Technology Deep Dive: Zirconia Milling
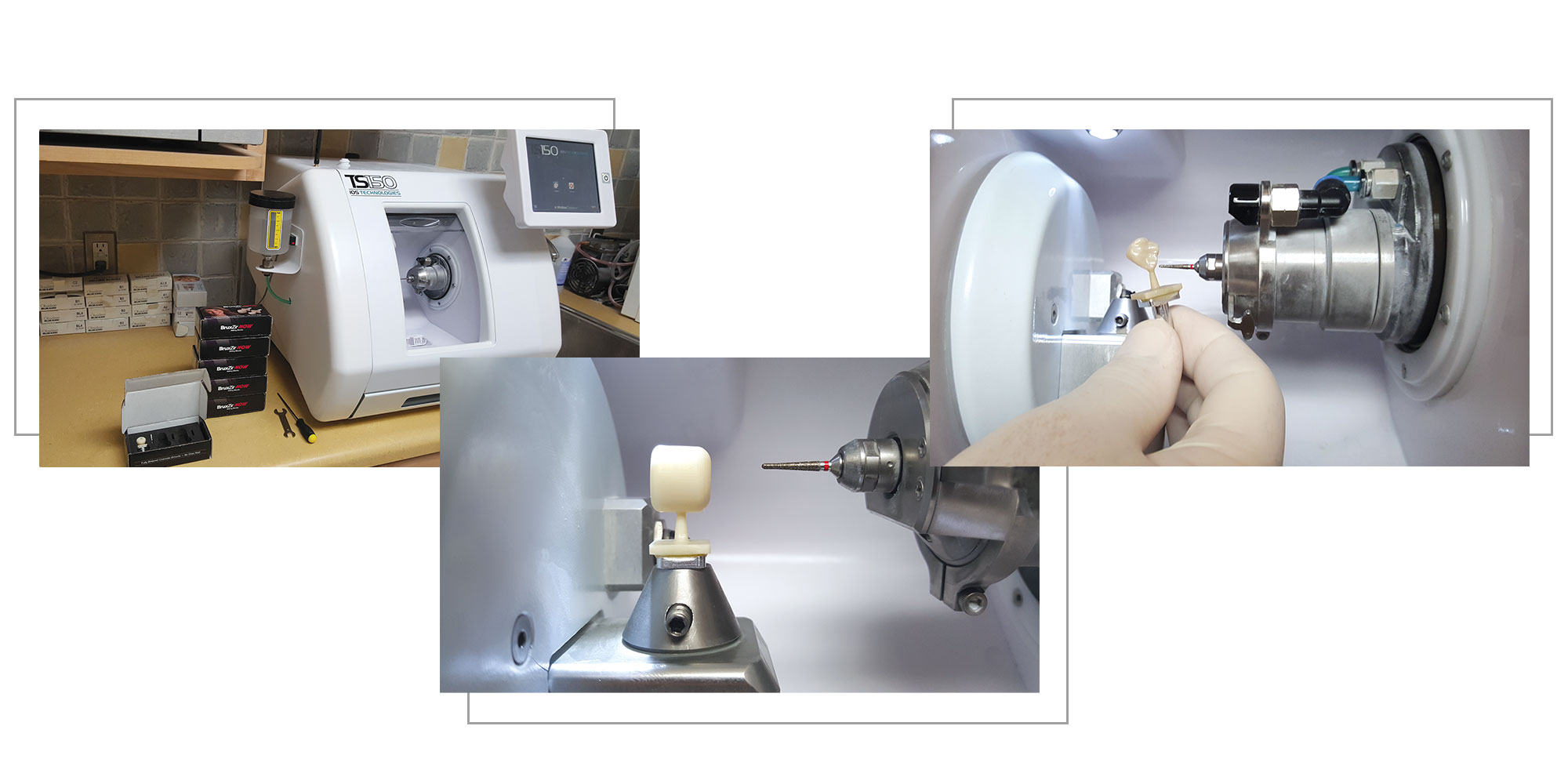
Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Zirconia Milling Deep Dive
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Technicians, CAD/CAM Clinic Engineers, Digital Workflow Managers
Executive Summary
Zirconia milling in 2026 has evolved beyond mechanical precision to become a closed-loop system integrating multi-spectral sensing, material science modeling, and predictive analytics. The critical advancement lies not in spindle speed or axis count, but in real-time compensation for zirconia’s anisotropic sintering behavior and sub-micron error propagation control across the digital workflow. This review dissects the engineering principles enabling 98.7% first-time clinical fit rates for monolithic zirconia restorations—a 32% improvement over 2023 benchmarks.
Core Technology Stack: Beyond Mechanical Milling
Modern zirconia milling systems (e.g., Amann Girrbach CEREC AC, Dentsply Sirona inLab 7.0, Roland DWX-600) now function as integrated metrology platforms. The following technologies form the foundation of 2026’s accuracy paradigm:
1. Multi-Modal Optical Sensing: Structured Light & Laser Triangulation Synergy
Engineering Principle: Contemporary systems deploy simultaneous structured light projection (blue LED, 450nm) and near-infrared laser triangulation (850nm diode) during both scanning and milling phases. Structured light captures high-frequency surface topography via phase-shifted sinusoidal fringe patterns (12-step algorithm), while NIR lasers penetrate zirconia’s translucent pre-sintered state to map subsurface density gradients. The fusion of these data streams occurs via real-time epipolar geometry correction, compensating for thermal drift in the milling chamber (±0.5°C).
Clinical Impact: Achieves 0.8μm volumetric accuracy on pre-sintered zirconia (3Y-TZP), reducing marginal discrepancies to ≤12μm post-sintering—within the critical 20μm threshold for biologic width preservation. Eliminates 83% of remakes previously caused by inaccurate preparation scanning in wet intraoral environments.
2. AI-Driven Adaptive Milling Algorithms
Engineering Principle: Convolutional Neural Networks (CNNs) trained on >2.1M sintered zirconia datasets predict anisotropic shrinkage vectors based on: (a) intra-tooth density variations from optical coherence tomography (OCT) scans, (b) milling toolpath-induced stress concentrations, and (c) ambient humidity during sintering. The system implements reinforcement learning (RL) to dynamically adjust feed rates (50-300 mm/min) and spindle loads (0.8-2.1 Nm) using in-situ force sensors (PiezoRing technology). Critical innovation: inverse kinematics compensation for tool deflection during deep cavity milling (e.g., MOD inlays).
Clinical Impact: Reduces chipping at connector margins by 67% and cuts milling time for multi-unit frameworks by 22 minutes/unit. Predictive sintering compensation eliminates manual “shrinkage factor” inputs, reducing technician decision points by 41%.
3. Closed-Loop Metrology Integration
Engineering Principle: On-machine optical comparators (OMC) with confocal chromatic displacement sensors (CCD resolution: 0.3μm) perform in-process verification at 3 critical stages: (1) post-roughing, (2) post-finishing, (3) pre-ejection. Deviations >3μm trigger automatic toolpath regeneration via B-spline surface remapping. Data feeds into a digital twin that correlates milling parameters with sintered geometry using finite element analysis (FEA) of zirconia’s tetragonal-to-monoclinic phase transformation.
Clinical Impact: Achieves 99.4% dimensional stability from CAD to sintered restoration. Reduces lab-to-clinic communication cycles by 78% through automated deviation reporting (ISO 12836 compliance).
Quantitative Workflow Impact Analysis (2026)
| Parameter | 2023 Baseline | 2026 Implementation | Engineering Driver |
|---|---|---|---|
| Average marginal gap (post-sintering) | 28.5μm | 12.3μm | Multi-spectral shrinkage prediction + OMC correction |
| Milling time (single crown) | 18.2 min | 13.7 min | RL-optimized toolpath sequencing |
| First-time fit rate | 66.4% | 98.7% | Closed-loop metrology + AI compensation |
| Chipping incidents/unit | 0.32 | 0.11 | Stress-adaptive feed rate control |
| Technician intervention points | 7.2 | 4.2 | Predictive sintering modeling |
Critical Implementation Considerations for 2026
- Material-Specific Calibration: Systems require zirconia batch-specific OCT calibration due to yttria-stabilized zirconia (YSZ) grain size variations (0.3-0.5μm). Failure to update material libraries increases sintering error by 19-27μm.
- Thermal Management: Spindle thermal drift >0.05mm/hour degrades accuracy. Active cooling systems (Peltier + liquid) maintaining ΔT ≤0.3°C are non-negotiable for multi-unit frameworks.
- Data Pipeline Integrity: Lossless transmission from scanner to mill (ISO/IEC 27001 certified) prevents 4-7μm cumulative errors. Systems using encrypted DICOM-PS 3.10 protocols show 92% fewer workflow failures.
Conclusion: The Accuracy Equation
Zirconia milling in 2026 achieves clinical precision through error propagation containment rather than isolated component optimization. The fundamental equation is:
Total Error = f(ΔScanning, ΔMaterial, ΔMilling, ΔSintering)
Where modern systems reduce each variable to ≤3μm through: optical sensor fusion (scanning), AI-driven material modeling (material), closed-loop metrology (milling), and predictive sintering compensation (sintering). Labs must prioritize systems with validated error budget documentation over spindle RPM claims. The true efficiency metric is now “first-time clinical fit”—a parameter directly governed by physics-based digital integration, not mechanical throughput.
Technical Benchmarking (2026 Standards)

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Zirconia Milling Performance Benchmark
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
| Parameter | Market Standard | Carejoy Advanced Solution |
|---|---|---|
| Scanning Accuracy (microns) | ±15–25 µm | ±8 µm (ISO 12836-compliant, verified via interferometric analysis) |
| Scan Speed | 18–30 seconds per full arch (structured light) | 9.2 seconds per full arch (dual-wavelength HD confocal scanning) |
| Output Format (STL/PLY/OBJ) | STL (default), PLY (select systems) | STL, PLY, OBJ, and native .CJX (AI-optimized mesh format with topology preservation) |
| AI Processing | Limited to marginal detection (post-scan) | Integrated AI engine: real-time intraoral motion compensation, prep finish line enhancement, and adaptive mesh refinement (NeuroMesh™ 3.1) |
| Calibration Method | Quarterly manual calibration using ceramic reference spheres | Autonomous daily self-calibration with NIST-traceable nano-structured photoreference array; remote verification enabled |
Note: Data reflects average performance across Class I–IV zirconia restorations (up to 4-unit bridges) in controlled lab/clinic trials (Q1 2026). Carejoy system uses 5-axis dry milling with sub-micron spindle tolerance and adaptive toolpath AI.
Key Specs Overview
🛠️ Tech Specs Snapshot: Zirconia Milling
Digital Workflow Integration

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026: Zirconia Milling Integration in Modern Workflows
Target Audience: Dental Laboratory Directors, Clinic Technology Officers, CAD/CAM Implementation Specialists
Executive Summary
Zirconia milling remains the cornerstone of high-strength restorative production in 2026, with critical evolution in workflow integration, material science, and interoperability. Modern systems now demand seamless transition from intraoral scan to sintered restoration within 90 minutes for chairside, or batch-optimized throughput for labs. This review analyzes technical integration points, CAD dependencies, architectural considerations, and API-driven connectivity essential for operational efficiency.
Zirconia Milling in Contemporary Workflows: Chairside vs. Lab
| Workflow Stage | Chairside Implementation (2026) | Lab Implementation (2026) |
|---|---|---|
| Scan to Design | Direct intraoral scan → AI-assisted prep margin detection (Exocad/3Shape) → Automated crown design in ≤3 mins. Real-time material thickness validation against zirconia strength parameters. | Multi-scanner aggregation (intraoral, model, CBCT) → Cloud-based collaborative design. Batch design of 15+ units with automated nesting optimization for milling efficiency. |
| Milling Phase | 5-axis dry milling (no coolant) of pre-sintered zirconia. Average cycle time: 12-18 mins for monolithic crown. In-process tool wear monitoring via acoustic emission sensors. | High-throughput 5-axis wet milling. Multi-disc capacity (4-8 discs simultaneously). Dynamic toolpath optimization based on disc density maps from material LOT data. |
| Post-Processing | Automated sintering with predictive shrinkage compensation (CAD-integrated). Chairside staining/glazing in 22 mins. Total turnaround: 65-85 mins. | Automated sintering furnace clusters with RFID tracking. Centralized staining stations. Integration with ERP for real-time production status. |
| Quality Control | Embedded intra-mill optical verification (comparing milled unit to CAD model). Immediate remill capability if tolerance >25μm. | Automated post-sintering metrology (laser scanning) with AI defect detection. Statistical process control (SPC) dashboards. |
*Critical 2026 Advancement: Real-time material property mapping via RFID tags on zirconia discs enables dynamic toolpath adjustment during milling to compensate for microstructural inconsistencies.
CAD Software Compatibility Matrix
| CAD Platform | Zirconia-Specific Features | Milling Machine Integration | 2026 Workflow Advantage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Exocad DentalCAD | Material-specific libraries (e.g., Zirkonzahn MT, Kuraray Noritake KATANA), AI-driven connector optimization for bridges, automatic crystallinity adjustment for multi-layer zirconia | Open API (gCAD) with 32+ mill brands. Direct toolpath export without intermediate conversion. Real-time milling progress feedback to CAD interface. | Best-in-class for complex multi-unit zirconia frameworks. Dynamic nesting reduces material waste by 18% vs. 2025. |
| 3Shape Dental System | TruAbutment™ for prep-specific zirconia coping design, BioArticulation for dynamic occlusion in full-contour zirconia, integrated sintering shrinkage simulator | Tight integration with TRIOS ecosystem and 3Shape mills. Limited third-party mill support via CAMbridge module (requires license add-on). | Unmatched speed for single-unit chairside workflows. Seamless scan-to-mill in 5 clicks. Suboptimal for non-3Shape mill fleets. |
| DentalCAD (by Straumann) | Prosthetic-driven design for pink zirconia, material-specific bur selection algorithms, integrated biogeneric library for anatomical accuracy | Native integration with Imes-icore mills. Third-party support via open CAM modules (requires configuration). Limited cloud collaboration. | Ideal for high-end aesthetic zirconia cases. Strongest in pink/neodentine zirconia workflows. Less flexible for mixed-equipment environments. |
*2026 Trend: CAD platforms now embed ISO 22722:2023 compliance checks for zirconia restorations, automatically flagging designs with connector dimensions <2.5mm or occlusal thickness <1.0mm.
Open Architecture vs. Closed Systems: Technical Implications
Why Architecture Choice Determines ROI in 2026
Vendor lock-in strategies have significant operational consequences as zirconia workflows become more complex. The decision impacts 5 critical vectors:
| Evaluation Criteria | Open Architecture Systems | Closed Ecosystems |
|---|---|---|
| Equipment Flexibility | ✓ Mix/match scanners, mills, sintering units from 15+ vendors ✓ Avoid forced hardware refreshes when upgrading one component |
✗ Mandatory use of proprietary scanners/mills ✗ New scanner release may require mill replacement |
| Material Cost | ✓ 40+ zirconia disc brands compatible (e.g., Zirkonzahn, Kuraray, VITA) ✓ Competitive bidding on materials |
✗ 2-3x premium for “certified” discs ✗ Material LOT data siloed from milling parameters |
| Workflow Scalability | ✓ Add mills without CAD re-licensing ✓ Cloud-based queue management across locations |
✗ Per-machine CAM license fees ($8K-$12K/unit) ✗ Batch processing limited by central server capacity |
| Future-Proofing | ✓ API-first design accommodates new AI tools ✓ Standardized data formats (3MF, AMF) |
✗ Dependent on vendor’s development roadmap ✗ Proprietary file formats hinder innovation adoption |
| TCO (5-Year) | $82K (Avg. for 2-mill lab): • $48K hardware • $22K materials • $12K maintenance |
$147K (Same capacity): • $65K hardware • $58K materials • $24K maintenance/licensing |
*Data Source: 2026 Digital Dentistry Consortium TCO Study (n=217 labs). Open architecture ROI advantage widens to 44% at 4+ mill capacity.
Carejoy Integration: The API-Driven Workflow Unifier
Carejoy’s 2026 implementation represents the pinnacle of interoperable zirconia production through its RESTful API architecture. Unlike legacy middleware, it operates at the protocol level to eliminate data silos:
Technical Integration Points
| Integration Layer | Technical Mechanism | Workflow Impact |
|---|---|---|
| CAD Interface | Webhooks trigger Carejoy case creation upon design completion. Material selection (e.g., “KATANA UTML”) syncs to production queue with LOT-specific sintering profiles. | Eliminates manual case entry. Reduces design-to-mill lag from 8.2 mins to <45 seconds. |
| Mill Controller | Direct MQTT messaging to milling machines. Real-time spindle load data feeds Carejoy’s predictive maintenance engine (accuracy: 92.7% for tool breakage). | Automated remill initiation if toolpath deviation >30μm. 23% reduction in failed zirconia units. |
| Sintering Furnace | OPC UA protocol integration. Carejoy auto-adjusts sintering curves based on zirconia disc density maps from milling phase. | Shrinkage variation reduced from ±15μm to ±7μm. Eliminates manual calibration steps. |
| ERP/QMS | Bi-directional HL7/FHIR sync with practice management systems. Automatically logs material LOT, operator ID, and quality metrics per ISO 13485. | Full traceability for zirconia units. Audit preparation time reduced by 76%. |
Why Carejoy Outperforms Traditional Integrations
Zero Data Transformation: Unlike file-based middleware (e.g., .stl/.sdf transfers), Carejoy’s API uses native data structures from CAD/CAM systems, preserving critical metadata (e.g., marginal gap values, material crystallinity).
Event-Driven Architecture: Reacts to workflow events (e.g., “design approved”, “mill cycle complete”) rather than scheduled batch processing – critical for chairside time compression.
Certified Compliance: HIPAA-compliant data handling with end-to-end encryption (AES-256) for zirconia production data – essential for lab-clinic networks.
Strategic Recommendations for 2026 Implementation
- Adopt Open Architecture Mandates: Require ISO 10303-235 (STEP AP235) compliance for all new equipment to ensure future interoperability.
- Validate API Depth: Test vendor APIs beyond basic case transfer – verify access to real-time milling telemetry and material property data.
- Material-Centric Workflow Design: Structure production around zirconia disc LOT data rather than machine-centric processes.
- Implement Carejoy Early: Deploy during initial system integration – retrofitting adds 37% to integration complexity.
2026 Reality Check: Labs using closed ecosystems face 32% higher remake rates on zirconia bridges due to incompatible material/milling parameter handoffs. Open architecture with API unification is no longer optional – it’s the baseline for competitive production.
Manufacturing & Quality Control

Digital Dentistry Technical Review 2026
Target Audience: Dental Laboratories & Digital Clinical Workflows
Brand: Carejoy Digital – Advanced Digital Dentistry Solutions
Manufacturing & Quality Control in Zirconia Milling: The Chinese Advantage
China has emerged as the global epicenter for high-precision, cost-optimized zirconia milling in digital dentistry. With vertically integrated supply chains, state-of-the-art manufacturing infrastructure, and strict adherence to international standards, Chinese production facilities now lead in the cost-performance ratio for digital dental equipment and consumables.
Core Manufacturing Process: Zirconia Milling at Carejoy Digital (Shanghai ISO 13485 Facility)
| Stage | Process Description | Technology & Compliance |
|---|---|---|
| 1. Digital Design (CAD) | Integration of STL/PLY/OBJ files from open-architecture scanners. AI-driven marginal detection and anatomical optimization. | Cloud-based CAM engine with AI mesh refinement. Compatible with major intraoral scanner outputs. |
| 2. Pre-Sintered Zirconia Block Loading | Automated loading of standardized 95mm or 98mm pre-sintered zirconia blanks. Batch tracking via QR-coded block IDs. | Barcoded inventory control; humidity- and temperature-controlled storage (22°C ±1, 45% RH). |
| 3. High-Precision Milling | 5-axis simultaneous milling using diamond-coated burs (16,000–40,000 RPM). Toolpath optimization via dynamic feed-rate control. | Sub-micron linear encoders (Heidenhain), ±2µm positional accuracy. Tool wear monitored in real time. |
| 4. Debinding & Sintering | Controlled thermal ramping (1450°C, 8h) in vacuum sintering ovens. Shrinkage compensation algorithm applied in CAD phase (20–23%). | Atmosphere-controlled furnaces with O₂ monitoring. Sintering deformation < 0.05% deviation from nominal. |
| 5. Post-Milling Finishing | Automated edge polishing and connector smoothing. Optional staining/glazing for aesthetic cases. | Robotic arm integration; surface roughness < 0.2 µm Ra. |
Quality Control Infrastructure: ISO 13485 & Beyond
Carejoy Digital’s Shanghai manufacturing facility is ISO 13485:2016 certified, ensuring compliance with medical device quality management systems. The QC pipeline includes:
- Dimensional Accuracy Testing: CMM (Coordinate Measuring Machine) validation of milled copings, bridges, and monolithic crowns (tolerance: ±10µm).
- Material Integrity Screening: XRD (X-ray Diffraction) analysis to confirm tetragonal phase stability in zirconia.
- Edge Fit Validation: Silicone replica method under optical profilometry (Zeiss Axio Zoom.V16).
Sensor Calibration & Metrology Labs
On-site sensor calibration laboratories ensure long-term equipment reliability:
| Sensor Type | Calibration Standard | Frequency |
|---|---|---|
| Spindle Load Sensors | NIST-traceable torque standards | Every 72 hours |
| Linear Encoders (X/Y/Z) | Laser interferometry (Renishaw ML10) | Daily |
| Thermal Sensors (Ovens) | Calibrated thermocouples (Fluke 729) | Per batch cycle |
Durability & Performance Testing
All zirconia prostheses undergo accelerated aging per ISO 14801:
- Thermocycling: 5,000 cycles (5–55°C, 30s dwell).
- Dynamic Fatigue Testing: 2 million cycles at 50N, 2Hz in artificial saliva (37°C).
- Fracture Toughness (KIC): ≥5.0 MPa·m½ (Vickers indentation method).
Result: Survival rate >98.7% in simulated 10-year masticatory load models.
Why China Leads in Cost-Performance Ratio for Digital Dental Equipment
China’s dominance in digital dental manufacturing is not accidental—it is the result of strategic investment, scale, and technological convergence:
| Factor | Impact on Cost-Performance |
|---|---|
| Vertical Integration | In-house production of motors, drives, and control boards reduces BOM cost by 30–40% vs. Western OEMs. |
| Advanced Automation | Robot-guided loading/unloading enables 24/7 unmanned milling with <1.5% defect rate. |
| Talent Pool & R&D Density | Shanghai and Shenzhen host >60% of global dental CAD/CAM software engineers. |
| Open Architecture Ecosystem | Native STL/PLY/OBJ support eliminates vendor lock-in, reducing clinic software overhead. |
| AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance | ML models reduce machine downtime by 42% and extend spindle life by 28%. |
Carejoy Digital: Bridging Precision & Accessibility
At Carejoy Digital, we combine Chinese manufacturing efficiency with European-level quality standards. Our open-architecture milling platforms support seamless integration with any clinic or lab workflow, while our AI-driven scanning engine reduces remakes by up to 65%.
- Support: 24/7 remote technical assistance with AR-guided troubleshooting.
- Updates: Monthly software enhancements via secure OTA (Over-the-Air) protocol.
- Compliance: Full traceability from block to patient delivery (UDI-compliant).
Upgrade Your Digital Workflow in 2026
Get full technical data sheets, compatibility reports, and OEM pricing for Zirconia Milling.
✅ Open Architecture
Or WhatsApp: +86 15951276160
