Introduction: Navigating the Global Market for dental implants with payment plans
Navigating the global market for dental implants presents unique challenges and opportunities for B2B buyers, particularly those sourcing from diverse regions such as Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe. The demand for dental implants is on the rise, driven by an increasing focus on oral health and aesthetics. However, the high costs associated with these procedures often deter potential patients and complicate purchasing decisions for dental practices. This is where payment plans come into play, offering a viable solution to make dental implants more accessible.
In this guide, we delve into the essential aspects of dental implants, including various types and materials available, along with insights into manufacturing processes and quality control measures. We will also provide a comprehensive overview of key suppliers in the market, a breakdown of cost structures, and current market trends. Additionally, we address frequently asked questions to equip buyers with the knowledge they need to make informed decisions.
By empowering B2B buyers with this valuable information, this guide aims to streamline the sourcing process, ensuring that dental practices can offer affordable solutions to their patients without compromising on quality. Understanding the landscape of dental implants and the financing options available will enhance your ability to meet the needs of your clientele effectively, fostering growth in a competitive market.
Understanding dental implants with payment plans Types and Variations
| Type Name | Key Distinguishing Features | Primary B2B Applications | Brief Pros & Cons for Buyers |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-House Payment Plans | Flexible, direct financing options offered by dental practices. | Dental clinics, private practices | Pros: Simple setup, no third-party involvement. Cons: May have limited financing options. |
| Third-Party Financing | Partnerships with financial institutions like CareCredit or LendingClub. | Dental suppliers, clinics | Pros: Broader financing options, competitive interest rates. Cons: Potentially complex application process. |
| Membership Plans | Subscription-based models providing discounts on services. | Dental practices, insurance companies | Pros: Predictable costs, significant savings. Cons: Requires ongoing commitment, may not cover all procedures. |
| Insurance-Based Plans | Coverage through dental insurance that includes implants. | Insurance brokers, dental networks | Pros: Reduces out-of-pocket expenses. Cons: Limited coverage and may involve waiting periods. |
| Flexible Payment Installments | Customizable payment schedules allowing gradual payments. | Dental equipment suppliers, clinics | Pros: Alleviates financial burden, easy budgeting. Cons: Longer payment periods may incur interest. |
In-House Payment Plans
In-house payment plans are tailored financial solutions offered directly by dental practices. These plans allow patients to pay for their dental implants over time, often without interest. For B2B buyers, this model is appealing as it simplifies the financing process, allowing clinics to attract more patients who may be deterred by upfront costs. However, the range of financing options might be limited compared to third-party solutions.
Third-Party Financing
Third-party financing involves partnerships between dental clinics and financial institutions, such as CareCredit or LendingClub. This arrangement enables patients to secure loans specifically for dental procedures, including implants. For B2B buyers, this option is advantageous as it offers a variety of financing terms and competitive interest rates. However, the application process can be more complex, requiring thorough vetting of financial providers.
Membership Plans
Membership plans are subscription models that provide patients with discounts on dental services in exchange for a monthly fee. For B2B buyers, this model can enhance patient loyalty and predictability in revenue streams. Practices can benefit from consistent cash flow while offering patients substantial savings on implants and other services. However, these plans require a commitment from patients, which may not appeal to everyone.
Insurance-Based Plans
Insurance-based plans involve traditional dental insurance policies that cover a portion of the costs associated with dental implants. For B2B buyers, partnering with insurance brokers or networks can facilitate patient access to necessary treatments while reducing their overall costs. However, the limitations on coverage and potential waiting periods can deter some patients, making it essential for practices to clearly communicate these terms.
Flexible Payment Installments
Flexible payment installment plans allow patients to spread the cost of dental implants over a set period. This model can be customized based on patient needs and financial situations. For B2B buyers, offering such plans can make dental services more accessible, potentially increasing patient volume. However, longer payment periods may come with interest, which could discourage some patients from opting for this solution.
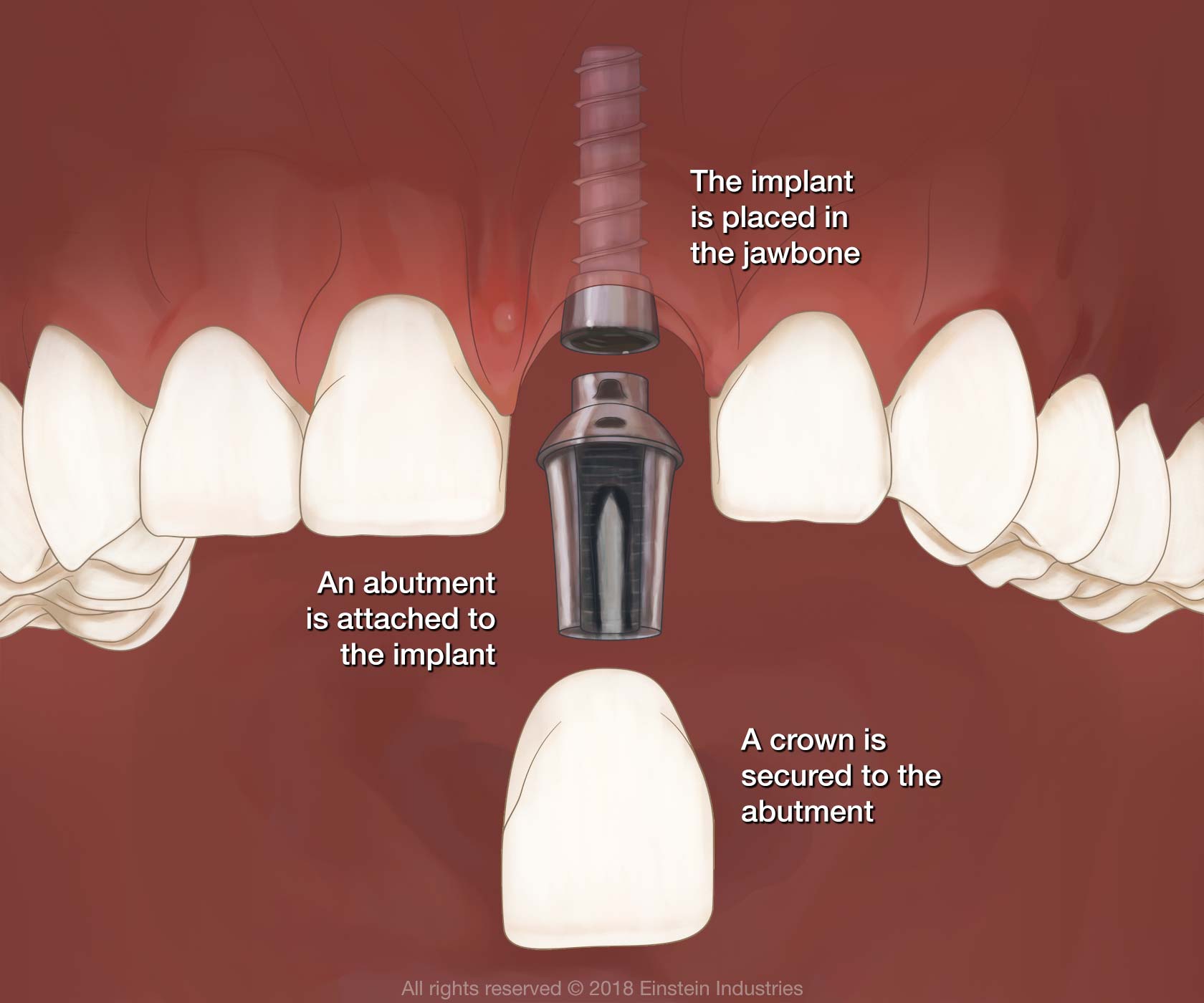
Related Video: Step by Step Guide to Your Dental Implant Procedure
Key Industrial Applications of dental implants with payment plans
| Industry/Sector | Specific Application of dental implants with payment plans | Value/Benefit for the Business | Key Sourcing Considerations for this Application |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dental Clinics | Offering dental implants as part of flexible payment plans | Attracts more patients, increases treatment acceptance rates | Ensure payment plans are easy to manage and clearly communicated |
| Insurance Providers | Partnering with dental clinics for implant coverage | Expands coverage options, enhances patient satisfaction | Evaluate clinic partnerships for quality and reputation |
| Medical Device Suppliers | Providing financing options for dental implant products | Improves sales through affordability, attracts diverse clientele | Verify compliance with local regulations and quality standards |
| Health and Wellness Centers | Integrating dental implants into holistic health packages | Increases service offerings, promotes overall health benefits | Consider partnerships with trusted dental professionals |
| Corporate Wellness Programs | Offering dental implant benefits as part of employee health plans | Enhances employee satisfaction and retention rates | Assess affordability and coverage options for employees |
Detailed Applications
Dental Clinics
Dental clinics can significantly enhance patient acquisition and retention by offering dental implants with flexible payment plans. Many patients shy away from expensive procedures due to high upfront costs. By providing manageable payment options, clinics can increase acceptance rates for dental implants, thereby boosting revenue. International buyers should consider clinics that utilize transparent payment structures to ensure patients clearly understand their financial commitments.
Insurance Providers
Insurance providers can expand their offerings by partnering with dental clinics to include coverage for dental implants. This collaboration not only enhances patient satisfaction but also positions the insurance provider as a comprehensive solution for dental health. For international B2B buyers, it is essential to assess the quality and reputation of partnered clinics to maintain high service standards and ensure compliance with local regulations.
Medical Device Suppliers
Suppliers of dental implant products can improve their marketability by offering financing options to dental clinics. This approach makes dental implants more accessible, thereby driving sales and fostering relationships with a broader range of clinics. Buyers in this sector should prioritize suppliers that meet local regulatory requirements and offer high-quality products, as this ensures patient safety and satisfaction.
Health and Wellness Centers
Health and wellness centers can integrate dental implants into their holistic health packages, promoting the importance of dental health as part of overall well-being. This strategy not only increases service offerings but also enhances the perceived value of the center’s services. For international buyers, aligning with reputable dental professionals is crucial to ensure that the quality of care matches the wellness center’s standards.
Corporate Wellness Programs
Incorporating dental implants into corporate wellness programs can significantly enhance employee satisfaction and retention. Companies can attract and retain talent by offering comprehensive health benefits, including dental implants. For B2B buyers, evaluating the affordability and coverage options of these plans is essential to ensure they meet the diverse needs of employees while remaining financially sustainable for the organization.
Related Video: How to Perform Dental Implants by MIS -Tutorial (3D Dental Animation)
Strategic Material Selection Guide for dental implants with payment plans
When selecting materials for dental implants, particularly for those considering payment plans, it is essential to evaluate the properties, advantages, disadvantages, and compliance considerations of each material. This analysis will help international B2B buyers make informed decisions that align with their operational needs and financial strategies.
Titanium
Key Properties: Titanium is known for its excellent biocompatibility, corrosion resistance, and strength-to-weight ratio. It can withstand the pressures of chewing and is resistant to the corrosive effects of saliva.
Pros & Cons: Titanium implants are durable and have a long track record of success in dental applications. However, they can be more expensive than other materials, and their manufacturing process can be complex, requiring specialized equipment and expertise.
Impact on Application: Titanium is compatible with various dental restorative materials, making it suitable for a wide range of applications. Its strength allows it to support single crowns or full-arch restorations effectively.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers from regions like Africa and South America should ensure that titanium implants meet local regulatory standards, such as ISO 13485 for medical devices. Compliance with ASTM standards for material quality is also crucial.
Zirconia
Key Properties: Zirconia is a ceramic material known for its high strength, aesthetic appeal, and excellent biocompatibility. It is less prone to corrosion compared to metals.
Pros & Cons: Zirconia implants offer superior aesthetics, making them ideal for visible areas. However, they can be more brittle than titanium, which may limit their use in certain applications. The cost of zirconia implants is generally high due to the complexity of their manufacturing.
Impact on Application: Zirconia is particularly suitable for patients who are allergic to metals or prefer a metal-free option. Its compatibility with various dental prosthetics enhances its versatility.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers must verify that zirconia implants comply with local regulations and standards, such as CE marking in Europe and FDA approval in the U.S. Understanding the supply chain for zirconia can also be critical, as sourcing may vary by region.
Stainless Steel
Key Properties: Stainless steel is known for its strength, ductility, and resistance to corrosion. It is often used in temporary dental implants or as a framework for other types of implants.
Pros & Cons: While stainless steel is cost-effective and easy to manufacture, it may not provide the same long-term durability as titanium or zirconia. Additionally, its aesthetic appeal is lower, which can be a concern for visible implants.
Impact on Application: Stainless steel is suitable for short-term applications or as part of a multi-component implant system. It is often used in pediatric dentistry or in cases where immediate loading is required.
Considerations for International Buyers: Compliance with ASTM standards is necessary for stainless steel implants, especially regarding corrosion resistance. Buyers should also consider the availability of stainless steel implants in their region and the associated costs.
PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone)
Key Properties: PEEK is a high-performance polymer known for its strength, lightweight nature, and biocompatibility. It is resistant to high temperatures and has good chemical resistance.
Pros & Cons: PEEK offers excellent flexibility and can be manufactured in various shapes, making it suitable for customized implants. However, it is generally less durable than metal options and may not be suitable for all applications.
Impact on Application: PEEK is often used in conjunction with other materials to create hybrid implants. Its compatibility with imaging techniques like MRI is a significant advantage.
Considerations for International Buyers: Buyers should ensure that PEEK implants meet international standards, such as ISO 10993 for biocompatibility. Understanding the regulatory landscape in different regions is crucial for compliance.
| Material | Typical Use Case for dental implants with payment plans | Key Advantage | Key Disadvantage/Limitation | Relative Cost (Low/Med/High) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Titanium | Permanent dental implants, full-arch restorations | Excellent biocompatibility and durability | Higher cost and complex manufacturing | High |
| Zirconia | Aesthetic dental implants, metal-free options | Superior aesthetics and biocompatibility | Brittle and high manufacturing cost | High |
| Stainless Steel | Temporary implants, pediatric dentistry | Cost-effective and easy to manufacture | Lower long-term durability and aesthetics | Low |
| PEEK | Customized implants, hybrid systems | Lightweight and flexible with good biocompatibility | Less durable than metals | Medium |
This strategic material selection guide provides a comprehensive overview of the materials available for dental implants, enabling international B2B buyers to make informed decisions that align with their operational and financial goals.
In-depth Look: Manufacturing Processes and Quality Assurance for dental implants with payment plans
Manufacturing dental implants is a complex process that requires precision and adherence to strict quality control measures. For B2B buyers, particularly those in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe, understanding the manufacturing and quality assurance (QA) processes is crucial for making informed purchasing decisions. This section will provide an in-depth look at the typical manufacturing stages, quality control standards, and verification methods relevant to dental implants with payment plans.
Manufacturing Processes
Material Preparation
The manufacturing of dental implants begins with the careful selection and preparation of materials. Titanium and its alloys are commonly used due to their biocompatibility and strength. The initial stage involves:
- Material Sourcing: Ensure materials meet international standards for safety and quality.
- Pre-Treatment: Materials may undergo surface treatments to enhance osseointegration, such as sandblasting or acid-etching.
Forming
The forming stage is where the raw materials are shaped into the desired implant structures. This typically involves:
- Machining: Utilizing CNC (Computer Numerical Control) machines to precisely cut and shape the implants.
- Molding and Forging: In some cases, molds are used to form complex geometries. Forging can also be applied for strength.
Assembly
While dental implants are generally singular components, some systems may include abutments and other parts. The assembly process includes:
- Joining Components: If applicable, parts are joined using techniques like laser welding or adhesive bonding.
- Integration with Other Dental Solutions: Some manufacturers might offer implants as part of a broader dental solution, necessitating careful integration.
Finishing
The final stage involves refining the implants for optimal performance. This includes:
- Surface Finishing: Techniques such as polishing or coating with bioactive materials to improve integration with bone.
- Sterilization: Implants must be sterilized before packaging to ensure they are free from contaminants.
Quality Assurance
Quality assurance is paramount in the manufacturing of dental implants, as it directly impacts patient safety and product effectiveness. The following standards and checkpoints are essential:
International Standards
B2B buyers should ensure that suppliers comply with relevant international quality standards, including:
- ISO 9001: General quality management systems.
- ISO 13485: Specific for medical devices, ensuring consistent quality in design, manufacturing, and distribution.
- CE Marking: Indicates conformity with health, safety, and environmental protection standards for products sold within the European Economic Area.
Quality Control Checkpoints
Quality control is integrated throughout the manufacturing process, with several critical checkpoints:
- Incoming Quality Control (IQC): Verification of raw materials against specifications before production.
- In-Process Quality Control (IPQC): Continuous monitoring during the manufacturing process to ensure compliance with standards.
- Final Quality Control (FQC): Comprehensive testing of finished products to ensure they meet all specifications before distribution.
Common Testing Methods
Quality control testing methods may include:
- Mechanical Testing: Assessing the strength and durability of implants through tensile, compression, and fatigue tests.
- Biocompatibility Testing: Ensuring materials do not provoke an adverse biological response.
- Sterility Testing: Confirming that the final product is free from microbial contamination.
Verifying Supplier Quality Control
For B2B buyers, particularly those operating in diverse international markets, verifying a supplier’s quality control processes is vital. Here are actionable steps to consider:
- Conduct Supplier Audits: Regularly assess suppliers’ manufacturing facilities and quality control processes to ensure compliance with required standards.
- Request Quality Reports: Suppliers should provide documentation demonstrating adherence to quality standards, including test results and compliance certificates.
- Engage Third-Party Inspectors: Utilizing independent inspection services can provide an unbiased evaluation of the supplier’s quality control practices.
Navigating Quality Control Nuances
International B2B buyers should be aware of the nuances in quality control requirements across different regions:
- Regulatory Variations: Understand that regulatory requirements may differ significantly between regions (e.g., CE marking in Europe vs. FDA approval in the U.S.).
- Cultural Considerations: Different regions may have varying expectations regarding product quality and safety. Engage with local experts to align with these expectations.
- Payment Plans and Financing: When considering payment plans for purchasing dental implants, ensure that the financing options do not compromise the quality assurance processes.
Conclusion
Understanding the manufacturing processes and quality assurance measures for dental implants is crucial for international B2B buyers. By focusing on material preparation, forming, assembly, and finishing, alongside rigorous quality control standards, buyers can make informed decisions that prioritize patient safety and product reliability. Establishing strong relationships with suppliers who adhere to international standards will not only enhance product quality but also ensure smooth transactions, particularly when exploring payment plans.
Related Video: Inspection and Quality control in Manufacturing
Comprehensive Cost and Pricing Analysis for dental implants with payment plans Sourcing
Understanding the cost structure and pricing dynamics of dental implants, especially when considering payment plans, is crucial for international B2B buyers. This section delves into the key components that influence pricing and offers actionable insights for effective sourcing.
Cost Components
- Materials: The cost of dental implants significantly hinges on the type of materials used. High-quality titanium or zirconia implants are standard, with prices varying based on the source and certification. Expect to pay $500 to $2,500 per implant.

Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
-
Labor: Skilled labor is essential for both the surgical placement of implants and the manufacturing process. Labor costs can range from $100 to $1,000 depending on the complexity of the procedure and the expertise required.
-
Manufacturing Overhead: This includes costs associated with facility maintenance, utilities, and administrative expenses. Typically, overhead can contribute 20-30% to the overall cost of production.
-
Tooling and Equipment: Specialized tools are necessary for both the creation of implants and their surgical placement. Initial investment in tooling can be substantial, influencing the pricing of implants.
-
Quality Control (QC): Rigorous testing and quality assurance are mandatory to meet regulatory standards. QC processes can add 10-15% to the overall cost, ensuring that the implants meet safety and efficacy requirements.
-
Logistics: Distribution costs vary based on location and shipping methods. Factors such as distance, Incoterms, and shipping modes (air vs. sea) can lead to significant variations in costs.
-
Margin: Suppliers often add a margin to cover their risks and operational costs. Margins can vary from 15% to 40%, depending on market conditions and competition.
Price Influencers
-
Volume/MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity): Larger orders often result in lower per-unit costs. Negotiating favorable terms based on projected volume can lead to significant savings.
-
Specifications and Customization: Custom implants or specific configurations may incur higher costs. Buyers should assess whether standard options can meet their needs to avoid unnecessary expenses.
-
Supplier Factors: Supplier reputation, reliability, and certification (like ISO or CE) affect pricing. Engaging with certified suppliers can ensure compliance but may come at a premium.
-
Incoterms: Understanding shipping terms is crucial. Different Incoterms (e.g., FOB, CIF) can impact the total landed cost, affecting overall budgeting.
Buyer Tips
-
Negotiation: Engaging suppliers in discussions about pricing and payment terms can yield better deals. Leverage volume commitments to negotiate lower prices.
-
Cost-Efficiency: Consider the Total Cost of Ownership (TCO), which includes purchase price, shipping, handling, and long-term maintenance costs. This holistic view can inform better purchasing decisions.
-
Pricing Nuances for International Buyers: Be aware of currency fluctuations, tariffs, and import duties that can affect final costs. Establishing relationships with local suppliers may mitigate some of these costs.
-
Market Research: Conduct thorough market research to understand pricing trends in different regions. This knowledge can empower buyers to make informed decisions and avoid overpaying.
Disclaimer
The prices indicated throughout this analysis are for illustrative purposes only and may vary based on specific conditions, supplier agreements, and market fluctuations. Buyers should conduct due diligence and obtain multiple quotes to ensure competitive pricing.
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for dental implants with payment plans
Essential Technical Properties and Trade Terminology for Dental Implants with Payment Plans
When navigating the complex landscape of dental implants, particularly when considering payment plans, understanding the essential technical properties and trade terminology is crucial for B2B buyers. This knowledge not only facilitates informed purchasing decisions but also ensures that the solutions acquired meet the specific needs of clinics and dental practices.
Key Technical Properties of Dental Implants
-
Material Grade
– Definition: The classification of the materials used in dental implants, often involving titanium or zirconia.
– Importance: High-grade materials ensure biocompatibility, durability, and resistance to corrosion. For B2B buyers, selecting implants made from reputable materials is critical to guarantee long-term success and patient satisfaction. -
Surface Treatment
– Definition: The processes applied to the implant surface, such as sandblasting or acid etching, to enhance osseointegration.
– Importance: A well-treated surface fosters better integration with the bone, leading to improved stability. Buyers should evaluate the surface treatment techniques used by manufacturers to ensure optimal performance. -
Implant Diameter and Length
– Definition: The specific dimensions of the implant, which can vary based on the anatomical requirements of the patient.
– Importance: Customization in size allows for better adaptation to different clinical situations. B2B purchasers must ensure that suppliers offer a range of sizes to accommodate diverse patient needs. -
Tolerance Levels
– Definition: The permissible limits of variation in the dimensions of the implant components.
– Importance: High tolerance levels ensure that all components fit together seamlessly, reducing the risk of complications during procedures. Buyers should seek manufacturers that maintain stringent quality control measures. -
Bone Density Requirements
– Definition: The minimum bone density needed for successful implant placement.
– Importance: Understanding bone density requirements is essential for selecting the right implant type and ensuring successful outcomes. B2B buyers need to assess whether the implants they are considering are suitable for varying bone conditions.
Common Trade Terminology
-
OEM (Original Equipment Manufacturer)
– Definition: A company that produces parts or equipment that may be marketed by another manufacturer.
– Relevance: In the dental implant industry, knowing the OEM is vital for ensuring quality and compliance with industry standards. Buyers should seek reputable OEMs to ensure product reliability. -
MOQ (Minimum Order Quantity)
– Definition: The smallest quantity of a product that a supplier is willing to sell.
– Relevance: Understanding MOQ helps buyers manage inventory effectively and negotiate better pricing. Buyers should align their order quantities with their projected needs to avoid excess costs. -
RFQ (Request for Quotation)
– Definition: A document issued by a buyer to request pricing and terms from suppliers.
– Relevance: An RFQ is crucial for comparing different suppliers’ offerings. B2B buyers should prepare detailed RFQs to receive accurate and comprehensive quotes. -
Incoterms (International Commercial Terms)
– Definition: A set of predefined international trade terms published by the International Chamber of Commerce.
– Relevance: Familiarity with Incoterms helps buyers understand the responsibilities and liabilities of both parties in a transaction. This knowledge is essential for managing shipping and delivery costs effectively. -
Payment Plans
– Definition: Financial arrangements that allow buyers to spread the cost of dental implants over time.
– Relevance: Payment plans can significantly enhance affordability for clinics, making it easier to acquire necessary equipment without immediate financial strain. B2B buyers should evaluate the payment options available from suppliers to optimize cash flow.
By understanding these technical properties and trade terms, B2B buyers in the dental implant market can make more informed decisions, ensuring they select the best products and financing options tailored to their specific operational needs.
Navigating Market Dynamics, Sourcing Trends, and Sustainability in the dental implants with payment plans Sector
Market Overview & Key Trends
The global dental implants market is rapidly evolving, driven by an increase in dental tourism, rising disposable incomes, and a growing aging population. International B2B buyers are particularly influenced by factors such as enhanced dental technology, the rise of digital dentistry, and the increasing adoption of payment plans that make procedures more accessible. Countries in Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe are experiencing a surge in demand for dental implants, spurred by greater awareness of oral health and the availability of financing options.
Emerging trends include the integration of advanced technologies such as 3D printing and computer-aided design (CAD) in the manufacturing of dental implants. This innovation not only reduces production costs but also improves accuracy and patient outcomes. B2B buyers should consider sourcing from manufacturers that utilize these technologies, as they can offer competitive pricing and higher quality products.
Additionally, payment plans are becoming a standard offering in dental practices, allowing patients to manage costs more effectively. This is particularly relevant for buyers in regions where upfront payment is a barrier to treatment. Many practices now offer in-house financing or partnerships with third-party financing companies, which can enhance the attractiveness of their services to potential patients.
In summary, international buyers must navigate a landscape marked by technological advancements, evolving consumer financing options, and a growing emphasis on affordability to stay competitive.
Sustainability & Ethical Sourcing in B2B
Sustainability is becoming a central focus in the dental implants sector as environmental concerns gain traction globally. B2B buyers must consider the environmental impact of their sourcing decisions. This includes evaluating manufacturers’ waste management practices, energy consumption, and the sustainability of materials used in implant production. For instance, sourcing implants made from biocompatible and recycled materials can significantly reduce the ecological footprint.
Ethical supply chains are also crucial. Buyers should ensure that their suppliers adhere to fair labor practices and responsible sourcing standards. This is particularly important in regions where regulations may be lax. Certifications such as ISO 14001 for environmental management and ISO 13485 for quality management in medical devices can serve as indicators of a manufacturer’s commitment to sustainability and ethical practices.
Moreover, the growing consumer preference for environmentally friendly products means that offering sustainably sourced dental implants can enhance a practice’s marketability. By prioritizing suppliers that invest in green technologies and sustainable practices, B2B buyers can align their business models with contemporary consumer values, thereby fostering loyalty and trust.
Brief Evolution/History
The dental implants sector has undergone significant transformation since the first modern implants were introduced in the 1960s. Initially made from titanium, implants were primarily used for functional purposes. Over the decades, advancements in materials science and surgical techniques have led to the development of more effective and aesthetically pleasing options. Today, dental implants are not only seen as a solution for tooth loss but also as a vital component of comprehensive dental care that enhances quality of life.
The introduction of payment plans in the late 20th century marked a pivotal shift, making dental implants more accessible to a broader demographic. As the market continues to evolve, the focus is now on integrating technology, sustainability, and patient-centered financing solutions to meet the needs of a diverse global population.
Related Video: International Trade 101 | Economics Explained
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) for B2B Buyers of dental implants with payment plans
-
What should I consider when vetting suppliers for dental implants with payment plans?
When vetting suppliers, focus on their reputation, experience, and compliance with international standards. Request references from other B2B buyers and check for certifications such as ISO 13485 or CE marking. Evaluate their payment plan offerings, including interest rates and repayment terms. Additionally, assess their customer service responsiveness and support for international shipping to ensure they can meet your logistical needs. -
Can I customize dental implants according to my specific requirements?
Yes, many manufacturers offer customization options for dental implants. This can include variations in size, material, and design to suit specific patient needs. When negotiating with suppliers, clearly communicate your customization requirements and ask about the feasibility and costs associated with bespoke solutions. Ensure you also inquire about any additional lead times that may be required for custom orders. -
What are the minimum order quantities (MOQ) and lead times for dental implants?
MOQs for dental implants can vary significantly depending on the supplier. Many manufacturers may require a minimum of 50-100 units per order, while others might accommodate smaller orders for first-time buyers. Lead times typically range from 4 to 12 weeks, depending on the complexity of the order and the supplier’s production capabilities. Always confirm these details before placing an order to avoid unexpected delays. -
How do I ensure quality assurance and certification compliance for dental implants?
To ensure quality, request documentation of the supplier’s quality management system and relevant certifications. Look for ISO 13485 certification, which indicates compliance with international standards for medical devices. Additionally, inquire about their quality control processes, including batch testing and inspection methods. Consider conducting an on-site audit if possible, or requesting third-party testing results for added assurance. -
What logistics considerations should I keep in mind when sourcing dental implants?
Logistics are crucial in the procurement of dental implants. Confirm the supplier’s shipping capabilities, including their experience with international trade regulations and customs clearance. Discuss shipping options, costs, and estimated delivery times to ensure timely receipt of products. Additionally, consider the implications of potential duties and taxes in your country, and ensure your supplier can provide necessary documentation for customs. -
What steps should I take if I encounter a dispute with a supplier?
In case of a dispute, start by addressing the issue directly with the supplier through formal communication. Document all interactions and agreements. If the issue remains unresolved, refer to the terms outlined in your contract regarding dispute resolution, which may include mediation or arbitration. Involving legal counsel may be necessary if the dispute escalates. Building a positive relationship with suppliers can also help mitigate potential conflicts. -
Are there financing options available for purchasing dental implants in bulk?
Yes, many suppliers offer financing options for bulk purchases of dental implants. These options can include extended payment terms or installment plans that allow you to manage cash flow more effectively. Inquire about specific financing arrangements during negotiations and compare different suppliers’ terms. Additionally, consider alternative financing solutions such as trade credit or loans from financial institutions specializing in medical equipment.
Illustrative Image (Source: Google Search)
- How can I stay informed about market trends and innovations in dental implants?
Staying informed requires regular engagement with industry publications, attending dental conferences, and participating in relevant webinars. Join professional associations and online forums dedicated to dental technology and procurement to network with peers and gain insights. Subscribing to newsletters from leading manufacturers can also provide updates on new products and innovations in dental implant technology that could benefit your practice.
Important Disclaimer & Terms of Use
⚠️ Important Disclaimer
The information provided in this guide, including content regarding manufacturers, technical specifications, and market analysis, is for informational and educational purposes only. It does not constitute professional procurement advice, financial advice, or legal advice.
While we have made every effort to ensure the accuracy and timeliness of the information, we are not responsible for any errors, omissions, or outdated information. Market conditions, company details, and technical standards are subject to change.
B2B buyers must conduct their own independent and thorough due diligence before making any purchasing decisions. This includes contacting suppliers directly, verifying certifications, requesting samples, and seeking professional consultation. The risk of relying on any information in this guide is borne solely by the reader.
Strategic Sourcing Conclusion and Outlook for dental implants with payment plans
To navigate the complexities of sourcing dental implants with payment plans, international B2B buyers must prioritize strategic sourcing to enhance cost-effectiveness and accessibility. Understanding the diverse financing options, such as in-office membership plans and flexible payment structures, is essential for maximizing value. By collaborating with reputable suppliers and leveraging platforms like The Patient Marketplace, buyers can secure competitive pricing and favorable terms that resonate with their regional market conditions.
Moreover, the ongoing demand for dental implants, driven by increasing consumer awareness and the importance of oral health, presents a significant opportunity for suppliers. As prices continue to rise due to material costs and technological advancements, acting now to lock in favorable agreements will mitigate future financial pressures.
In conclusion, the strategic sourcing of dental implants with payment plans not only addresses immediate financial concerns but also positions buyers for long-term success in the evolving healthcare landscape. Take the next step—engage with suppliers, explore innovative financing options, and ensure that your organization is poised to meet the growing demand for quality dental solutions across Africa, South America, the Middle East, and Europe.
