned above. Buyers are encouraged to conduct thorough market research and request quotes from multiple suppliers to ensure competitive pricing.
Spotlight on Potential zirconia dental implants Manufacturers and Suppliers
This section looks at several manufacturers active in the ‘zirconia dental implants’ market. This is a representative sample for illustrative purposes; B2B buyers must conduct extensive due diligence before any transaction. Information is synthesized from public sources and general industry knowledge.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for zirconia dental implants
Zirconia dental implants are increasingly recognized for their superior properties and aesthetic appeal, making them a popular choice in the dental industry. Understanding the essential technical specifications and common trade terminology is crucial for B2B buyers to make informed purchasing decisions.
Key Technical Properties
-
Material Grade
– Definition: Refers to the classification of zirconia based on its composition and properties. Common grades include Yttria-Stabilized Zirconia (YSZ) and Fully Stabilized Zirconia (FSZ).
– B2B Importance: Different grades offer varying strength, toughness, and aesthetic qualities. Buyers must select the appropriate grade based on specific application needs, ensuring compatibility with dental procedures. -
Mechanical Strength
– Definition: The ability of zirconia to withstand stress and strain without failure, typically measured in megapascals (MPa).
– B2B Importance: High mechanical strength is critical for dental implants, especially in load-bearing situations. Suppliers should provide data on the compressive and flexural strength to ensure durability and longevity of the implants. -
Fracture Toughness
– Definition: A measure of a material’s resistance to crack propagation, expressed in MPa·m^1/2.
– B2B Importance: Zirconia’s fracture toughness is crucial in dental applications to prevent breakage under normal chewing forces. B2B buyers should evaluate suppliers based on their ability to provide materials with high fracture toughness, ensuring reliable performance. -
Biocompatibility
– Definition: The ability of zirconia to be compatible with biological tissues, minimizing adverse reactions in the body.
– B2B Importance: As dental implants are directly placed in patients, biocompatibility is vital for patient safety. Buyers should confirm that the zirconia meets international biocompatibility standards to reduce the risk of complications. -
Thermal Stability
– Definition: The ability of zirconia to maintain its properties at high temperatures, crucial in applications exposed to heat.
– B2B Importance: Thermal stability ensures that the implants will perform well in the oral environment, where temperature fluctuations can occur. B2B buyers should inquire about thermal performance data to guarantee product reliability.
Common Trade Terms
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Importance: Understanding OEM relationships helps buyers identify reliable suppliers who can provide high-quality zirconia implants under recognized brands. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Importance: Knowing the MOQ is essential for budgeting and inventory management. Buyers should negotiate MOQs to align with their purchasing capabilities and demand forecasts. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document that solicits price offers from suppliers for specified products or services.
– Importance: Submitting an RFQ allows buyers to compare prices and terms from multiple suppliers, fostering competitive pricing and better negotiation leverage. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined commercial terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce that define the responsibilities of sellers and buyers in international transactions.
– Importance: Familiarity with Incoterms is crucial for understanding shipping responsibilities, risk management, and cost allocation, ensuring smooth logistics and compliance in cross-border transactions. -
Lead Time
– Definition: The time it takes from placing an order to receiving the goods.
– Importance: Understanding lead times helps buyers manage their inventory levels effectively and plan for patient needs, reducing the risk of stockouts or delays in dental procedures.
By grasping these essential properties and terminology, B2B buyers can navigate the zirconia dental implant market with greater confidence, ensuring that their sourcing decisions align with both clinical requirements and business objectives.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the zirconia dental implants Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The zirconia dental implants market is experiencing robust growth, driven by increasing consumer demand for aesthetic, durable, and biocompatible dental solutions. Key global drivers include an aging population, rising awareness of dental health, and advancements in dental technology. In regions like Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, the demand for zirconia implants is further fueled by a growing middle class and increased access to healthcare services.
Emerging B2B sourcing trends are centered around digital procurement solutions and supply chain transparency. International buyers are increasingly leveraging technology to identify and evaluate suppliers, ensuring they meet quality and regulatory standards. Platforms that facilitate real-time communication and collaboration between manufacturers and buyers are becoming essential. Additionally, the adoption of just-in-time inventory practices helps businesses reduce costs and increase efficiency.
Market dynamics are influenced by competition among manufacturers and the regulatory landscape governing dental materials. Buyers should be aware of local regulations, particularly in regions like the EU, where compliance with stringent health and safety standards is critical. As the market evolves, B2B buyers must stay informed about innovations in zirconia processing techniques, such as additive manufacturing and advanced sintering methods, which enhance product quality and performance.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability has become a pivotal consideration in the zirconia dental implants sector. The environmental impact of zirconia production, including mining and processing, necessitates a focus on sustainable practices. B2B buyers are increasingly prioritizing suppliers who demonstrate a commitment to reducing their carbon footprint and employing eco-friendly production methods.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
Ethical sourcing is also gaining prominence. Buyers should seek suppliers with transparent supply chains that ensure fair labor practices and responsible sourcing of raw materials. Certifications such as ISO 14001 (Environmental Management) and ISO 26000 (Social Responsibility) can serve as indicators of a supplier’s commitment to sustainability.
Furthermore, the market is witnessing a rise in the availability of ‘green’ zirconia materials, which are produced with minimal environmental impact. These materials are often sourced from manufacturers that utilize renewable energy and sustainable practices. By prioritizing sustainability and ethical sourcing, B2B buyers can not only enhance their brand reputation but also meet the growing consumer demand for responsible products.
Brief Evolution/History
The use of zirconia in dental applications has evolved significantly over the past few decades. Initially, zirconia was primarily used in industrial applications due to its high strength and durability. However, the early 2000s marked a turning point with the introduction of zirconia as a material for dental implants and restorations.
Advancements in processing technologies, such as the development of yttria-stabilized zirconia, enhanced its mechanical properties and biocompatibility, making it a preferred choice for dental professionals. Over time, zirconia has gained recognition for its aesthetic qualities, leading to its widespread adoption in crowns, bridges, and implants. Today, it stands as a testament to the intersection of science and technology in enhancing patient outcomes and driving innovation in the dental field.
International B2B buyers must keep abreast of these historical developments to fully understand the material’s capabilities and market positioning, ensuring informed sourcing decisions in a competitive landscape.
Related Video: Zirconia Dental Implants vs. Titanium Implants
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of zirconia dental implants
-
What criteria should I consider when vetting suppliers of zirconia dental implants?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their quality certifications such as ISO 13485 for medical devices, and assess their production capabilities, including technology and materials used. Additionally, evaluate their track record in the industry by checking references or reviews from other B2B buyers. Ensure they have a robust quality assurance process in place to guarantee the consistency and reliability of their products. Lastly, consider their customer service and responsiveness, as these factors can significantly impact your purchasing experience. -
Can zirconia dental implants be customized to meet specific requirements?
Yes, many suppliers offer customization options for zirconia dental implants to meet specific aesthetic and functional needs. This may include variations in size, shape, and color, as well as the integration of advanced features such as surface coatings for enhanced biocompatibility. To ensure successful customization, communicate your precise requirements clearly during the initial discussions. Additionally, inquire about the supplier’s design capabilities and whether they utilize CAD/CAM technology for precision. -
What are the typical minimum order quantities (MOQs) and lead times for zirconia dental implants?
MOQs for zirconia dental implants can vary widely depending on the supplier and the complexity of the implants. Generally, expect MOQs to range from 50 to 200 units. Lead times can also vary, typically ranging from 4 to 12 weeks, depending on the customization required and the supplier’s production capacity. It’s crucial to discuss these details upfront to align your supply chain needs and avoid potential delays in procurement.
-
What payment terms are common when sourcing zirconia dental implants internationally?
Payment terms for international B2B transactions can differ significantly based on the supplier’s policies and the nature of the deal. Common arrangements include 50% upfront payment and the remaining 50% upon delivery, or net 30/60 days after invoice. Ensure to clarify terms regarding currency fluctuations and transaction fees. It’s advisable to use secure payment methods like letters of credit or escrow services to mitigate risks associated with international trade. -
How can I ensure the quality of zirconia dental implants being sourced?
To ensure quality, request detailed documentation from suppliers, including certificates of analysis and compliance with international standards. Implement a sample approval process where you assess the implants before placing a large order. Consider conducting third-party audits of the supplier’s facilities to verify their quality assurance processes. Regular communication with suppliers regarding quality metrics can also help maintain standards throughout the procurement process. -
What certifications should I look for in zirconia dental implants?
Look for certifications such as ISO 13485, which indicates compliance with international quality management standards for medical devices, and CE marking, which signifies conformity with health and safety regulations in Europe. Additionally, check for any FDA approvals if sourcing from the U.S. Understanding these certifications can help ensure that the implants meet safety and quality requirements in your region. -
How should I handle logistics when sourcing zirconia dental implants internationally?
Logistics can be complex when sourcing internationally. Work closely with your supplier to understand their shipping capabilities and timelines. Consider using freight forwarders to manage customs clearance and transport logistics efficiently. Ensure you have clear agreements on Incoterms to define responsibilities for shipping, insurance, and risk. Always factor in potential delays due to customs or regulatory checks, especially when sourcing from regions with stringent import regulations. -
What steps can I take to resolve disputes with suppliers of zirconia dental implants?
To mitigate disputes, establish clear contractual terms upfront, including delivery schedules, quality standards, and payment terms. In case of a dispute, maintain open communication with the supplier to address issues promptly. Document all interactions and agreements to support your position. If necessary, consider involving a third-party mediator or arbitrator for resolution. Utilizing dispute resolution clauses in contracts can also provide a structured approach to resolving conflicts amicably.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for zirconia dental implants
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of zirconia dental implants presents a wealth of opportunities for international B2B buyers across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. Understanding the various types of zirconia—such as monolithic, layered, and hybrid zirconia—enables buyers to make informed decisions that align with both clinical requirements and aesthetic demands. Key takeaways include the importance of evaluating material properties, supplier reliability, and compliance with regional standards to ensure high-quality procurement.
As the demand for durable and aesthetically pleasing dental solutions continues to grow, leveraging strategic sourcing practices can significantly enhance competitive positioning in the market. Buyers should prioritize partnerships with suppliers that demonstrate a commitment to quality control and innovative manufacturing processes.
Looking ahead, the zirconia dental implant market is poised for further growth, driven by advancements in technology and increasing consumer expectations. By staying informed and proactive in sourcing strategies, international buyers can not only meet current market demands but also anticipate future trends, ultimately leading to enhanced patient satisfaction and business success. Engage with industry leaders and explore emerging opportunities to solidify your position in this dynamic market.
